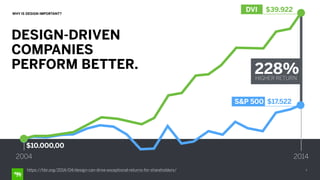
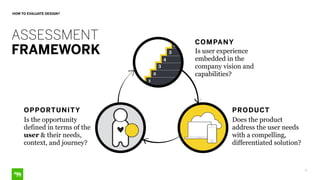
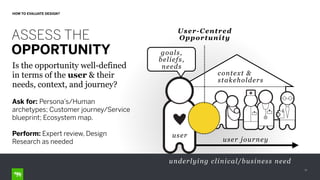
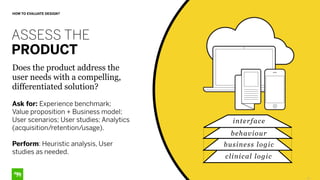
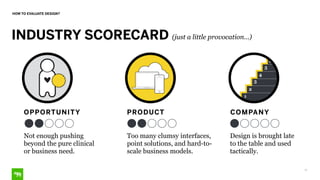
The document discusses the importance of design in health technology, emphasizing that design-driven companies tend to perform better by directly impacting business metrics and user experiences. It outlines key attributes and activities of effective design, as well as a framework for evaluating the alignment of products with user needs. The content highlights that good design meets real needs and is integral to the company vision and strategy.