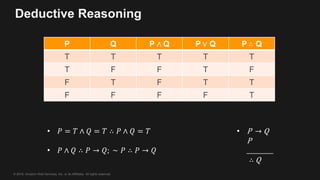
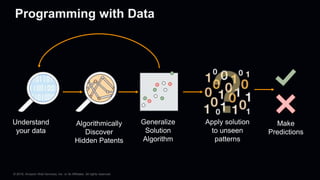
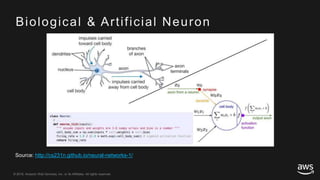
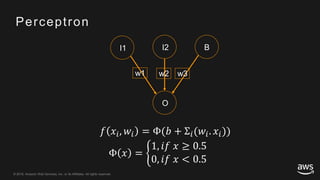
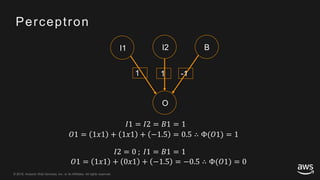
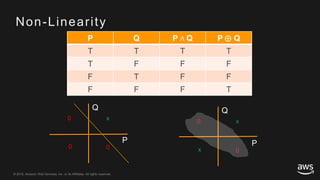
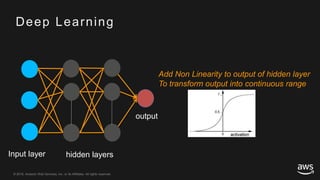
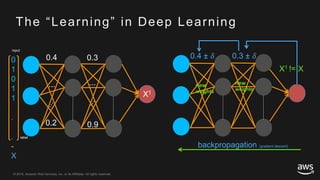
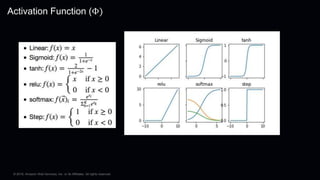
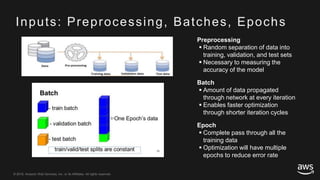
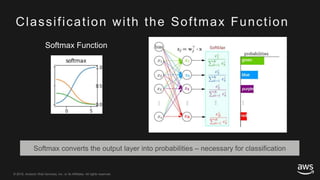
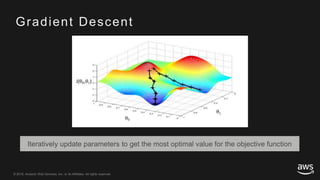
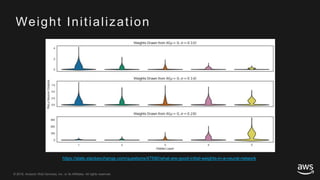
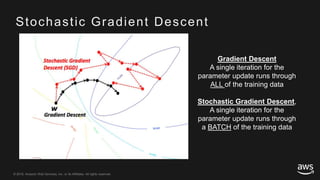
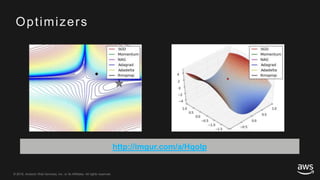
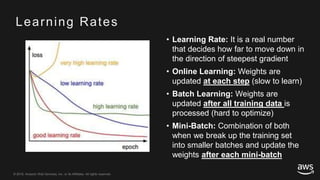
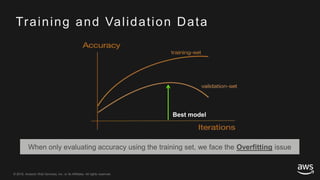
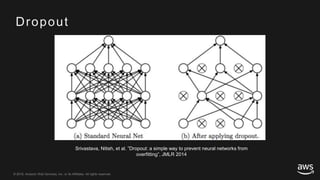
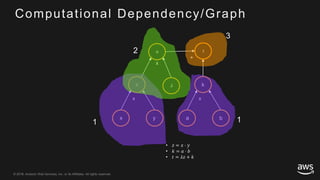
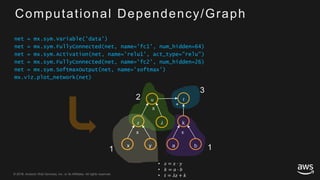
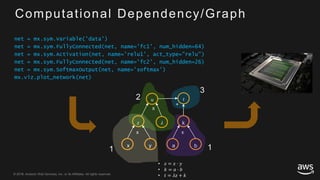
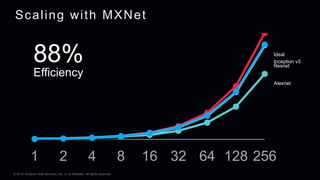
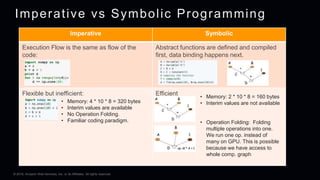
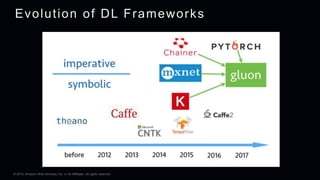
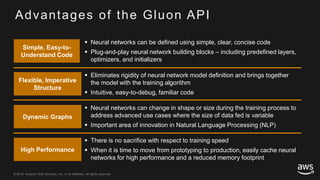
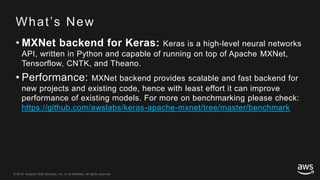
This document provides an overview of Apache MXNet and its Gluon API for building deep learning applications. It discusses key concepts in deep learning like neural networks, activation functions, loss functions, and optimization techniques. It also describes advantages of MXNet like its symbolic programming with computational graphs and Gluon's simple and flexible imperative programming interface. Gluon makes it easy to define neural networks with common layers and training algorithms.