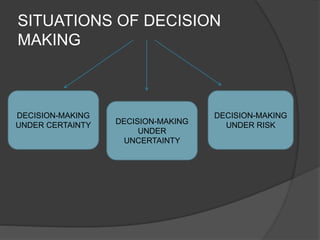
This document discusses decision theory and different types of decision making situations. It describes decision making as selecting the alternative course of action that best meets the objectives of the problem. The types of decision making situations covered are decisions under certainty, uncertainty, and risk. Decision making under certainty involves known consequences, while uncertainty is based on judgment and experience. Risk-based decisions involve predicting outcomes of events. The document provides examples of criteria used to evaluate alternatives under each type of decision making situation, such as expected monetary value and opportunity loss.