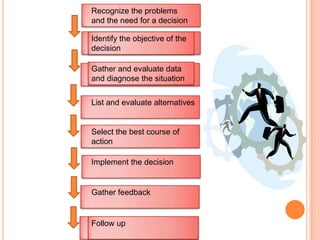
The document outlines the key steps in the decision making process: 1) Recognizing the problem, 2) Identifying the objective of the decision, 3) Gathering and evaluating relevant data, 4) Listing and evaluating alternative courses of action, 5) Selecting the best alternative, 6) Implementing the decision, and 7) Gathering feedback. It emphasizes that decision making involves tradeoffs between alternatives that are rarely clearly right or wrong. Managers must make decisions despite uncertainty and rely on others while ultimately being responsible. The process described aims to help managers select a desirable course of action to provide solutions to problems.