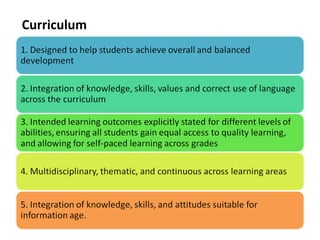
This document discusses the Malaysian Smart School initiative which aims to reconstruct learning institutions to fit the evolving digital world. It outlines 4 waves of implementation from 1999-2020:
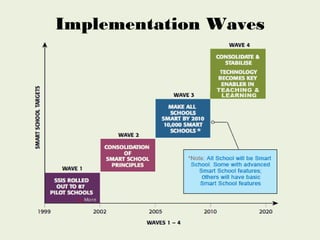
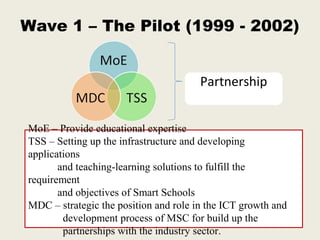
1) The Pilot (1999-2002) established partnerships between the Ministry of Education, Telekom Smart Schools, and the Multimedia Development Corporation.
2) The Post-Pilot (2002-2005) expanded infrastructure and resources like computer labs and online materials nationwide.
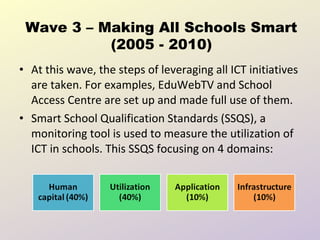
3) Making All Schools Smart (2005-2010) leveraged initiatives and the Smart School Qualification Standards for monitoring.
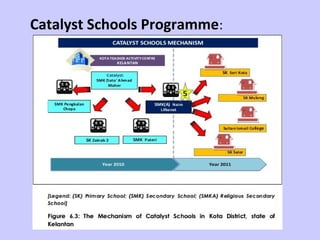
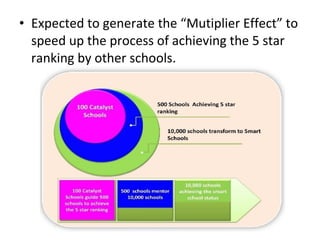
4) Consolidate and Stabilise (2011-2020) including the Catalyst Schools Programme to achieve 5-star ratings across