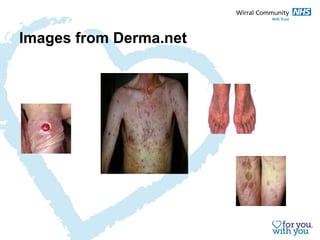
The document discusses common myths and facts about sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and HIV, emphasizing the importance of sexual health screening and proper prevention methods. It highlights that many STIs are asymptomatic, can be transmitted through various sexual activities, and certain misconceptions about condoms, testing, and infection risks. It also addresses the significance of STI testing for pregnant women and the potential impact of STIs on maternal and infant health.