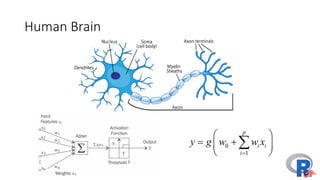
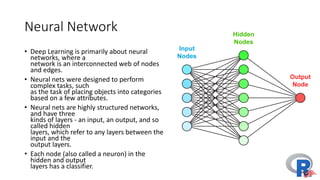
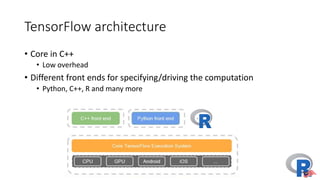
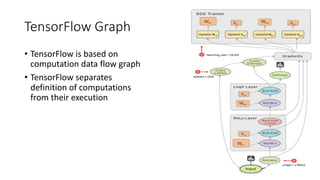
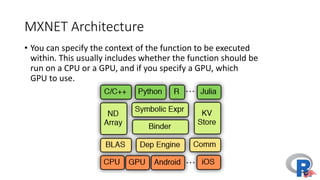
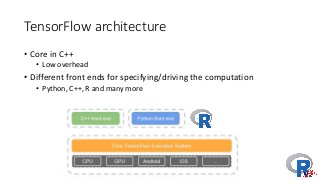
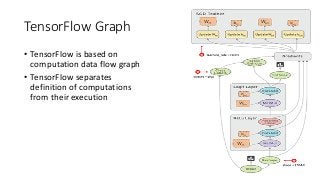
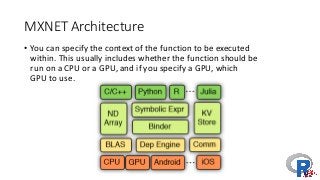
The document presents a comprehensive overview of deep learning, highlighting its history, concepts, strengths, weaknesses, and various libraries like TensorFlow and MXNet. It discusses the neural networks' architecture, including forward and backward propagation processes, as well as the applicability of deep learning in different domains. The presentation, delivered by Poo Kuan Hoong, emphasizes the robust nature of deep learning while also addressing its challenges and providing resources for further exploration.