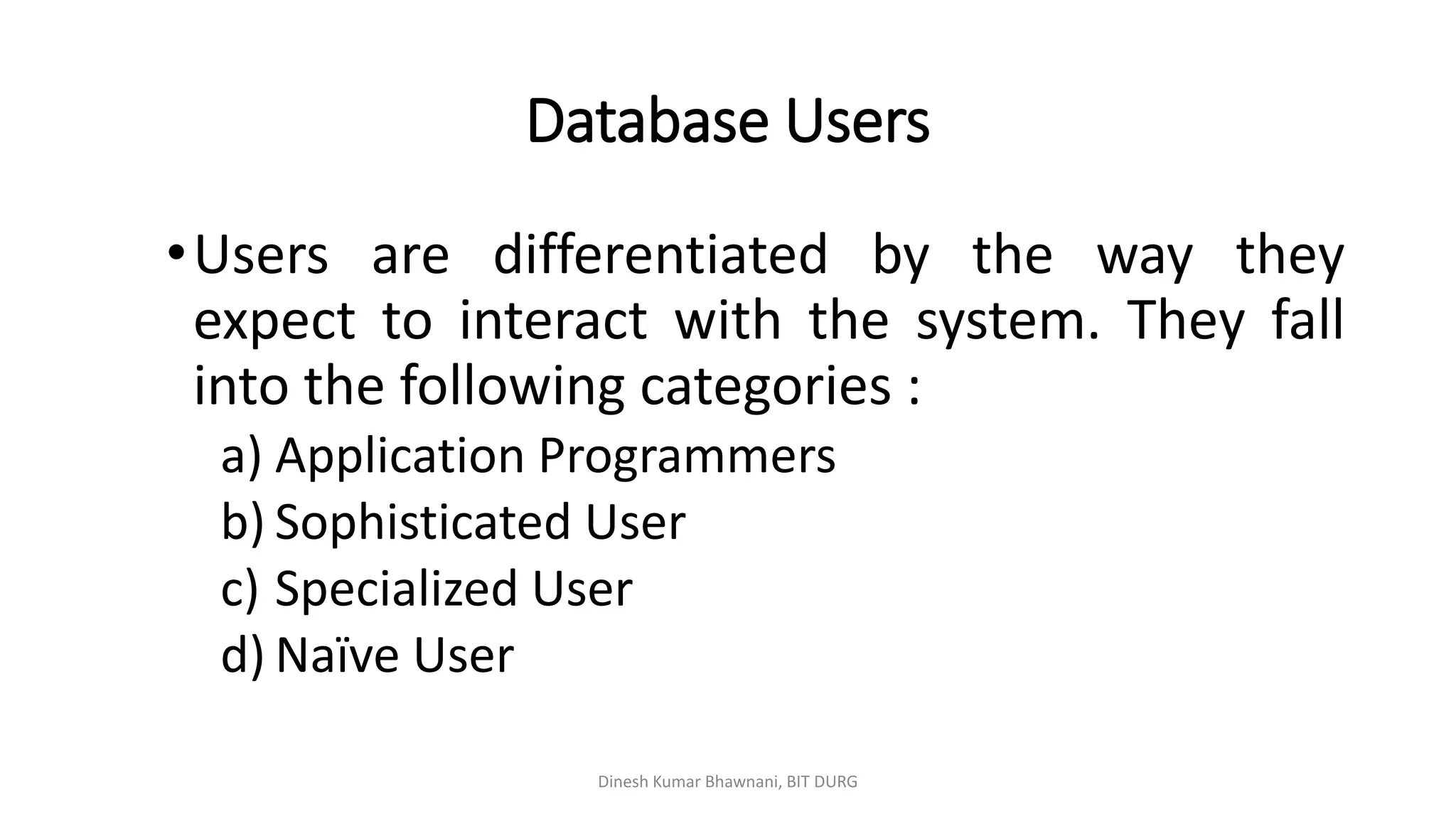
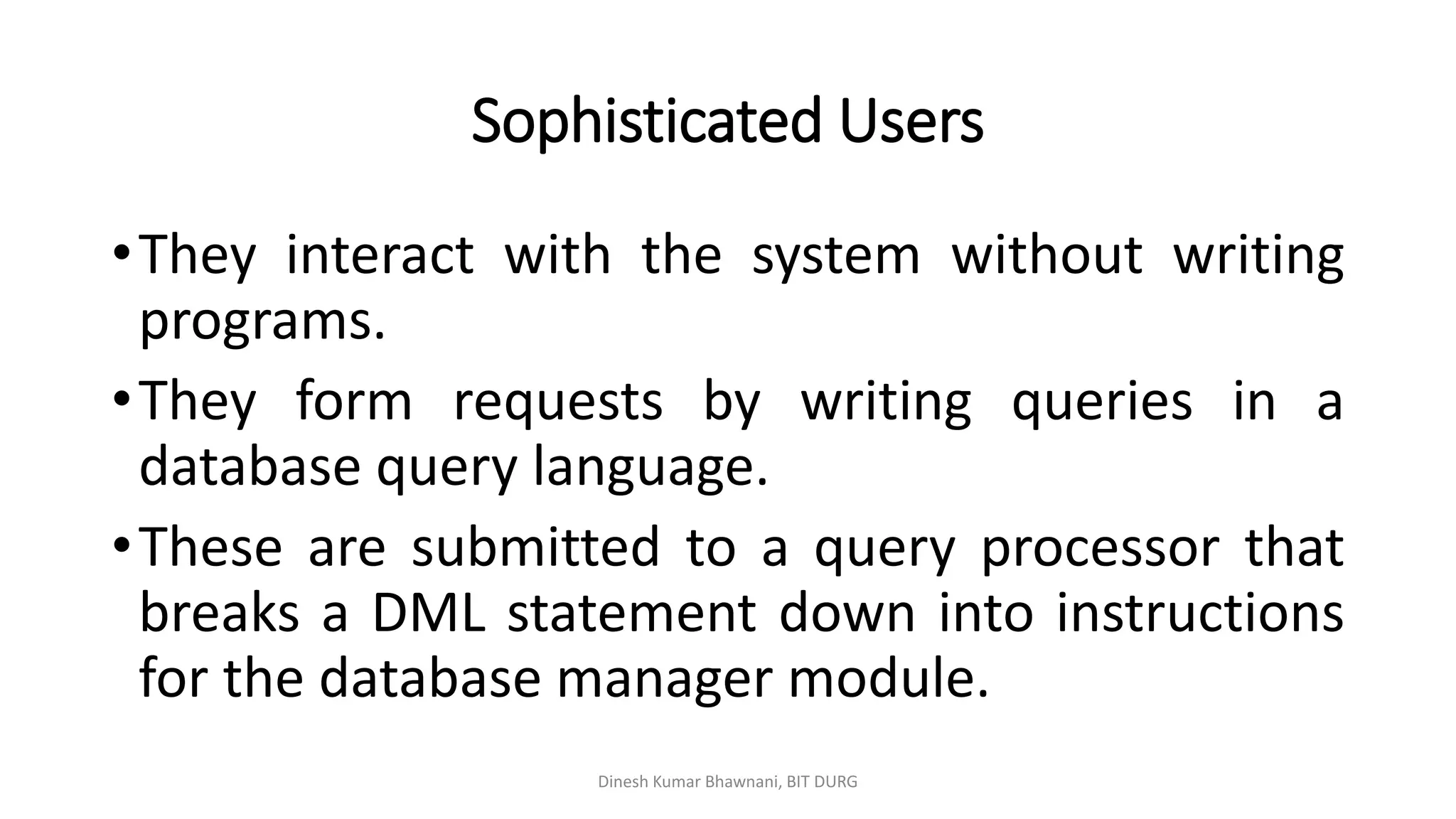
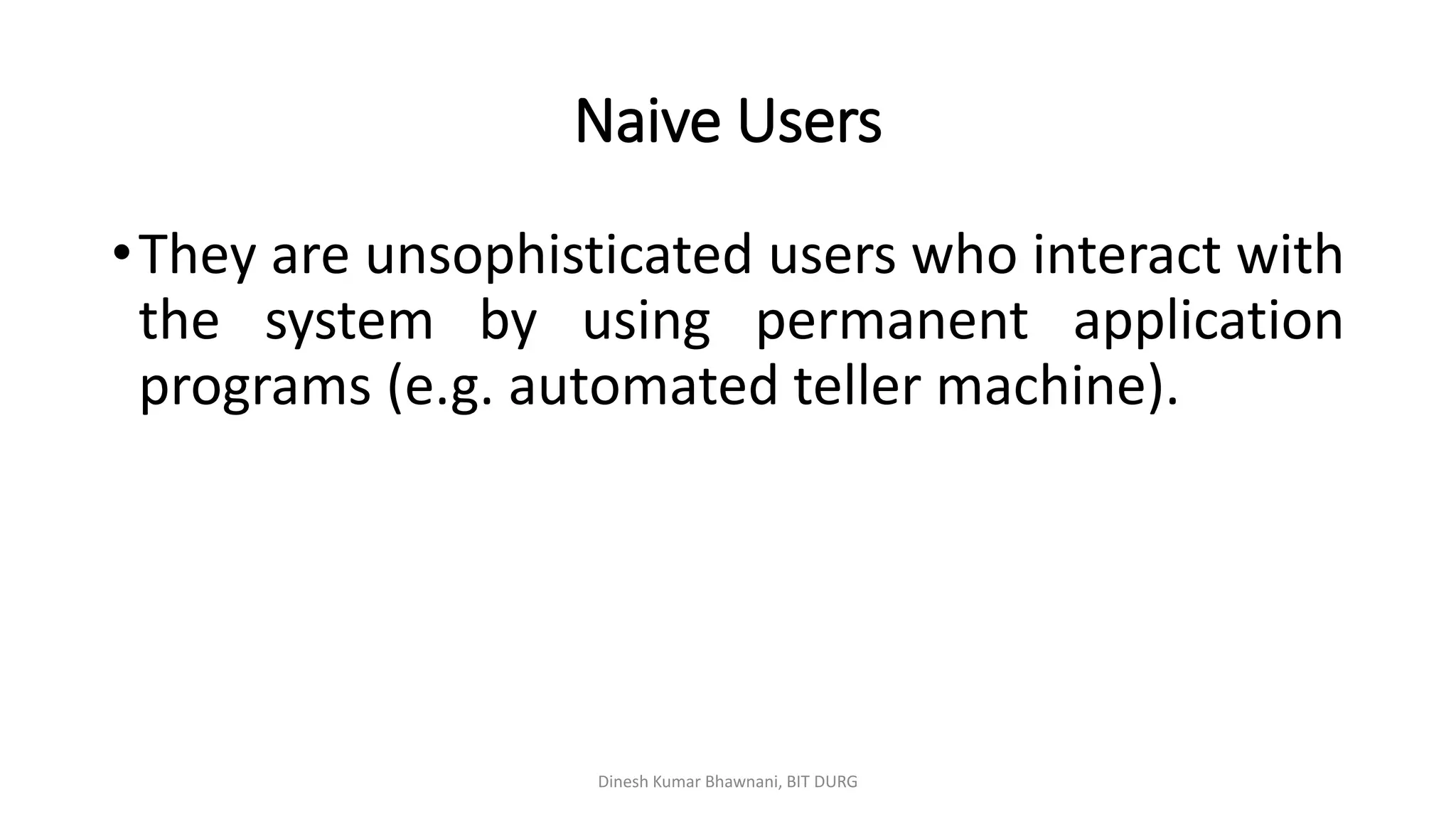
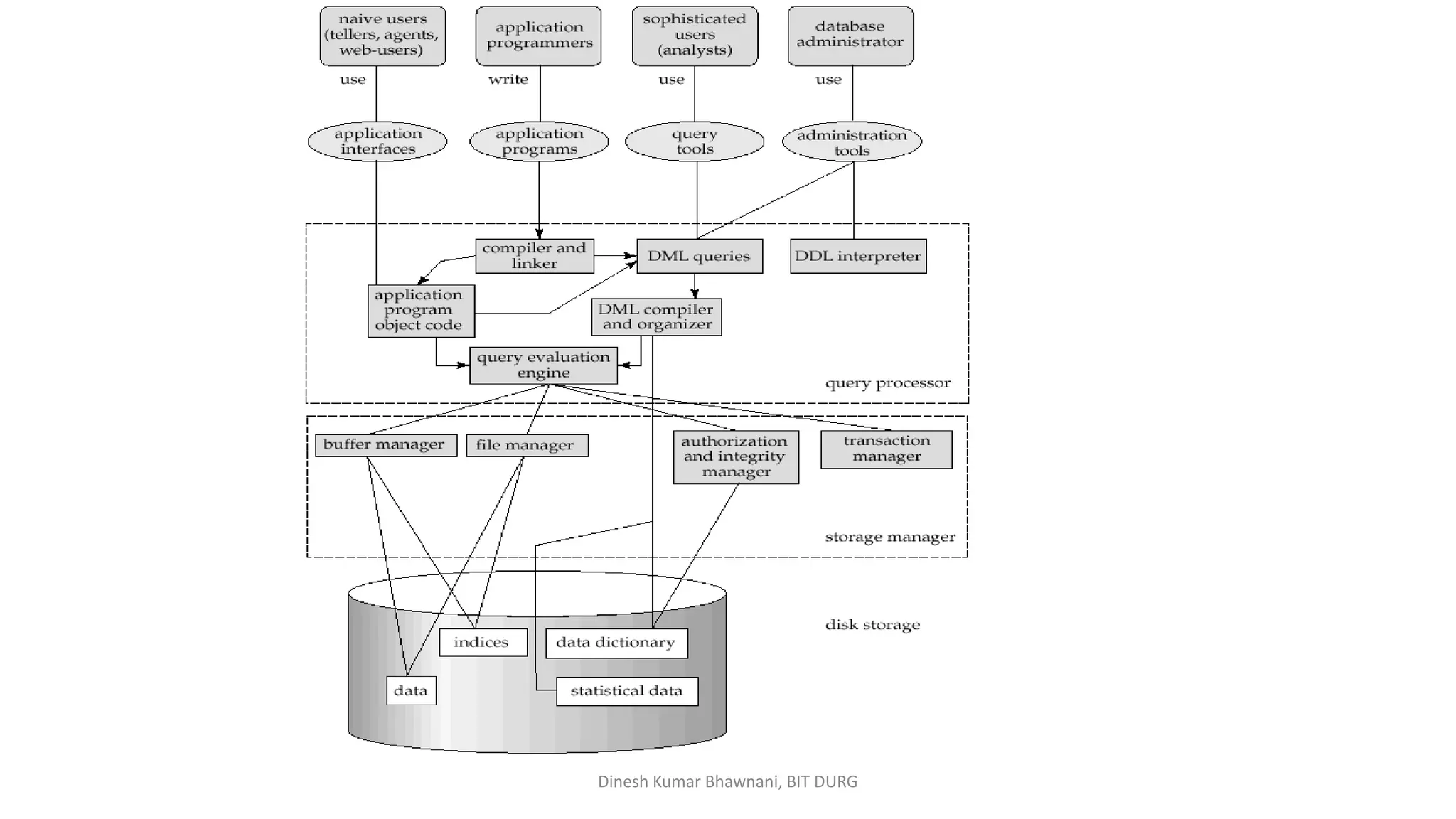
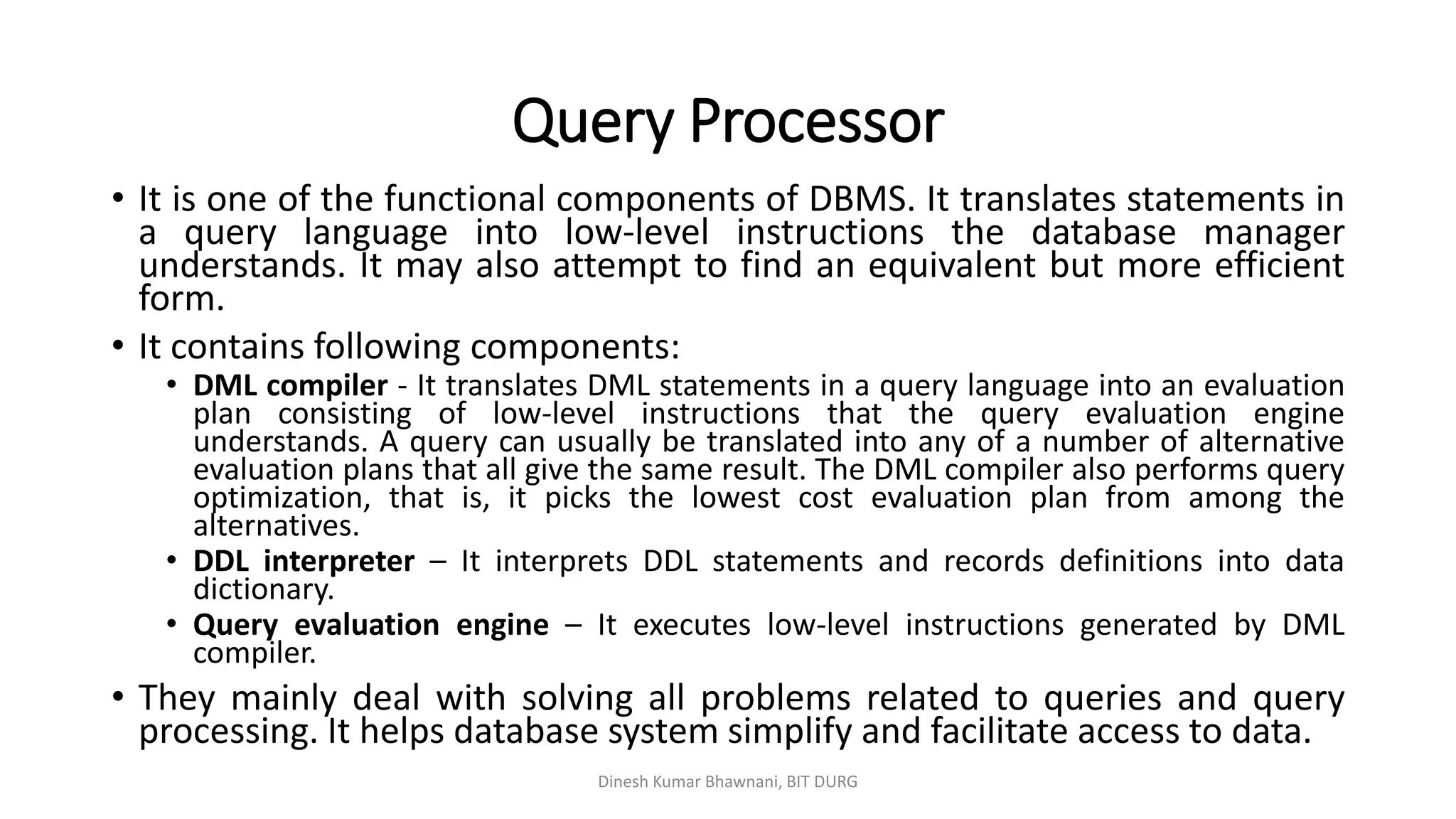
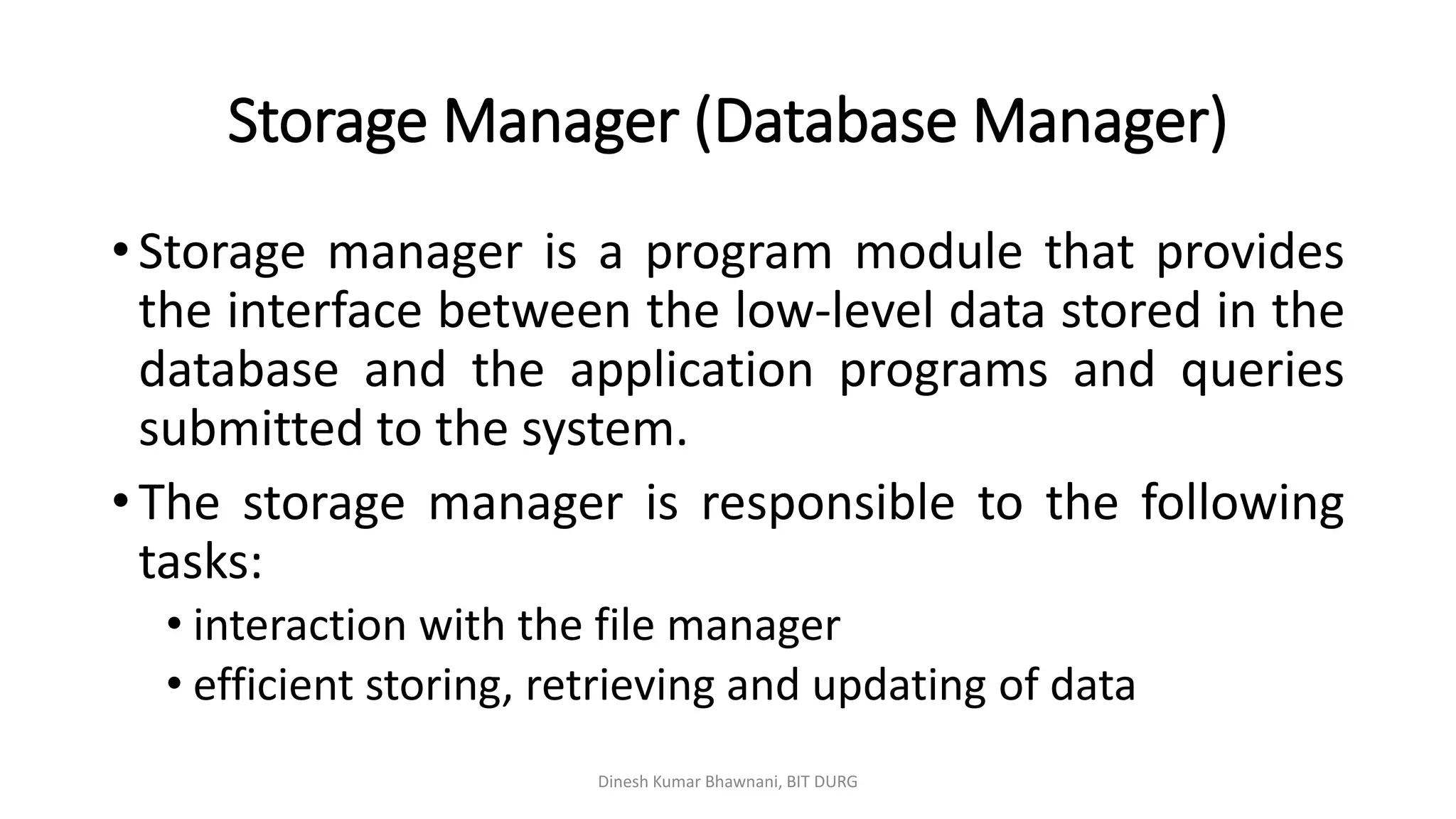
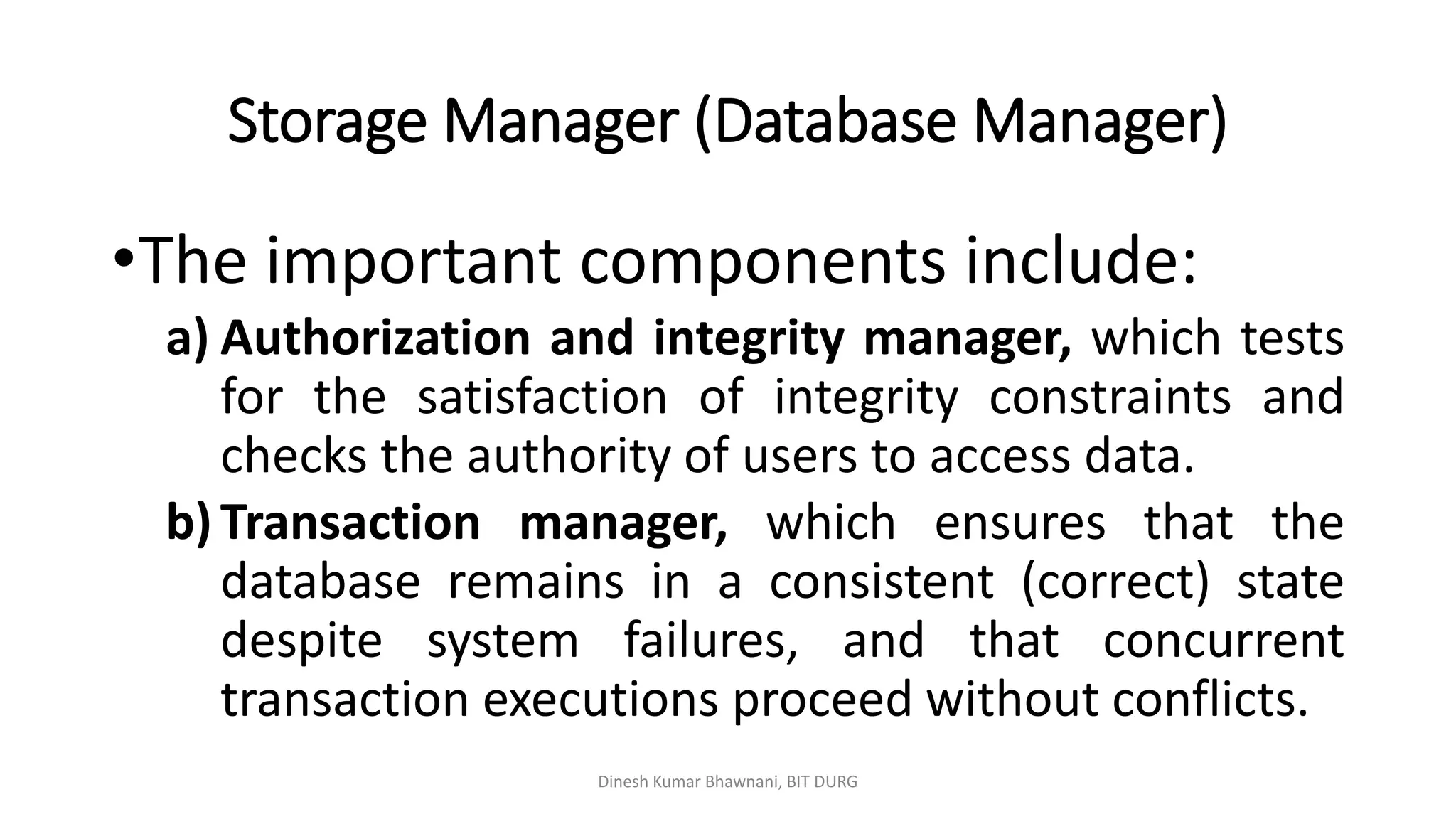
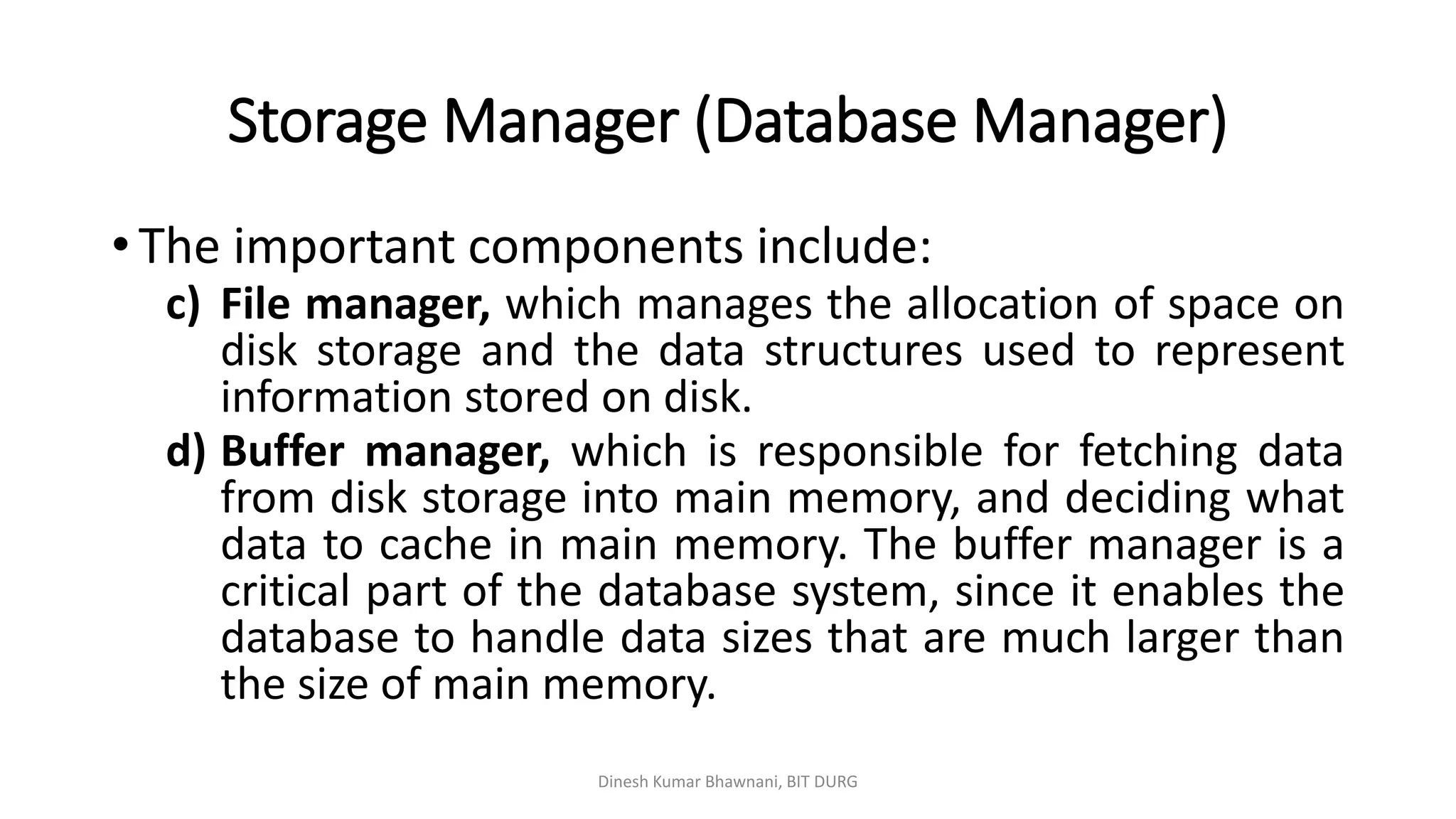
The document outlines different types of database users including application programmers, sophisticated users, specialized users, and naïve users, each defined by their interaction methods with database systems. It describes the role and functions of database administrators (DBAs), including schema definition, user authority management, and routine maintenance. Additionally, it details the structure of a database management system (DBMS), including components like the query processor and storage manager, and other essential data structures such as data files and dictionaries.




![University Questions
• Which type of user (database user) would perform the following
function for a billing system in a large company :
a) Write a program to generate monthly bills.
b) Develop schema for new kind of billing system?
[CSVTU CSE Dec 2007]
Dinesh Kumar Bhawnani, BIT DURG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dbmslec3-slideshare-200720133916/75/Dbms-Notes-Lecture-3-Types-of-database-users-18-2048.jpg)