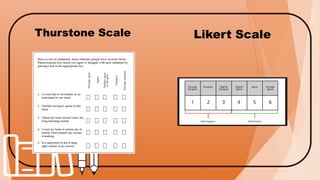
The document discusses assessment in the affective domain. It defines key terms like attitude, motivation, and self-efficacy. It also explains Kratwohl and Bloom's taxonomy of the affective domain, which includes receiving, responding, valuing, organization, and characterization. Various assessment tools for the affective domain are also defined, including self-report, rating scales like the Thurstone scale, Likert scale, and semantic differential scale, as well as checklists.