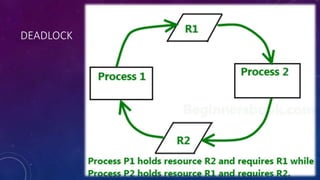
A deadlock is a situation in database management systems where two or more tasks are indefinitely waiting on each other to release resources, preventing any of them from completion. Coffman's four conditions for deadlock include mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. To prevent deadlocks, DBMS may employ schemes like wait-die, which allows older transactions to wait and younger ones to be restarted after a delay.