The document discusses key concepts related to databases including:
- Databases store data in an organized format and support functions like storage, retrieval, modification and deletion of data.
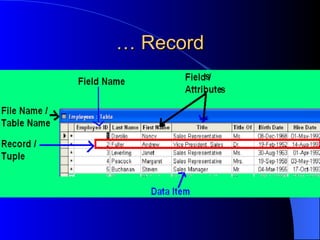
- Fields are items of information that make up a record and have a defined data type like text, numbers, dates etc. Records are collections of related fields that make up a row of data.
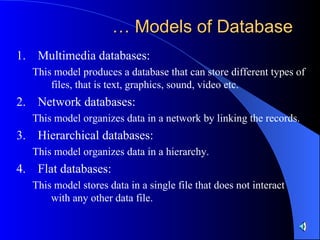
- Database management systems provide software to create, organize and query the data within databases and support different data models.