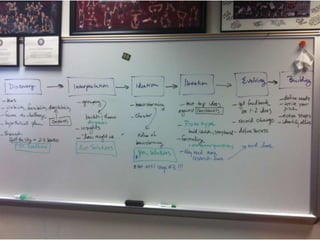
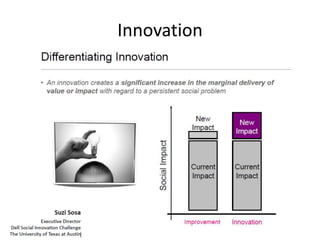
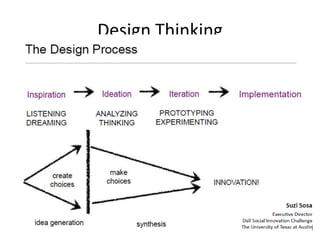
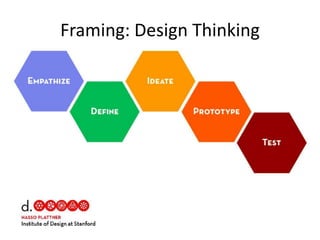
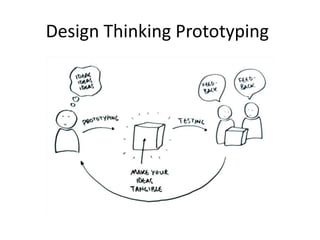
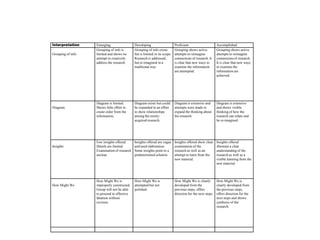
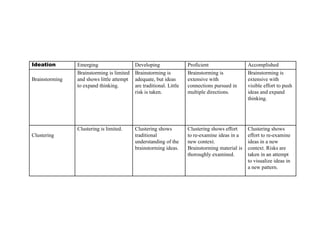
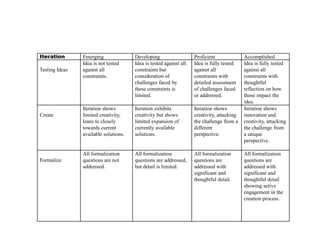
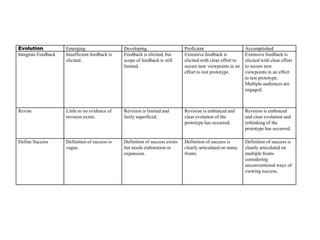
The document provides an overview of the design thinking process and outlines exercises for educators to work through each stage of design thinking with their students. It breaks down the process into key stages - discovery, interpretation, ideation, iteration, and evolution. For each stage, it describes the goals and tasks involved and provides rubrics to assess student work at emerging, developing, proficient, and accomplished levels. The overall purpose is to help educators learn and apply design thinking approaches in their classrooms.