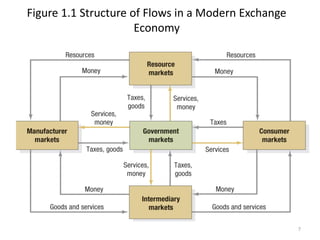
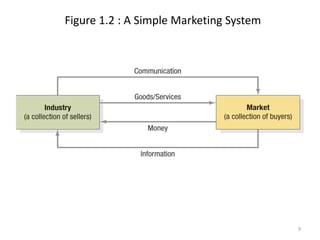
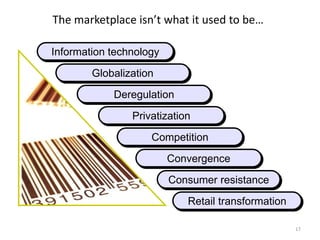
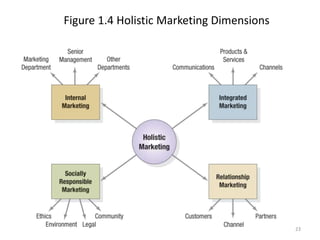
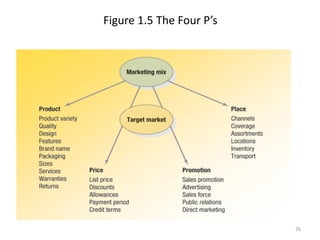
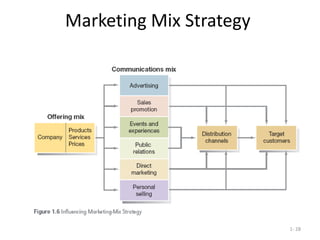
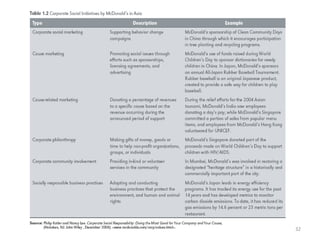
This document provides an overview of key marketing concepts and terms. It defines marketing as identifying and meeting human and social needs profitably. Marketing management is choosing target markets and growing customer value through superior offerings. The document outlines core marketing concepts like segmentation, branding, and distribution channels. It also discusses new orientations like relationship marketing and integrated marketing, as well as responsibilities like social responsibility.