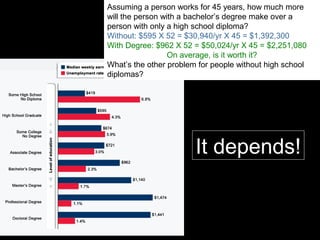
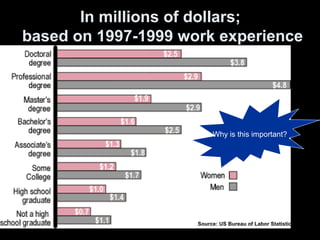
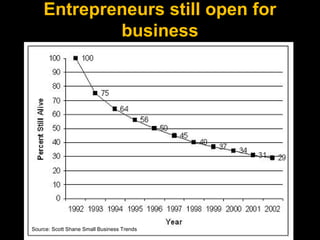
This document provides information about an economics course for students. It includes:
- An introduction and welcome to the course.
- Details about assignments, grading, and expectations.
- Explanations of key economic concepts like scarcity, opportunity costs, and factors of production.
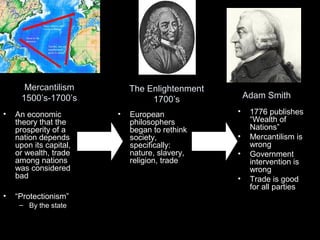
- Background on important economists and economic theories.
- Examples and activities to help students learn about entrepreneurship.