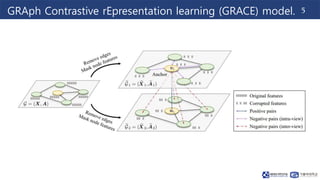
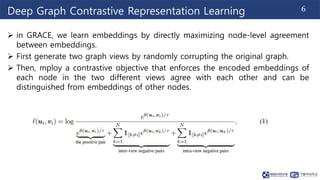
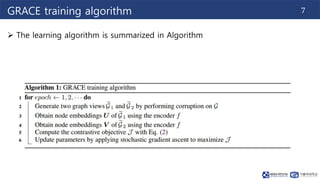
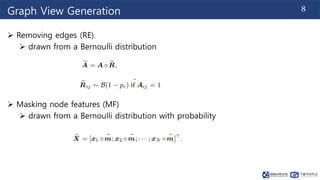
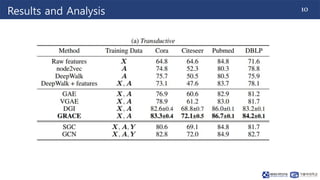
This document summarizes a research paper on graph contrastive representation learning (GRACE) using an unsupervised framework. GRACE generates two graph views through random corruption, then trains a model with a contrastive loss to maximize agreement between node embeddings in the two views. It considers corruption at both the topology and node attribute levels. Experiments on citation networks show GRACE achieves competitive performance for transductive and inductive node classification tasks.