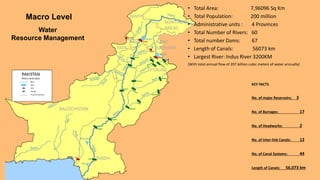
This document discusses water management in Pakistan. It covers the country's water resources, which include glaciers, rivers, lakes, rainwater and underground sources. It notes that 69% of water is used for agriculture, 23% for industry and 8% for domestic uses. The document then outlines Pakistan's macro and micro level water management approaches. At the macro level, it discusses dams, barrages, canals and irrigation channels. At the micro level, it discusses public water supply systems, irrigation channels and industrial use. It also lists several environmental impacts of current water management practices, such as damaged ecosystems and reduced wildlife habitat. Finally, the document provides suggestions to improve water management, such as building smaller dams and restoring natural river