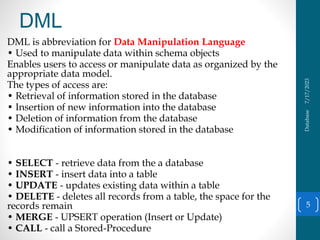
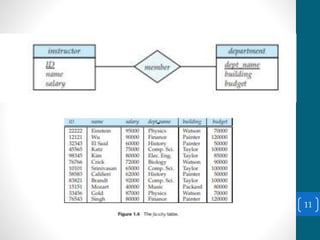
This document discusses database languages and SQL. It defines a query language as the portion of a data manipulation language (DML) used for information retrieval. SQL is introduced as the most widely used query language, which can be divided into more specific languages including DDL, DML, DCL, and TCL. DDL is used to define the database structure, DML manipulates data, DCL defines roles and permissions, and TCL manages transactions. The document provides examples of commands for each language. It also provides an example database design for a university.