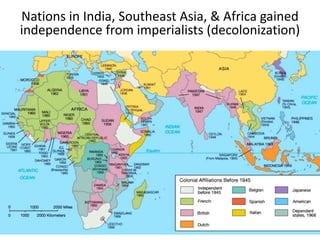
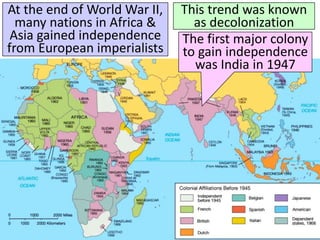
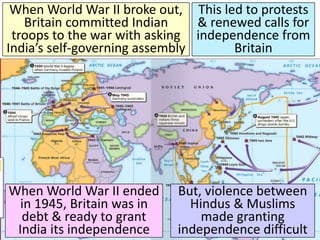
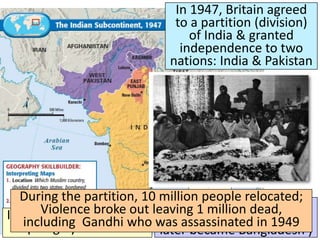
The document discusses the decolonization of India, which began with its independence from British colonial rule in 1947, following the leadership of Mohandas Gandhi and his non-violent resistance strategies. The partition of India and Pakistan led to significant violence and the displacement of millions, ultimately resulting in India's establishment as the world's largest democratic nation under the leadership of Jawaharlal Nehru. The aftermath of independence also saw progress for women and lower caste Hindus, as well as India's role in the Cold War as a leader among non-aligned nations.