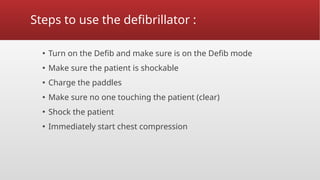
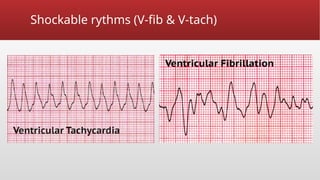
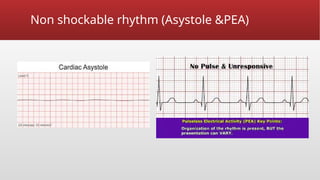
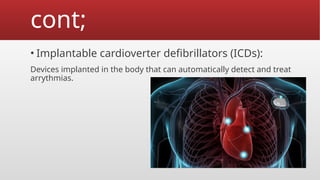
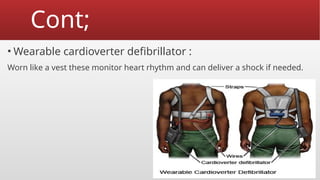
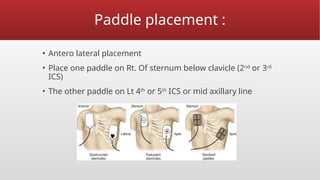
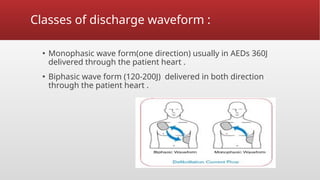
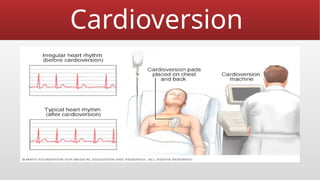
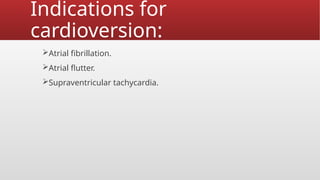
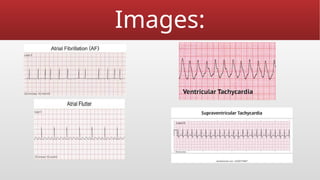
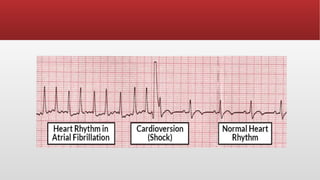
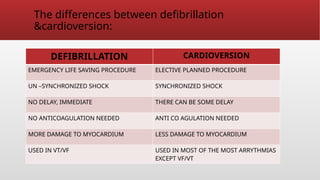
Defibrillation is a critical medical procedure using a defibrillator to treat life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation and tachycardia by delivering electrical shocks to the heart. Cardioversion is a related procedure that restores regular heart rhythm, particularly for conditions such as atrial fibrillation, using low-energy shocks or medications. Key differences between defibrillation and cardioversion include the timing of the procedure, synchronization of shocks, and the medications used.