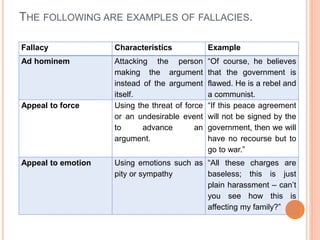
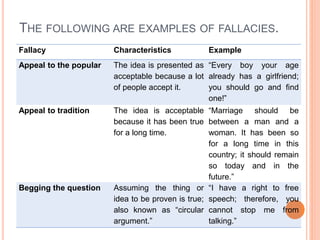
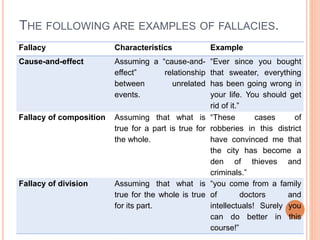
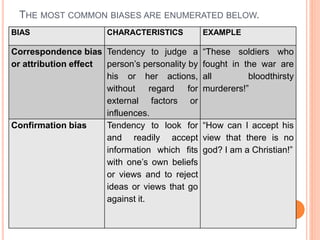
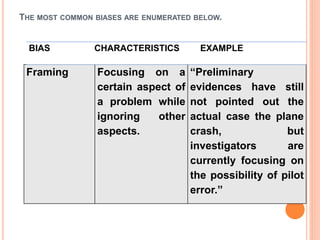
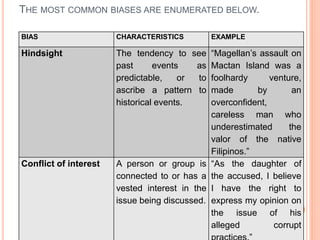
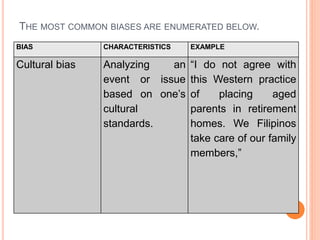
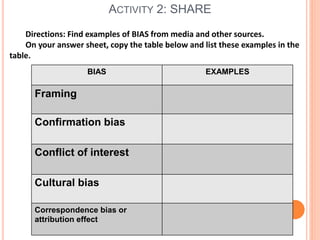
This document discusses how to determine truth and identify different types of arguments, facts, opinions, and biases. It provides examples of fallacies in reasoning like appeals to emotion, tradition, and popularity. Facts are defined as established truths that can be verified, while opinions express views and beliefs and may be biased. Common biases discussed include confirmation bias, hindsight bias, conflict of interest, and cultural bias. The document encourages identifying biases in media and other sources.