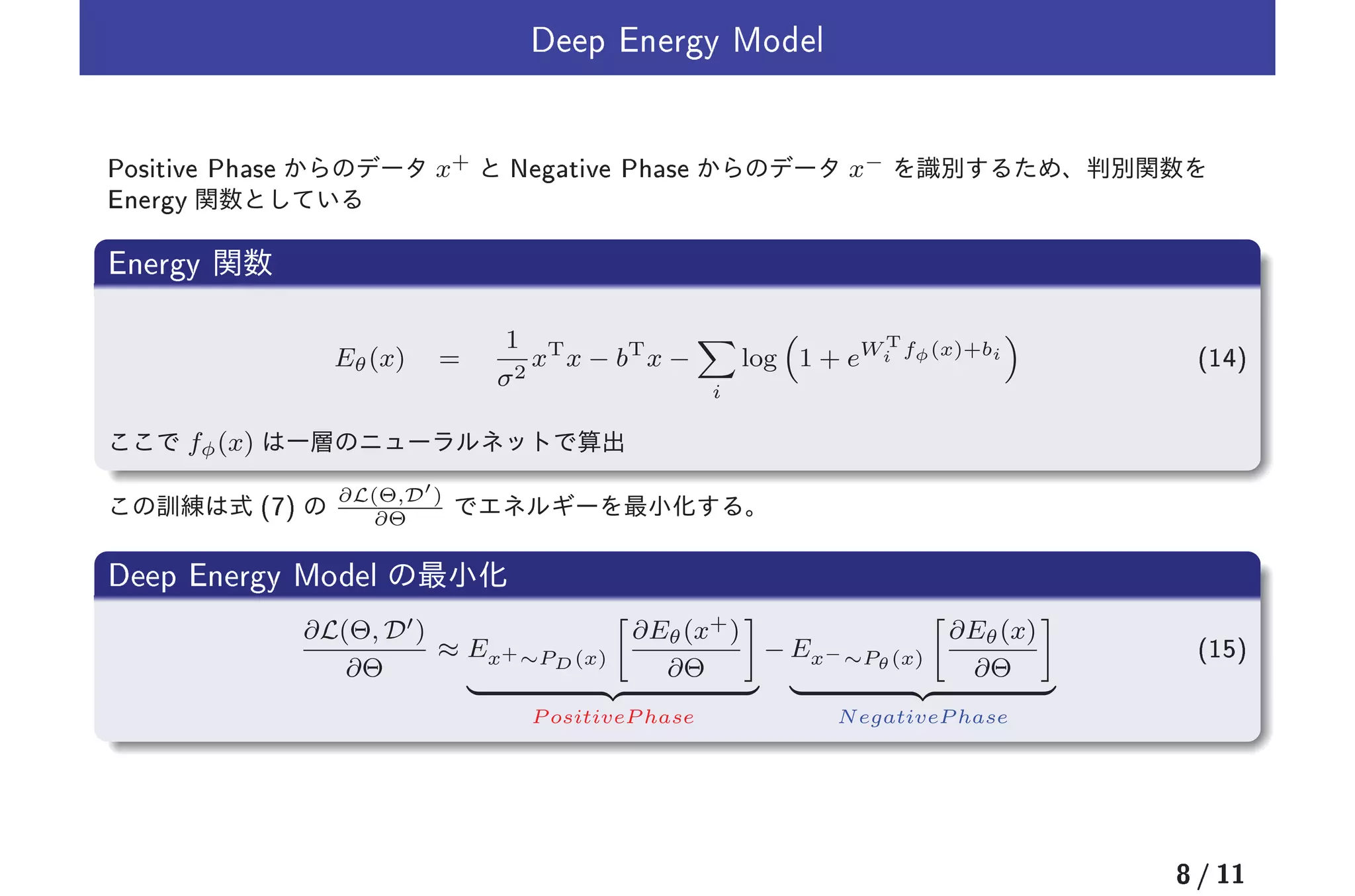
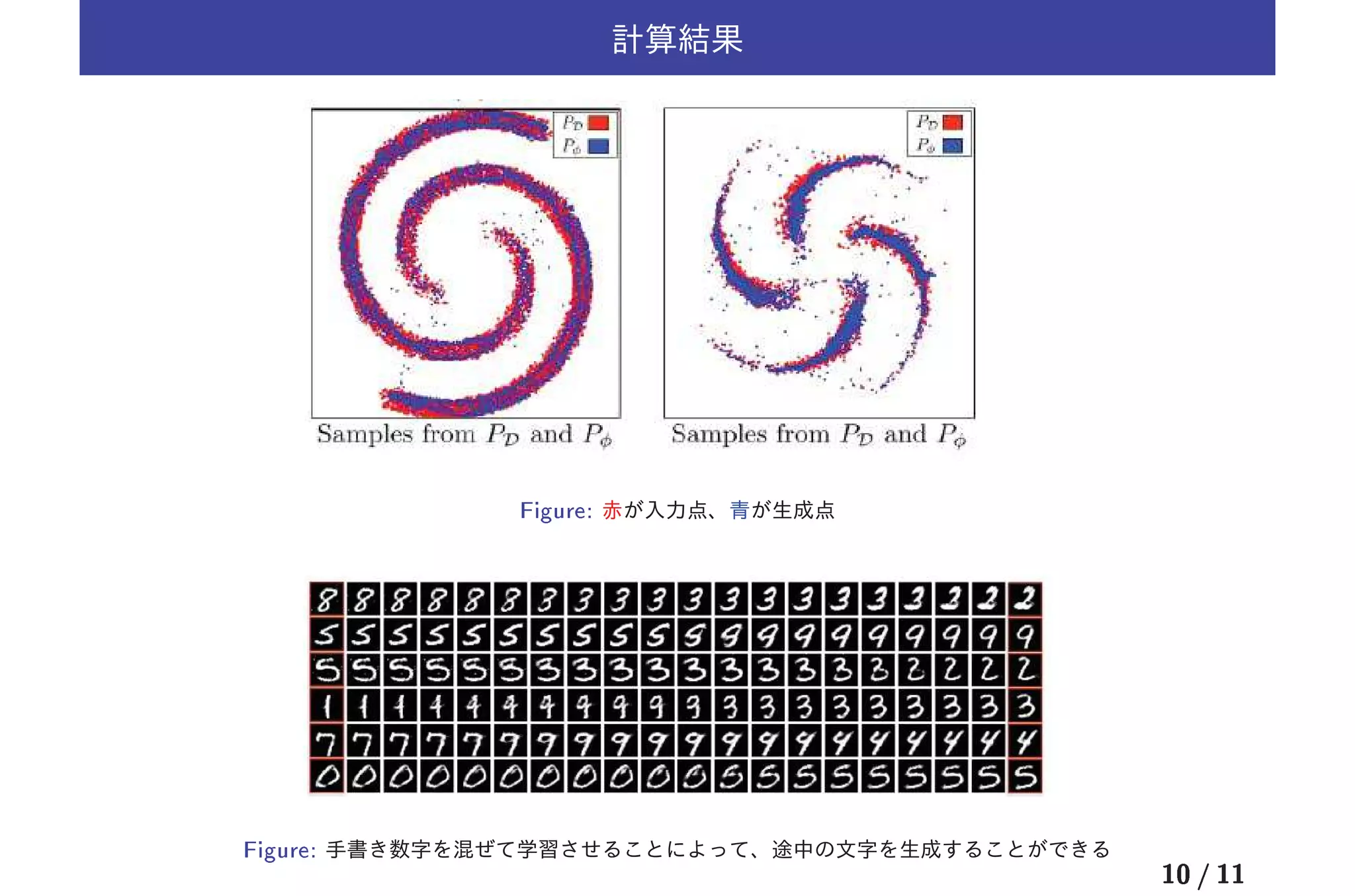
1) The document discusses deep directed generative models that use energy-based probability estimation. It describes using an energy function to define a probability distribution over data and training the model using positive and negative phases.
2) The training process involves using samples from the data distribution as positive examples and samples from the model's distribution as negative examples. The model is trained to minimize the difference in energy between positive and negative samples.
3) Applications discussed include deep energy models, variational autoencoders combined with generative adversarial networks, and adversarial neural machine translation using energy functions.