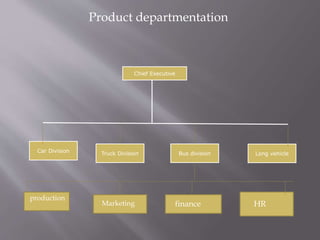
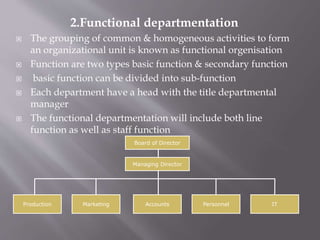
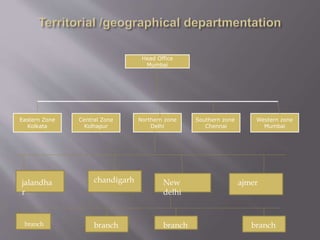
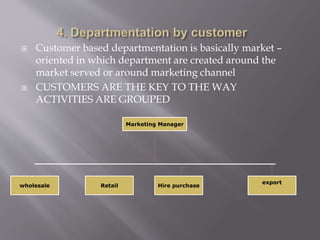
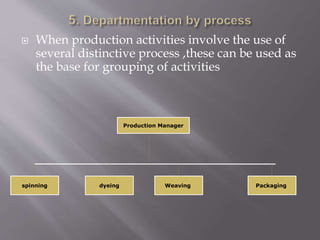
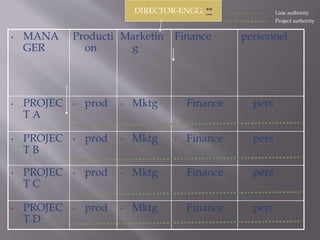
The document discusses different ways to structure organizations through departmentation. It describes five common types of departmentation: by product, by function, by region/territory, by customer, and by process. Each structure has advantages like specialization and focus but also disadvantages like potential lack of coordination or duplication of roles. The document also discusses matrix structures and emerging concepts like strategic business units and virtual organizations.