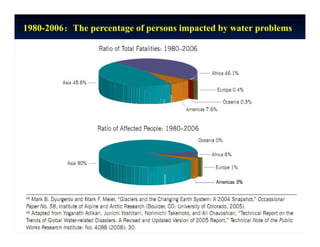
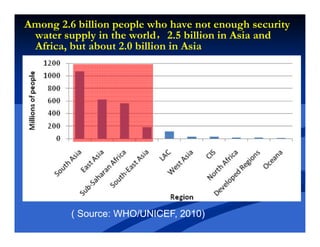
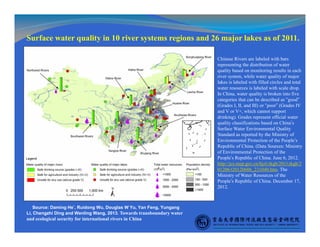
This document discusses issues, challenges, and opportunities for cooperation in transboundary waters between China and Africa. It notes that as developing countries facing water challenges, China and African countries share common interests in sustainably managing their transboundary rivers. Key points discussed include:
- China and Africa face common challenges like balancing development and conservation, and adapting to climate change.
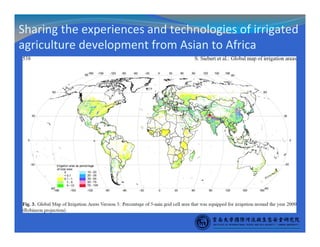
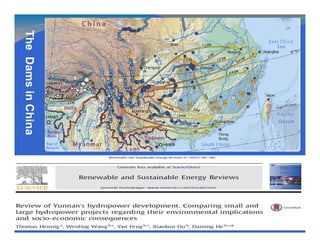
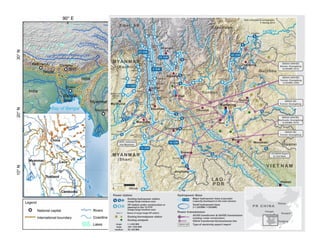
- Transboundary water management experiences could be shared, such as China's expertise in irrigation, hydropower, and integrated river basin management.
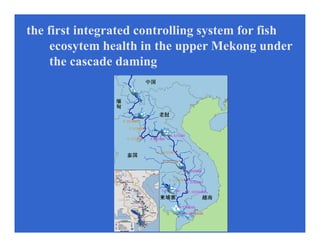
- Cooperative research on topics like the impacts of climate change and dams on river ecosystems could help address regional issues.
- Establishing mechanisms for equitable benefit-sharing, regional development, and transboundary environmental compensation could