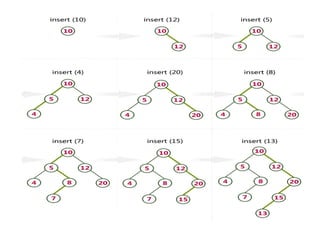
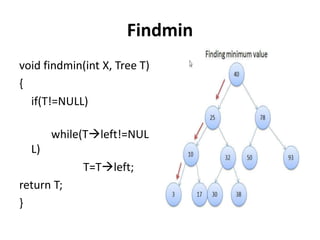
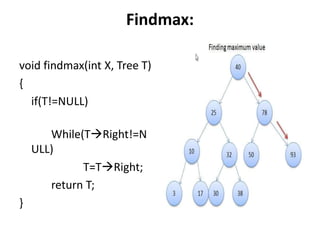
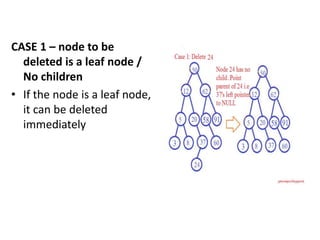
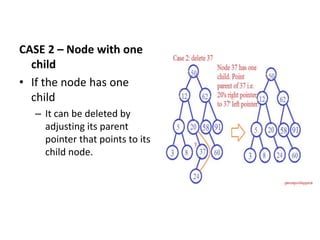
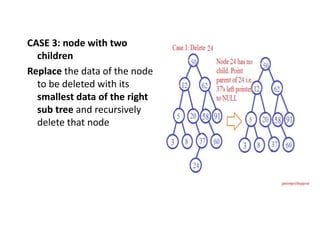
Binary search trees have nodes where the left child is less than the root and the right child is greater than the root. Nodes are inserted by traversing the tree recursively to find an empty spot. Values are found by recursively searching and comparing to the root. Minimum and maximum values are found by traversing all the way left or right. Nodes are deleted by case analysis on whether they have 0, 1, or 2 children and adjusting pointers or replacing with children accordingly.