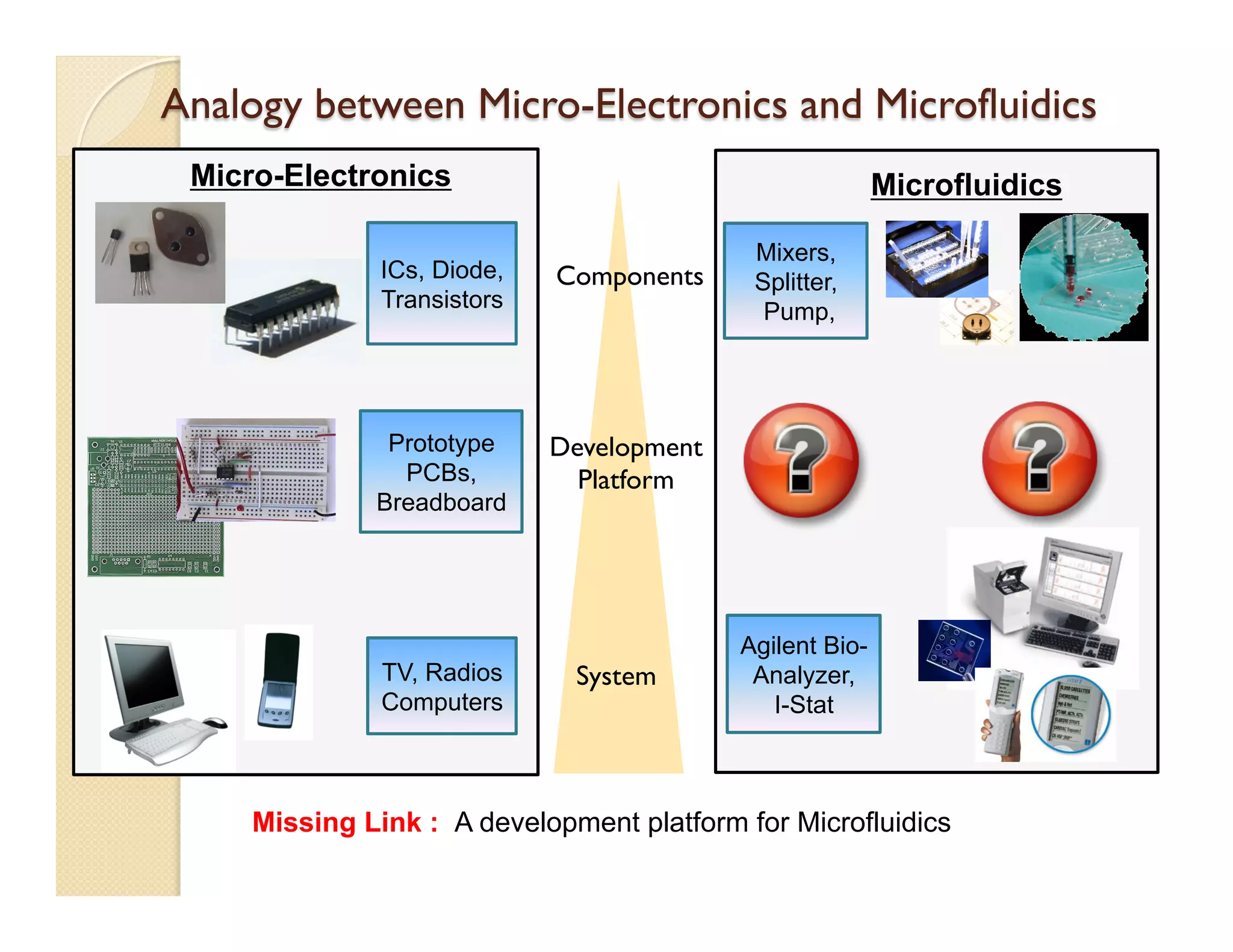
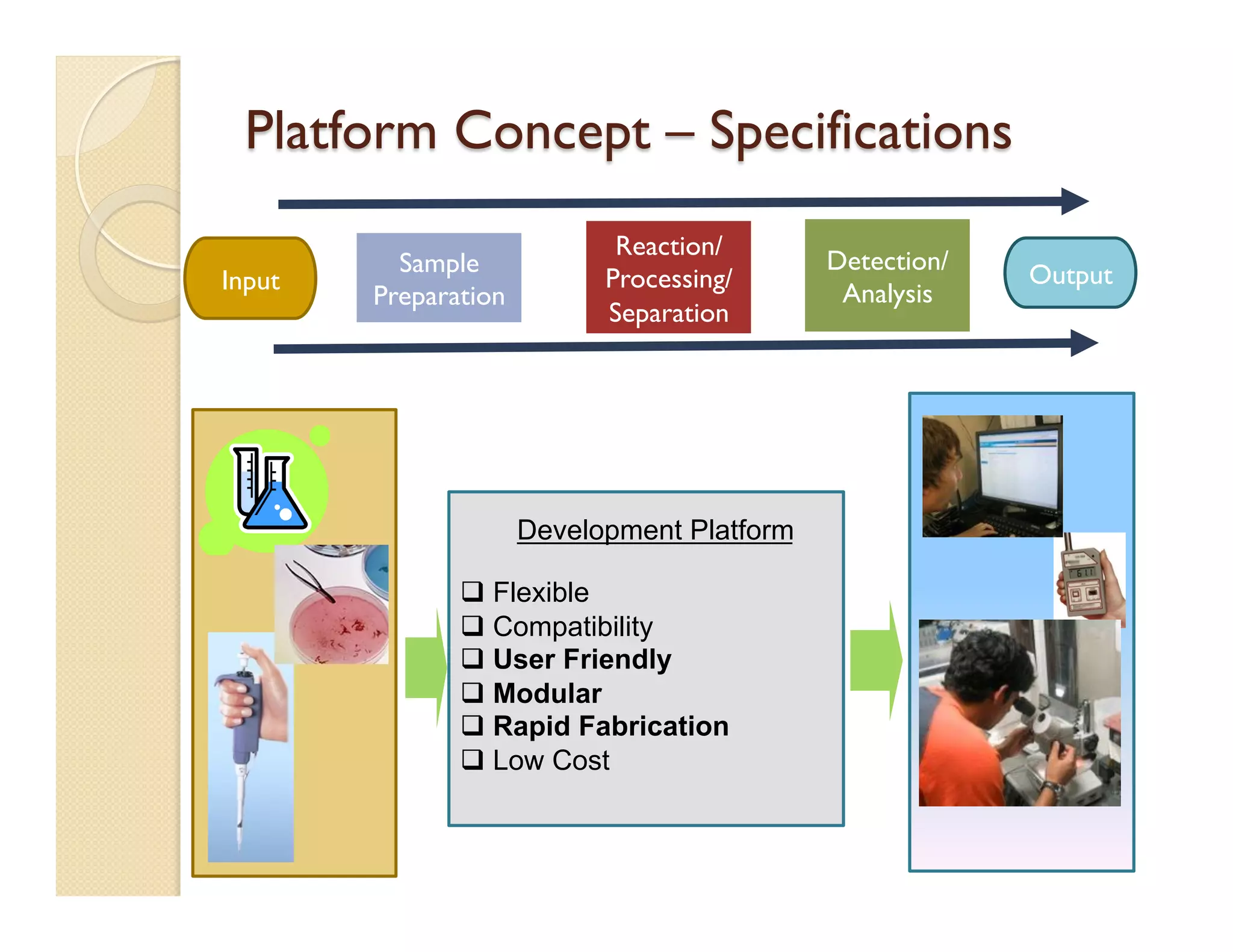
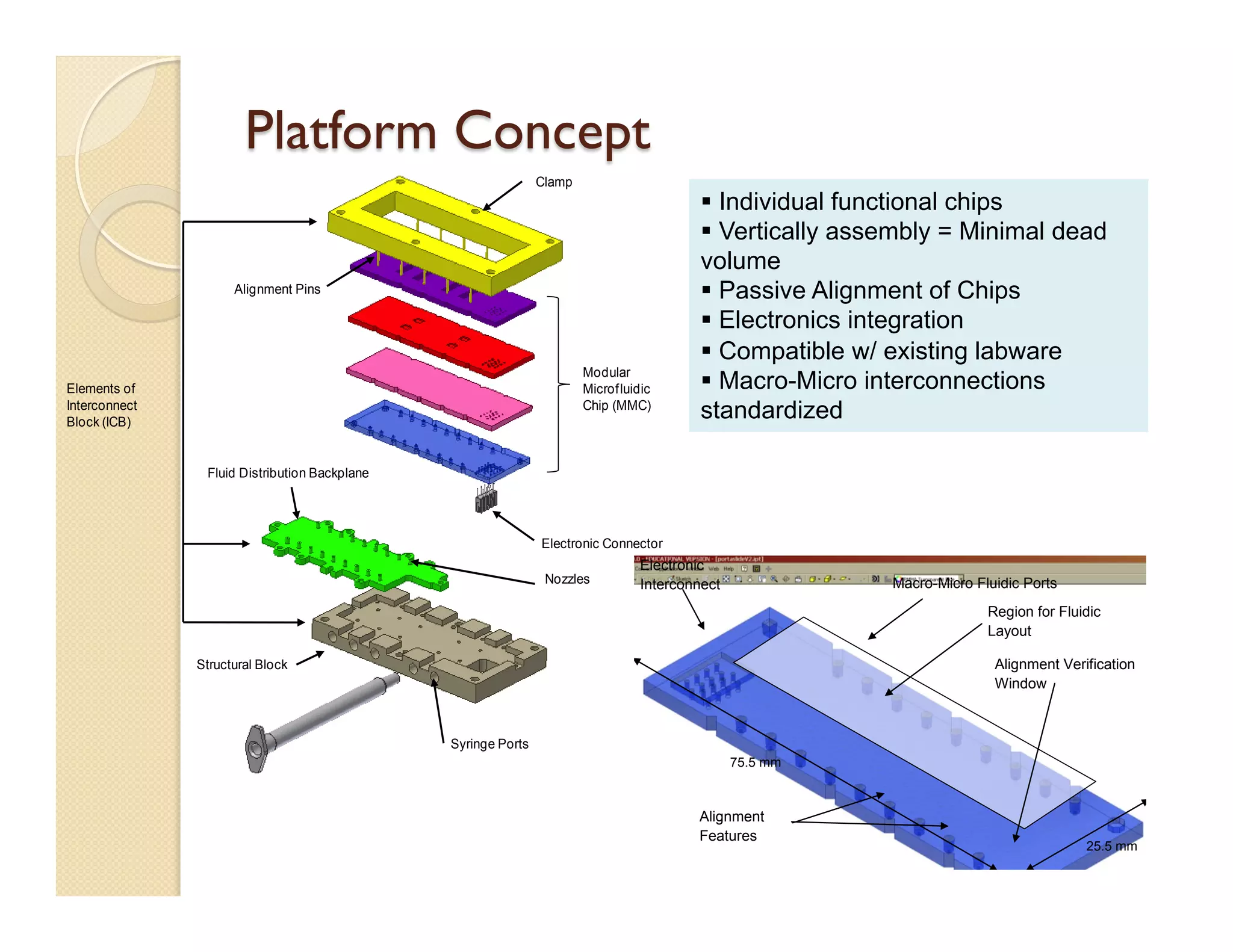
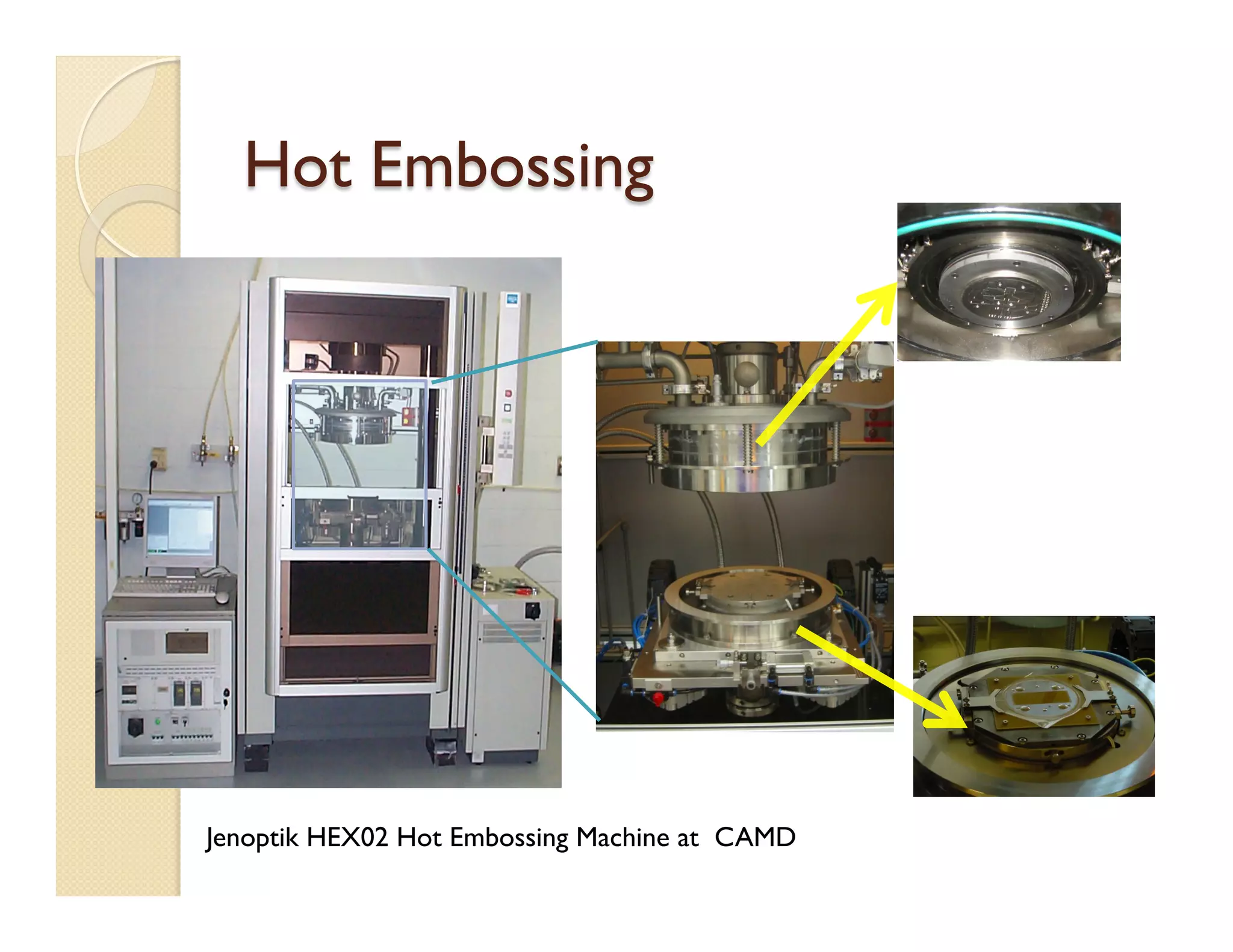
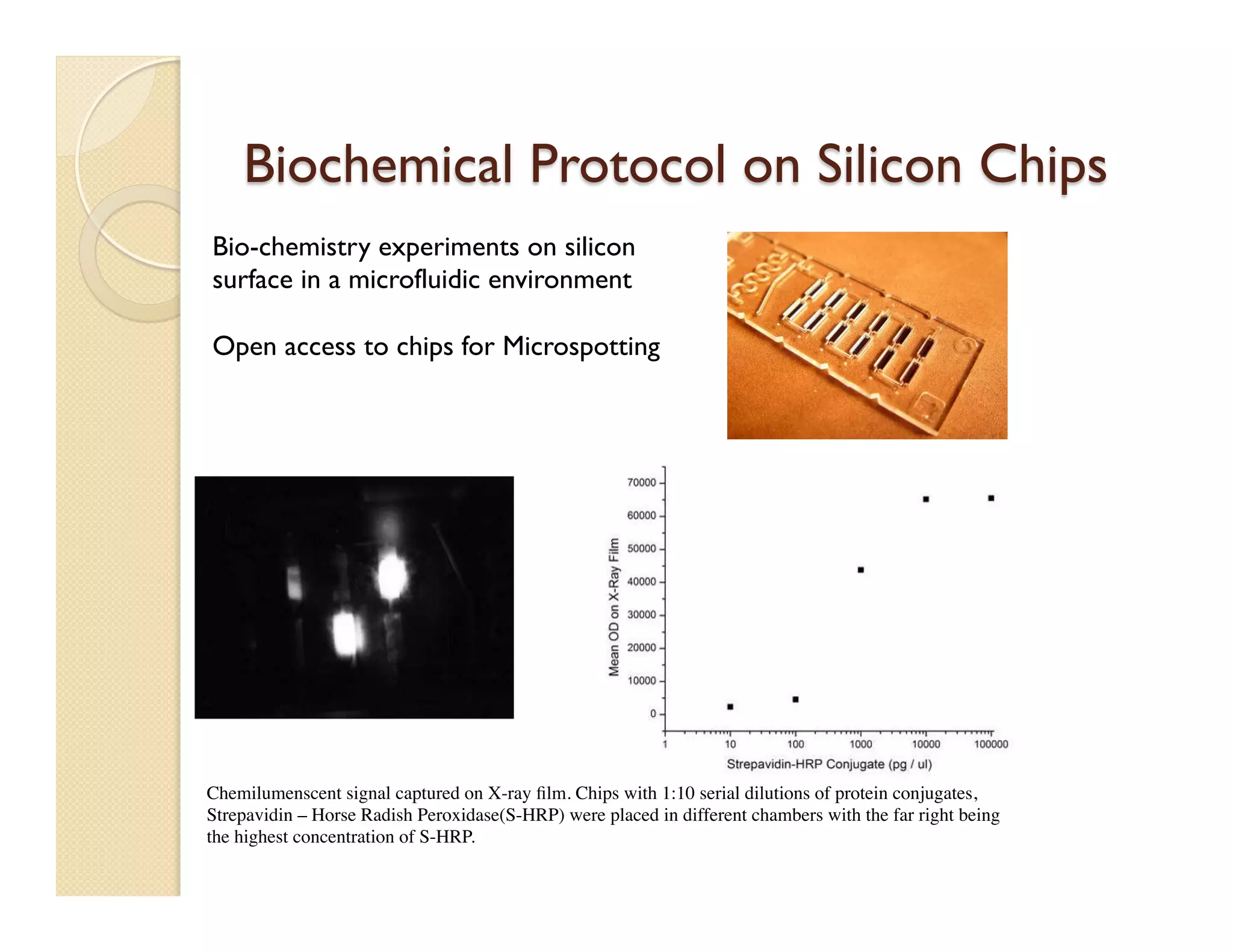
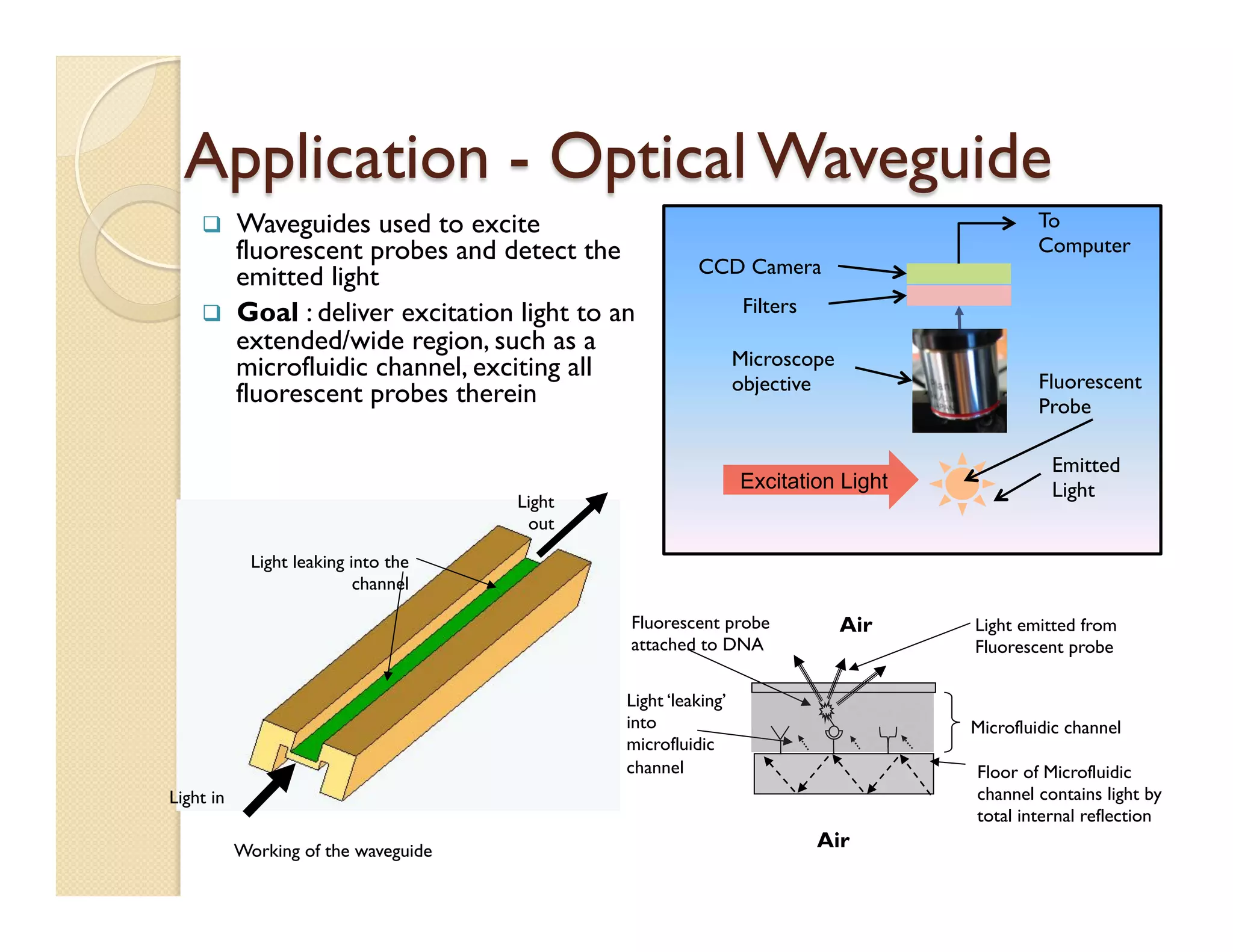
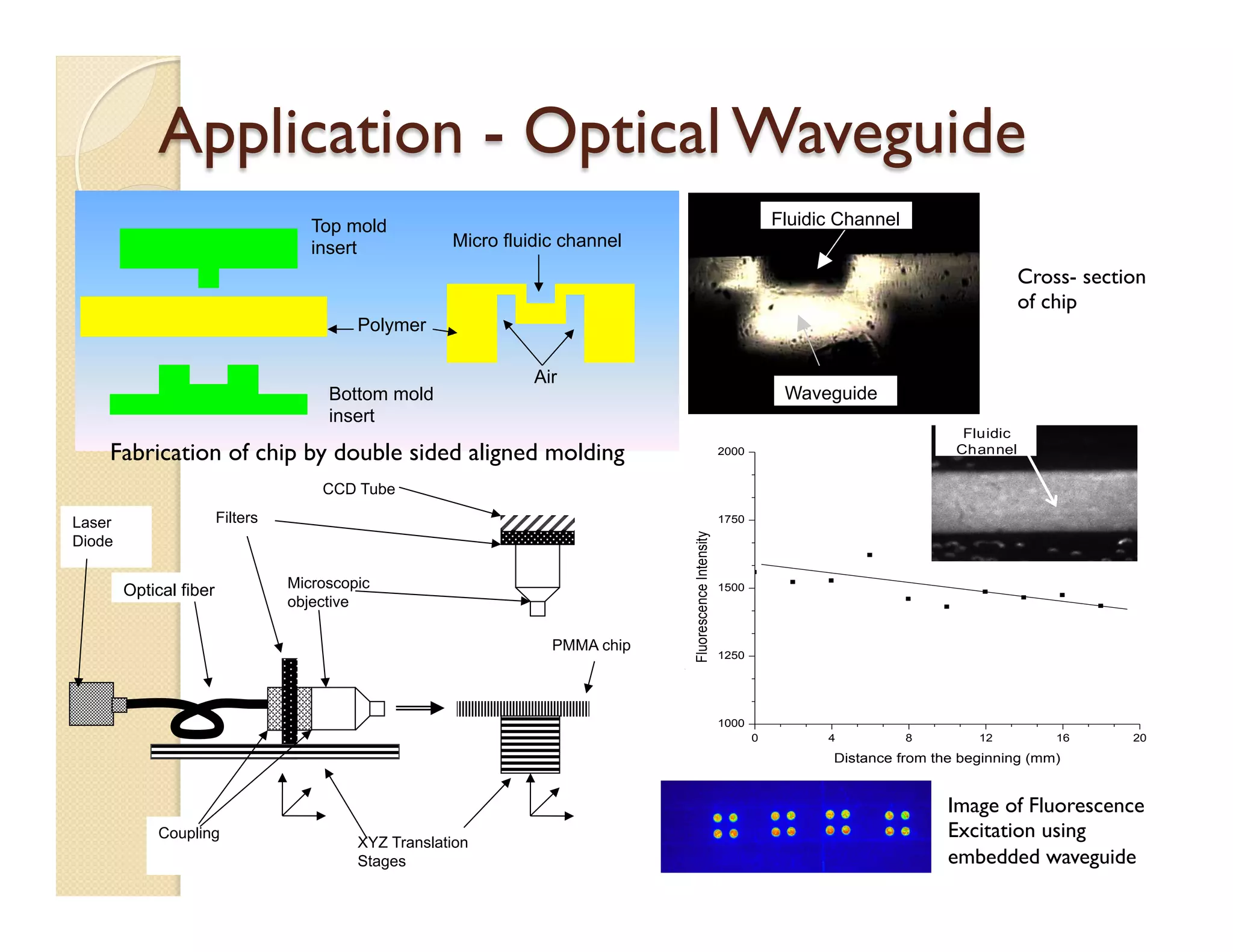
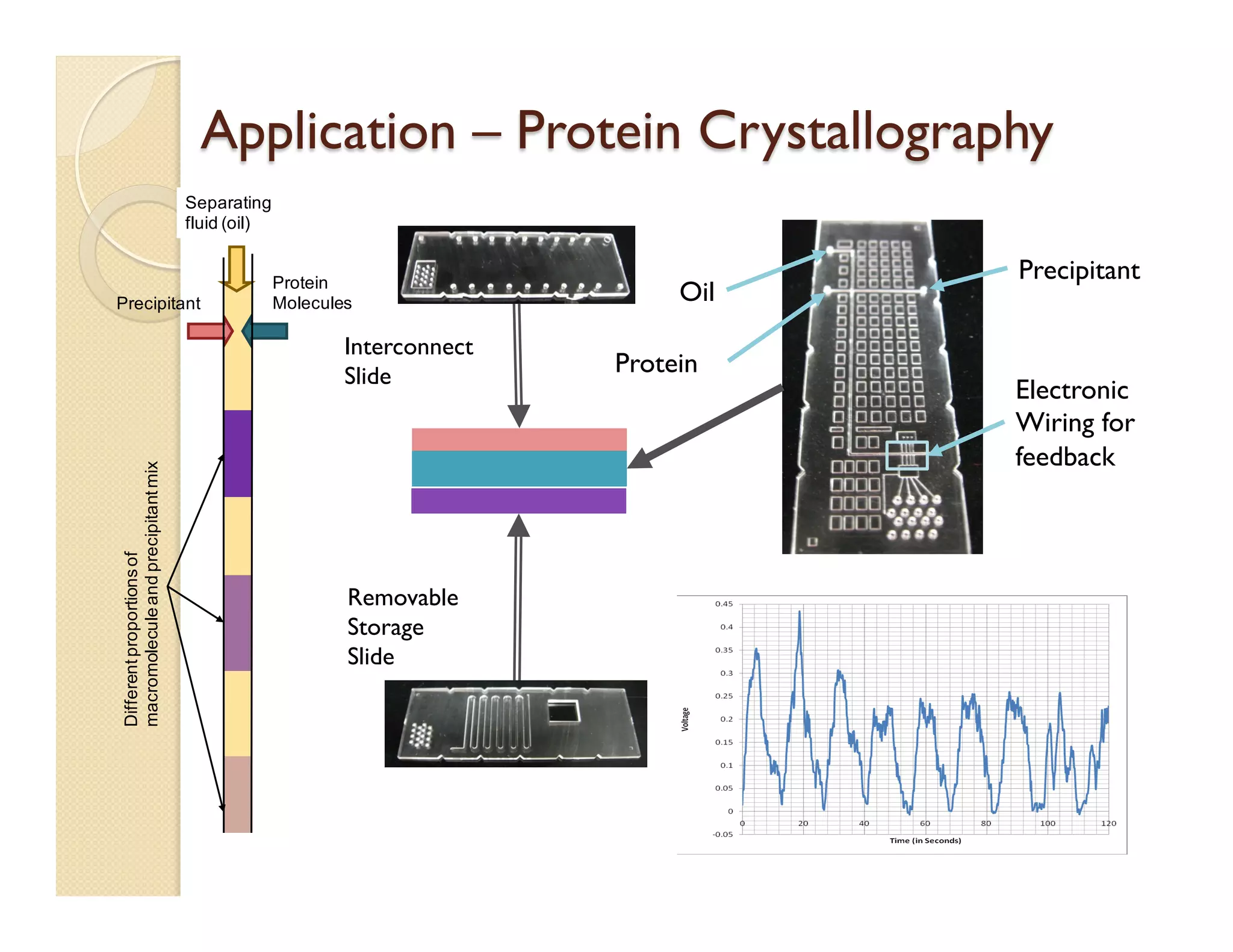
The document describes a modular polymeric development platform for microfluidic applications. Key points:
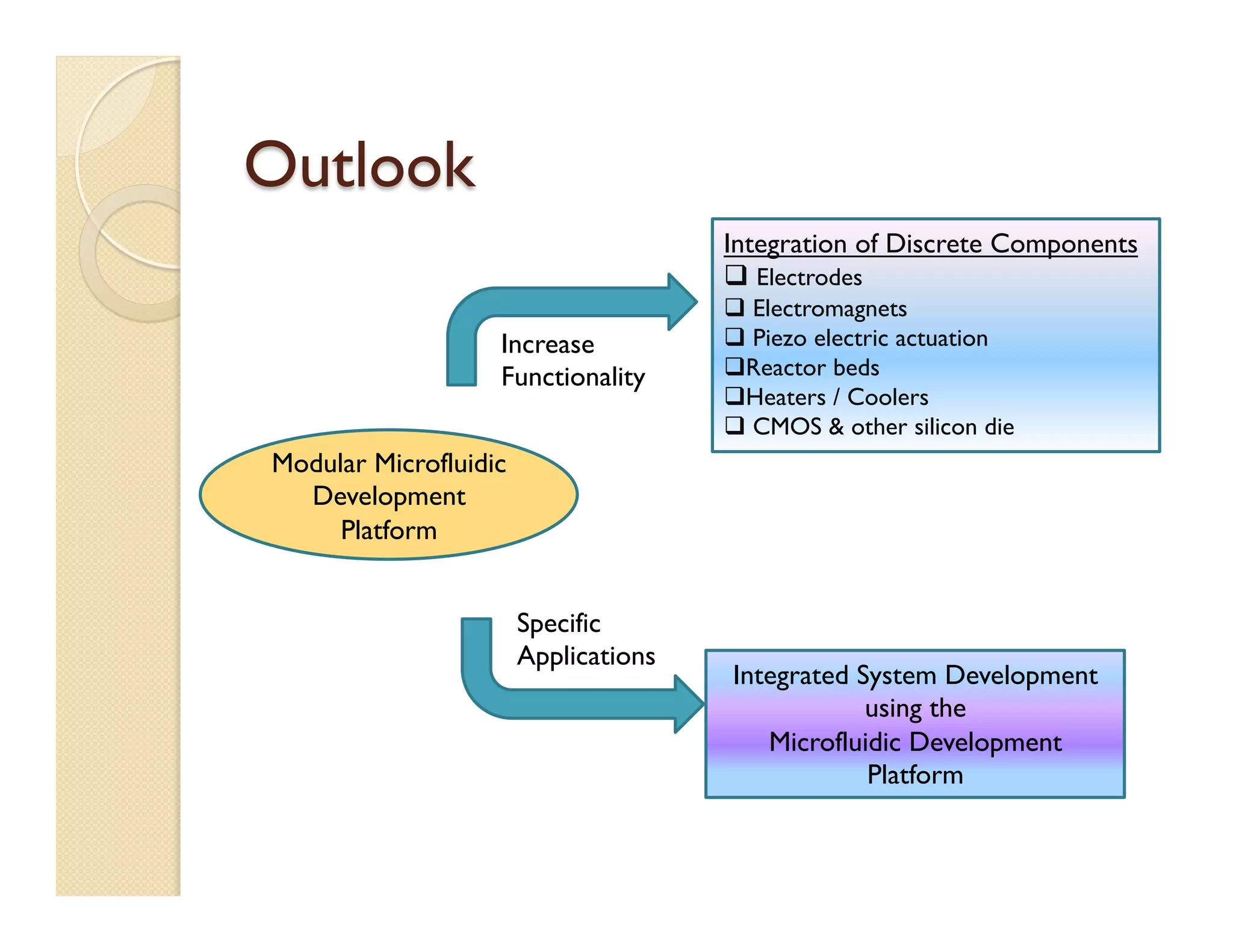
- The goal is to design, build, and test a general-purpose microfluidic development platform to enable transition from prototype to mass production.
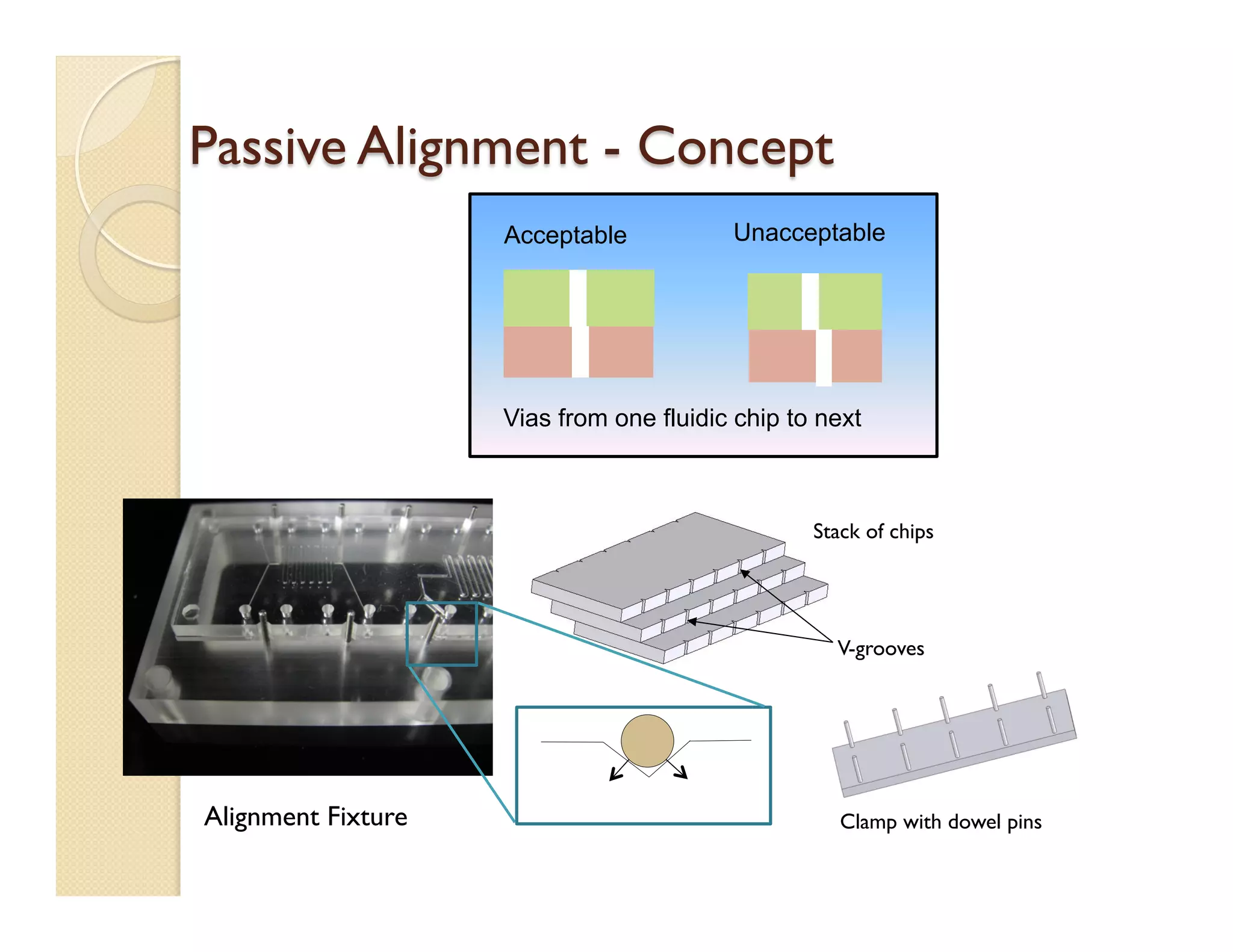
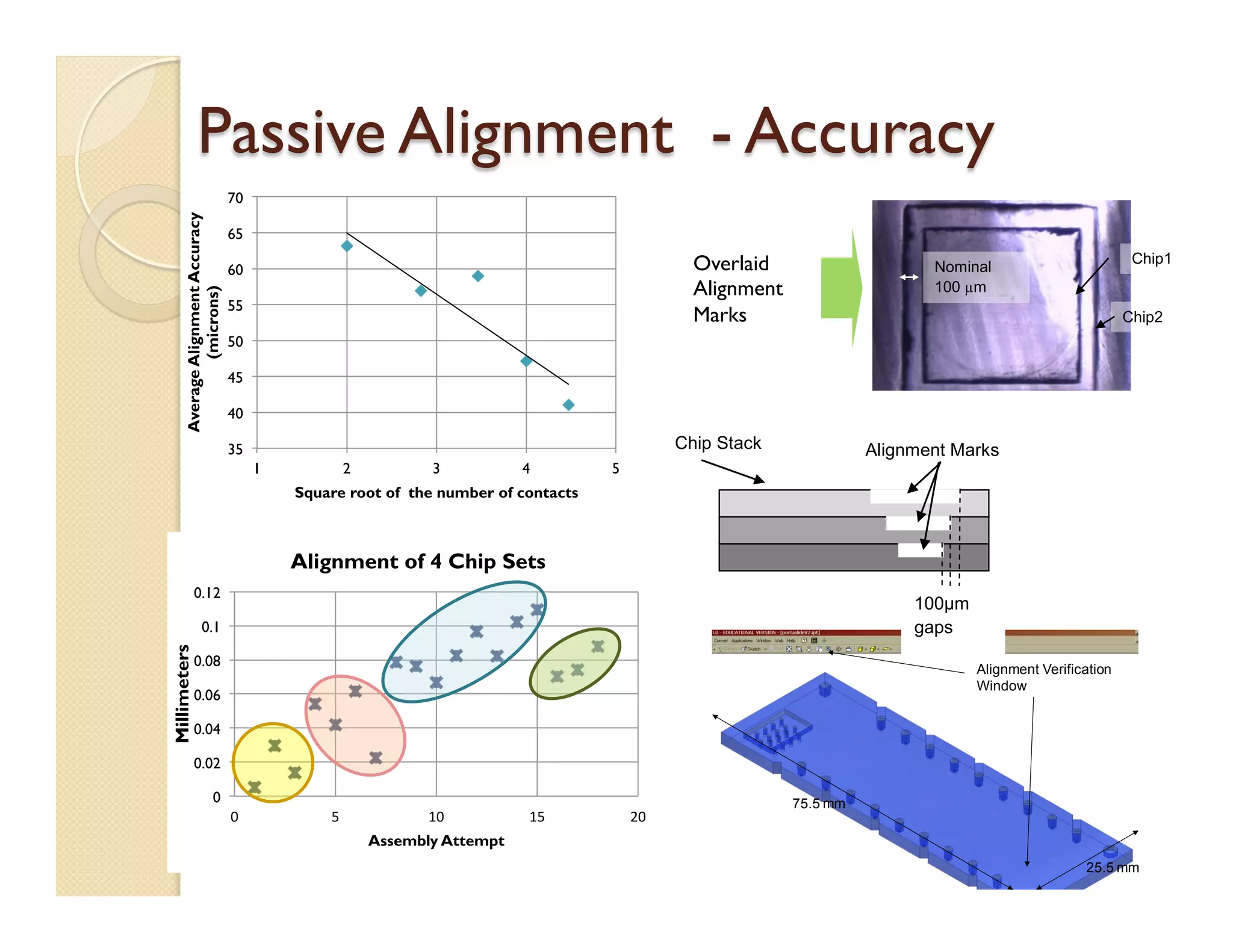
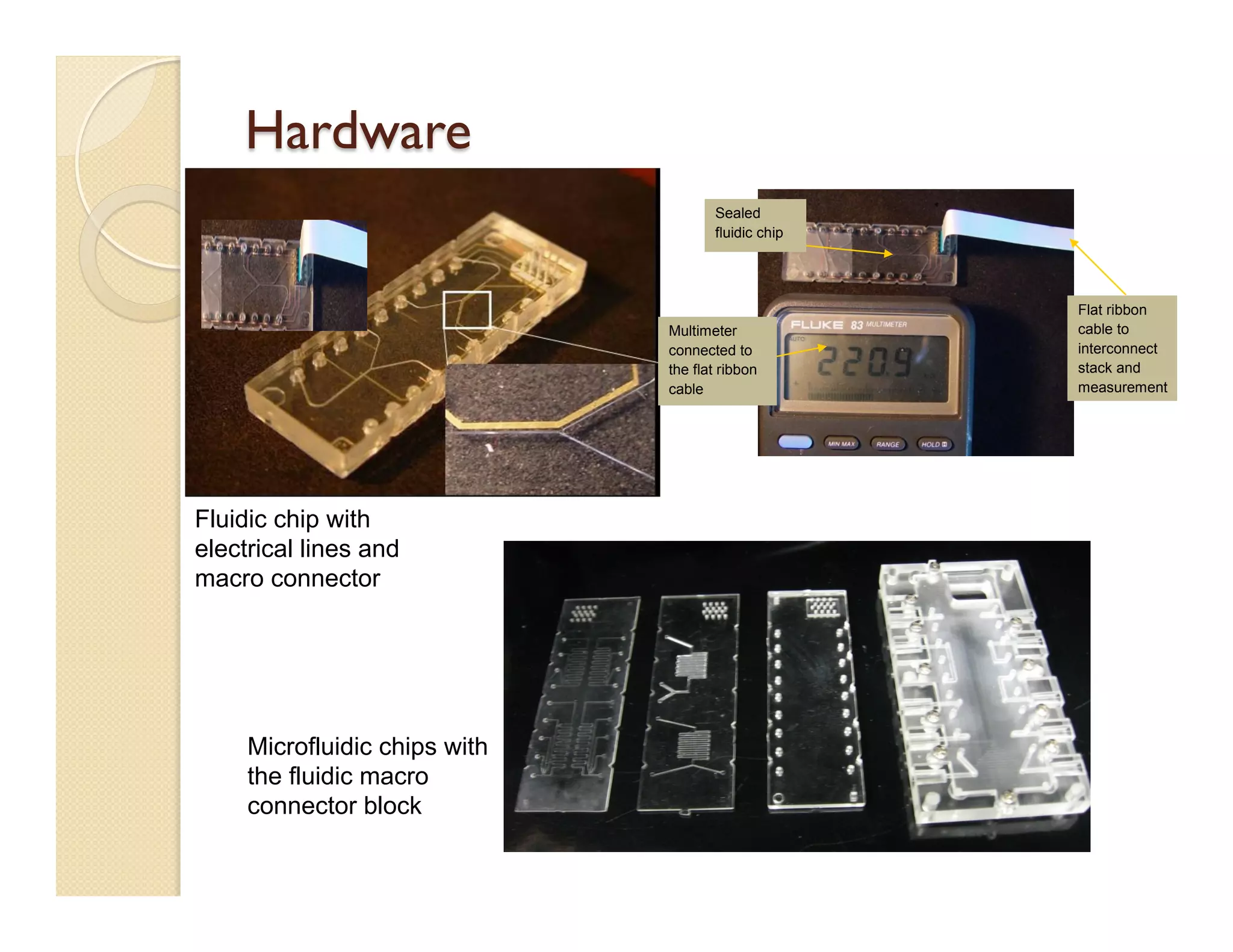
- The platform uses vertically stacked, modular microfluidic chips that can be easily assembled and interfaced with external components through fluidic and electrical interconnects.
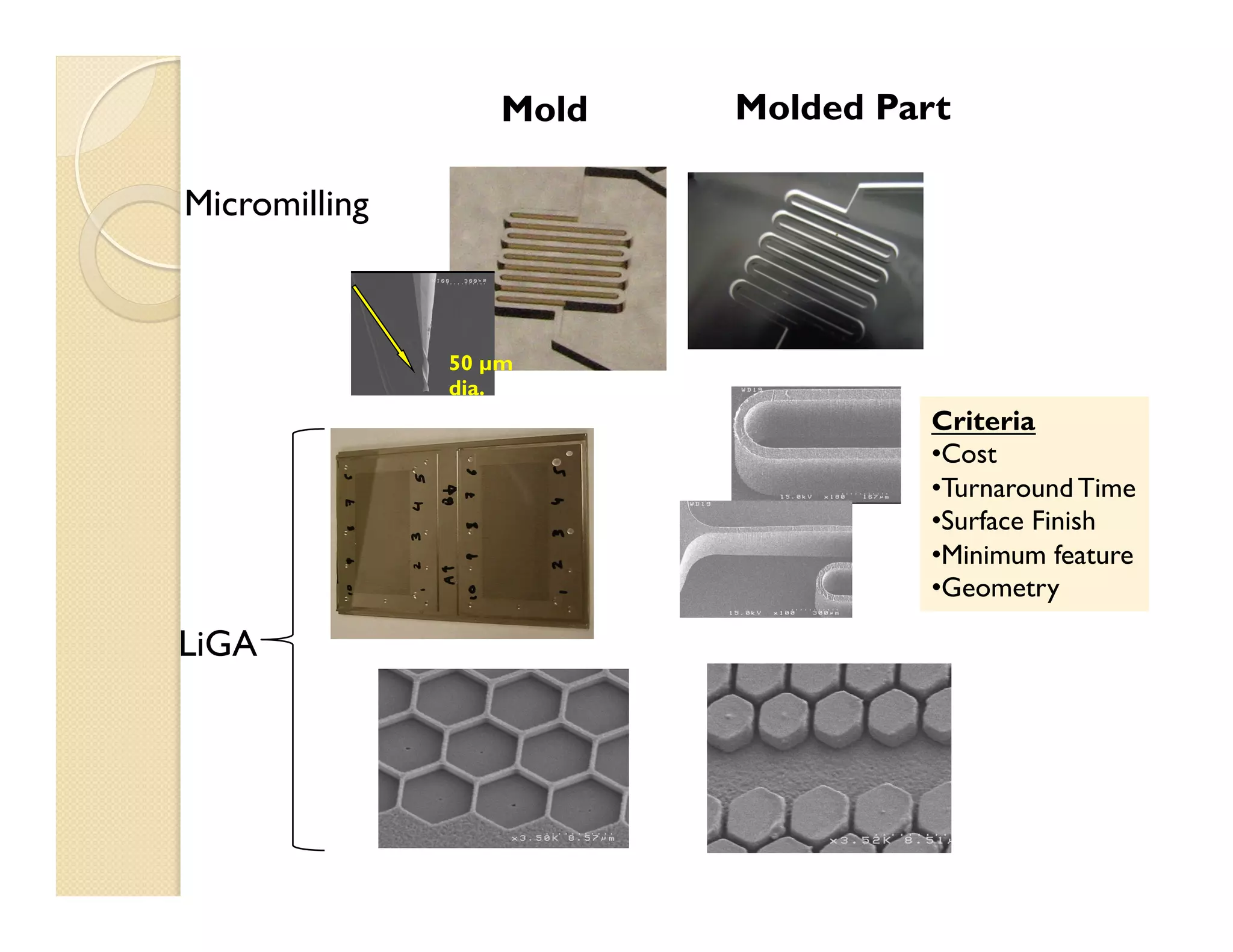
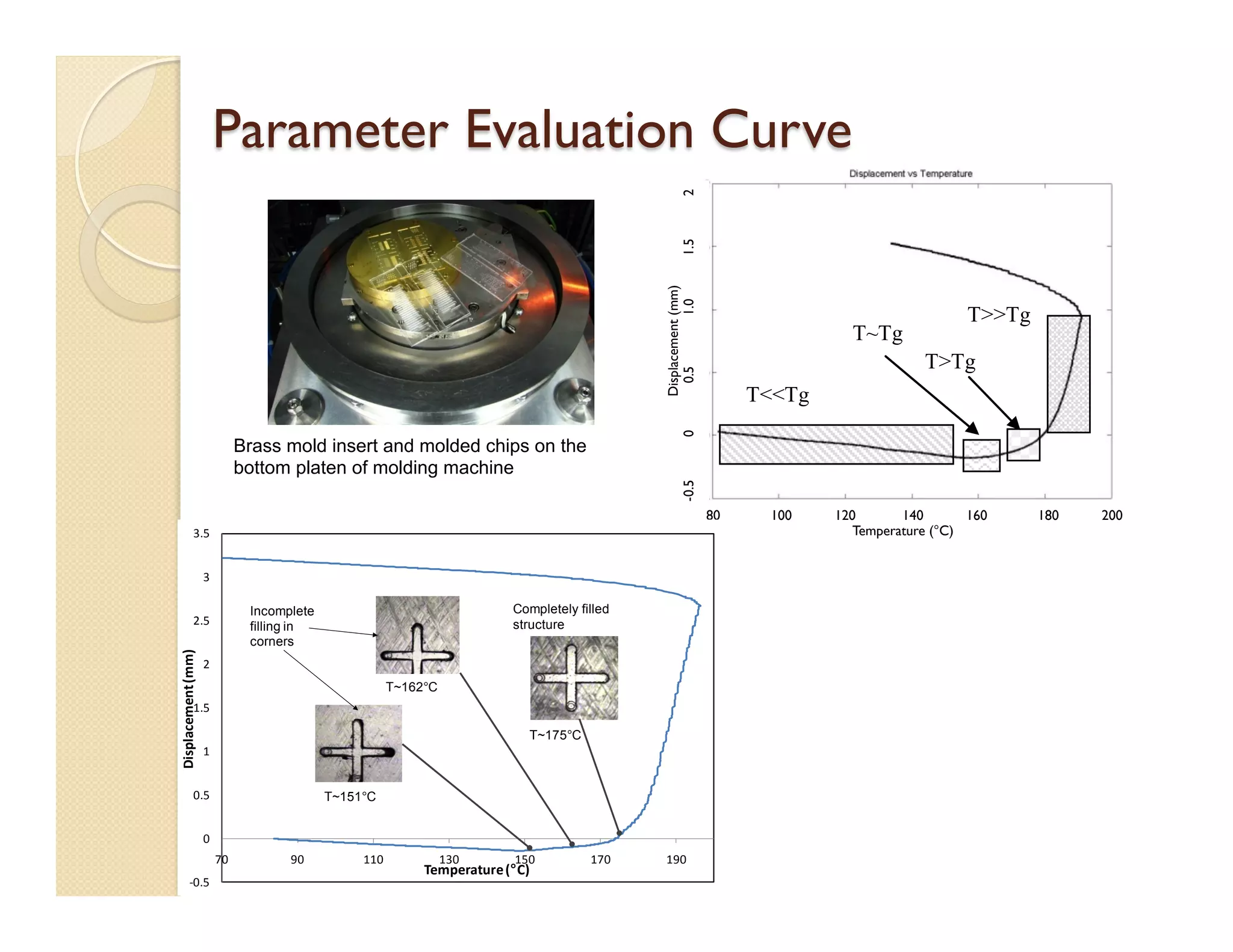
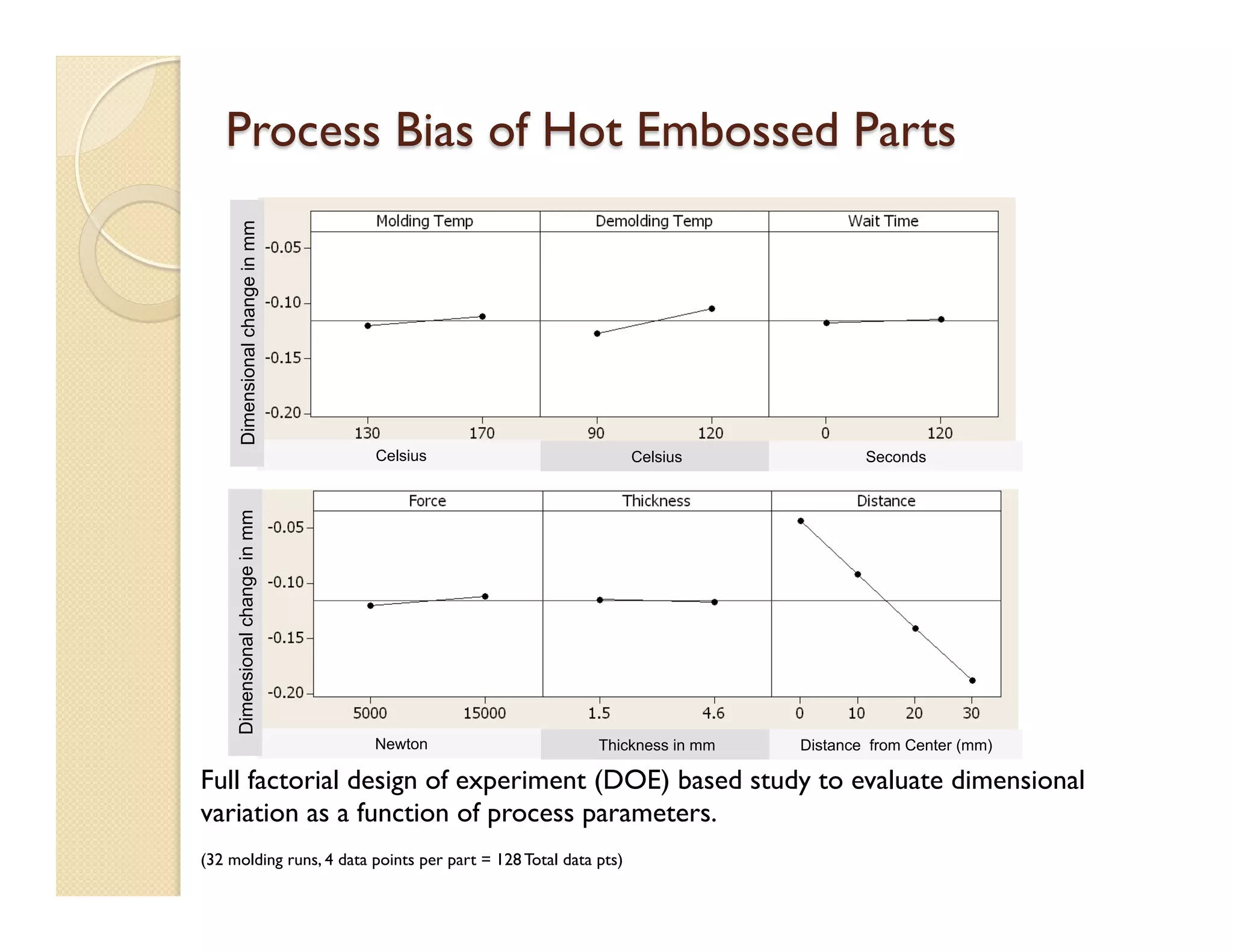
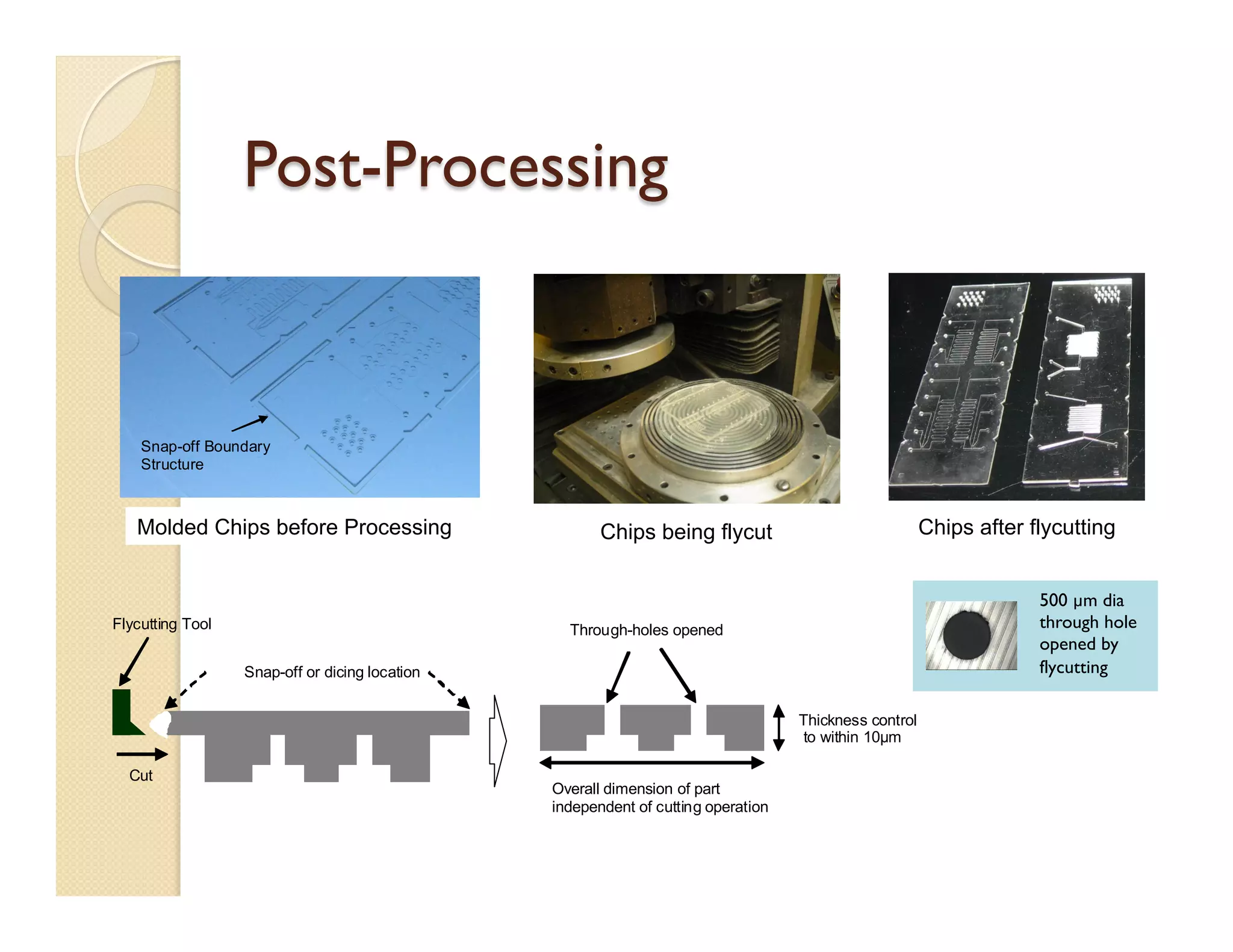
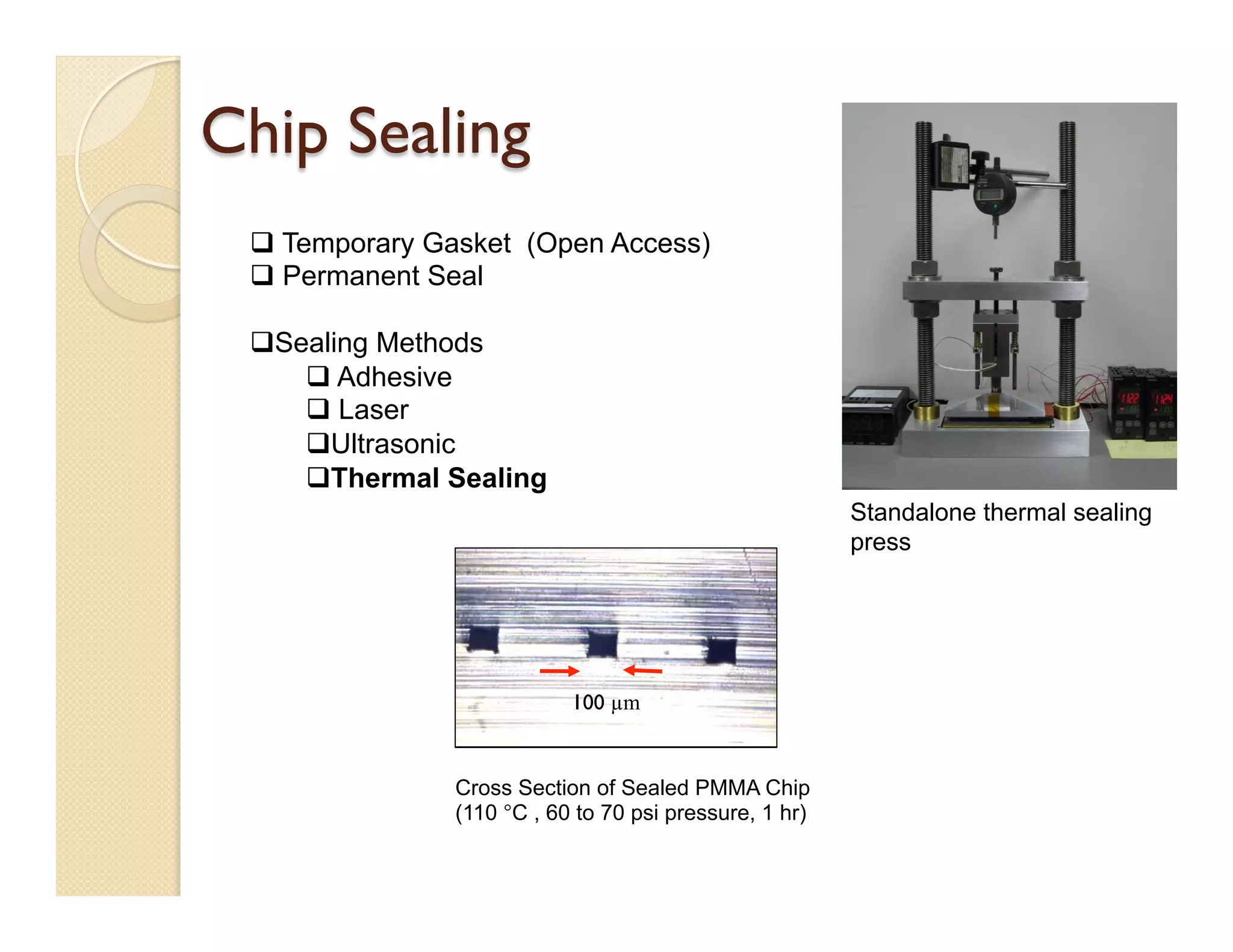
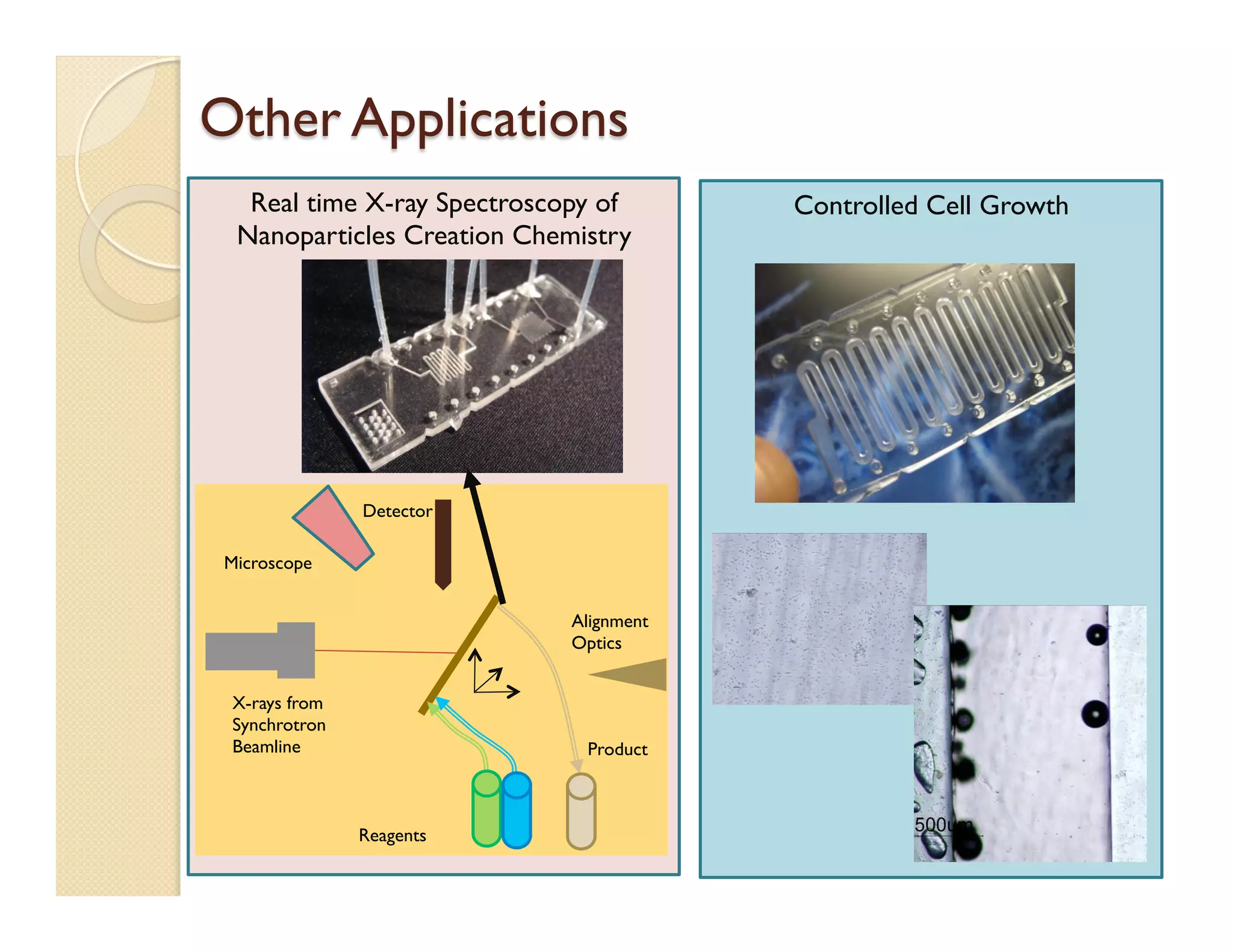
- Fabrication involves molding polymer chips using hot embossing, then post-processing like flycutting. Various applications are demonstrated including surface chemistry, optical waveguides, and protein crystallization.
- The platform provides a standardized, low-cost and user-friendly system for developing and testing microfluid