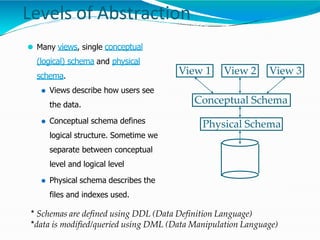
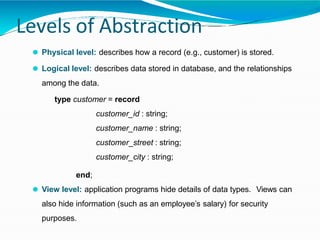
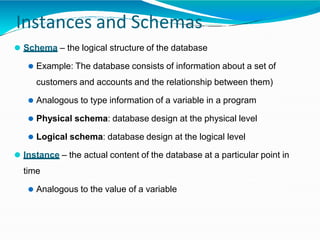
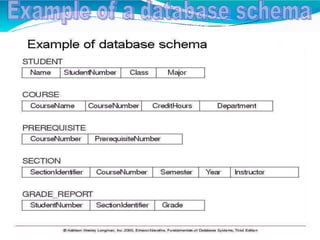
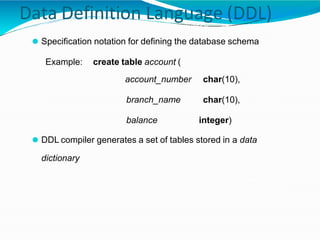
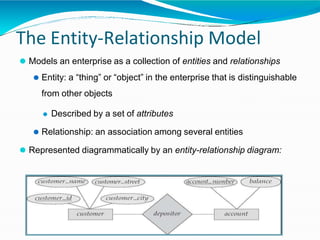
The document provides an overview of Database Management Systems (DBMS), defining them as software designed to store and manage large integrated collections of data while addressing issues related to file-based systems such as data redundancy, inconsistency, and security. It covers various database models, levels of abstraction, data manipulation and definition languages, and the role of database administrators in maintaining system integrity and performance. Additionally, the document discusses the evolution of database systems and their growing importance in managing diverse and voluminous datasets.