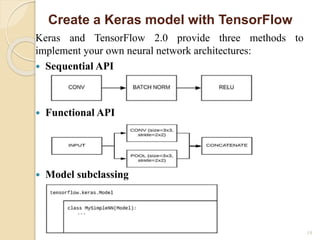
This document provides an introduction and overview of deep neural networks and Python environment setup for deep learning. It discusses what deep learning is, the mathematical concepts behind neural networks like loss functions and optimizers, and different neural network architectures like sequential and functional APIs in Keras. It also covers setting up the Python environment, installing key libraries like TensorFlow, Theano and Keras, and verifying the installations. Finally, it outlines some fundamentals of deep learning like defining the problem, collecting and splitting the data, choosing metrics, and developing and tuning models.