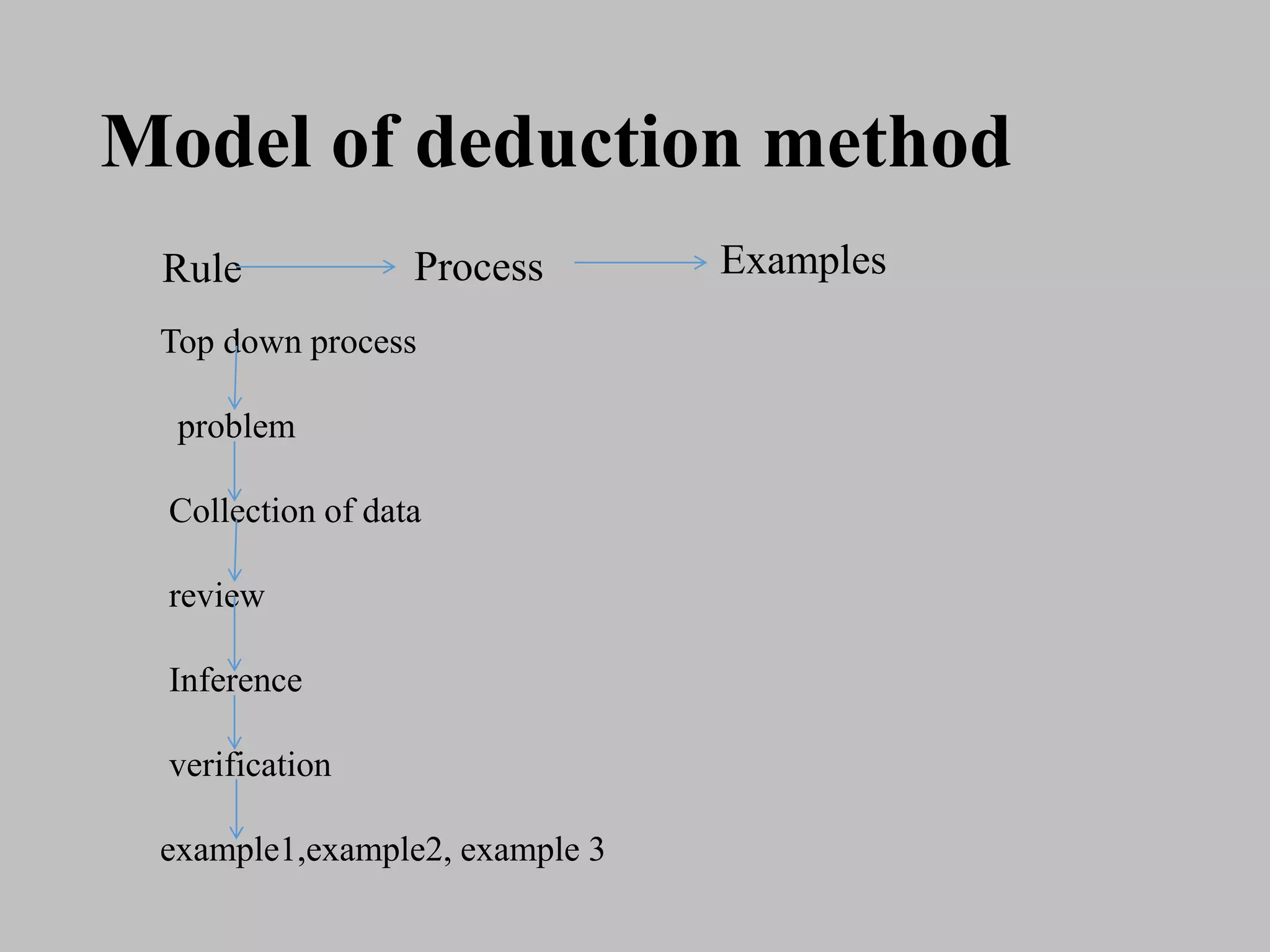
This document outlines the deductive method of teaching. It begins with an introduction to the topic and then discusses that deductive teaching presents rules and grammar structures before examples. It describes Aristotle as originating deductive reasoning and how it moves from general principles to specific cases. The document then lists the general stages of deductive teaching as planning, execution, and evaluation. It provides examples of deductive reasoning and outlines the steps as collecting information, reviewing it, drawing inferences, and verification. Finally, it discusses the merits of being time saving and simplifying work for the teacher, and the demerits of being difficult for beginners to understand and risking mechanical learning.