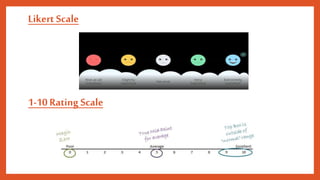
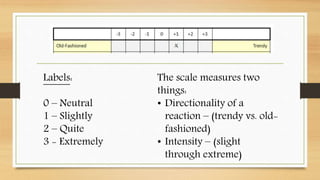
Assessment tools in the affective domain have been developed to measure attitudes, interests, motivations, and self-efficacy. Self-report is the most common tool, where individuals provide accounts of their own attitudes. Rating scales use categories to elicit information about quantitative attributes, such as Likert scales from 1-10. Semantic differential scales assess reactions to words or concepts using bipolar adjective scales to determine directionality and intensity of reactions. These tools have been validated in studies of attitude formation, organizations, jobs, and minorities.