The document provides an overview of key concepts in database management systems including:
- DBMS allows for convenient and efficient data storage and access while avoiding problems with file systems like data redundancy and inconsistency.
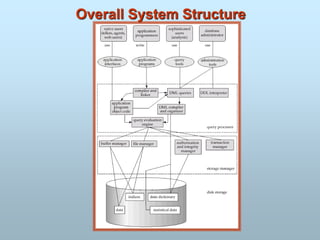
- Data is represented at multiple levels of abstraction from physical storage to logical relationships to application views.
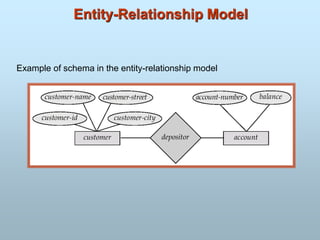
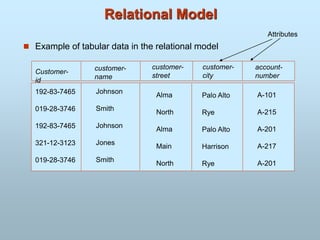
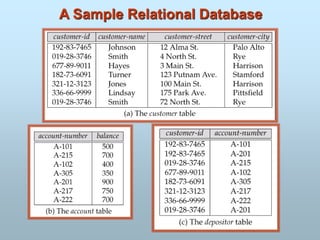
- Popular data models include the entity-relationship model and relational model which use schemas to define data.
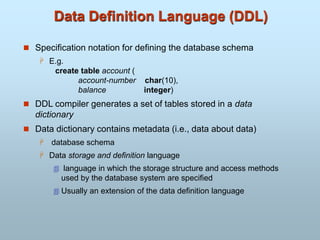
- Languages like SQL are used for data manipulation while DDL defines the database schema.