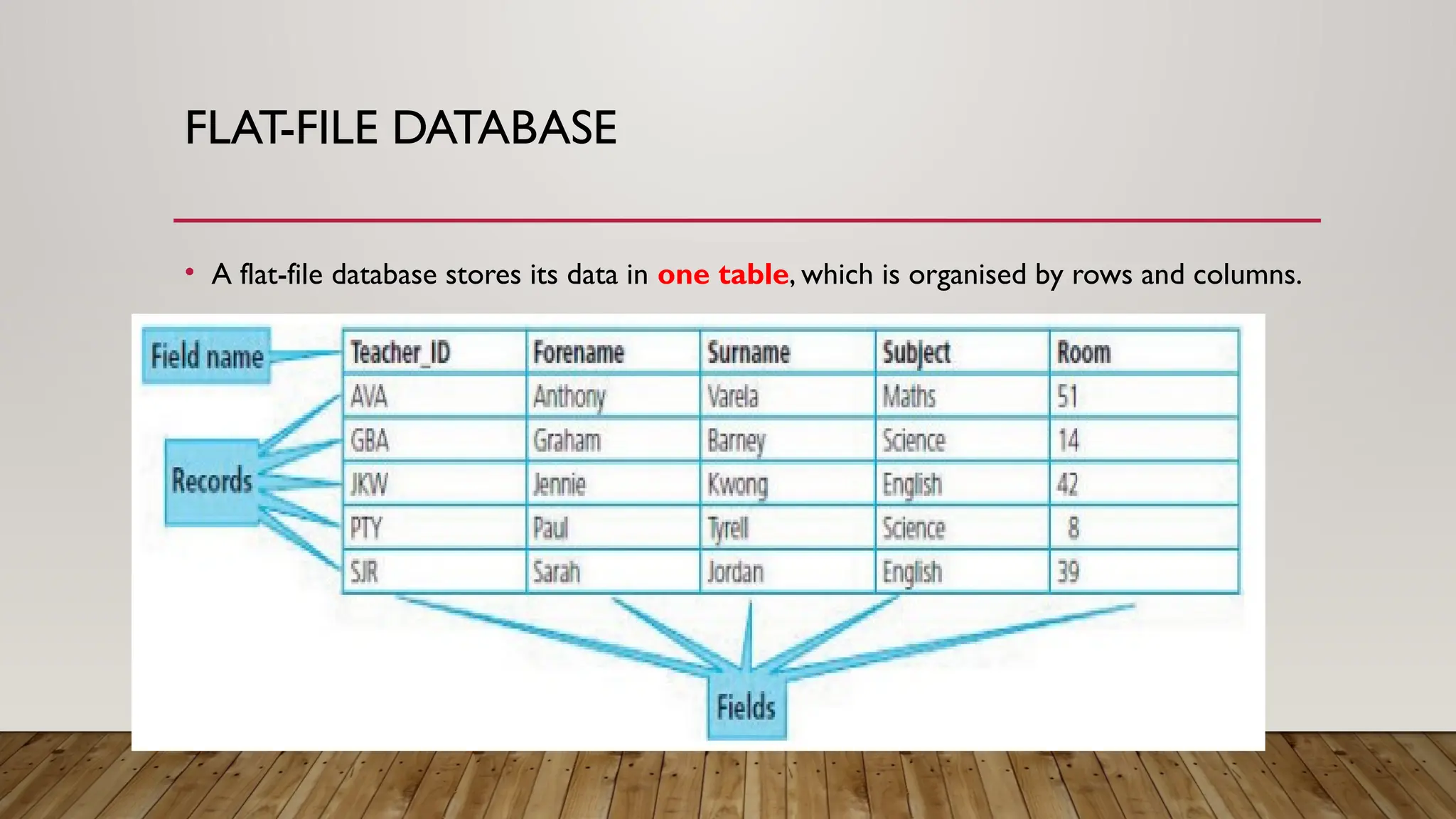
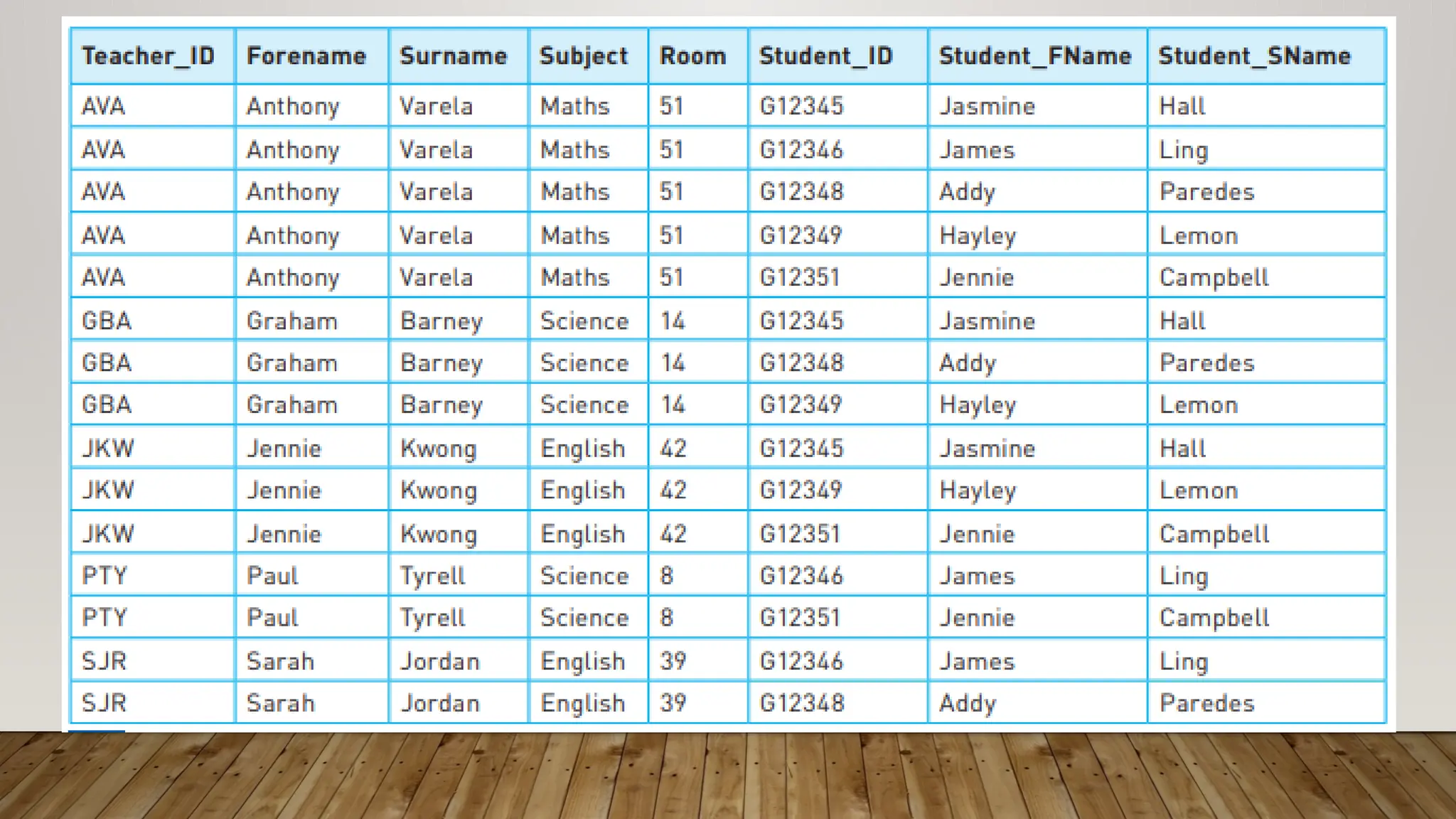
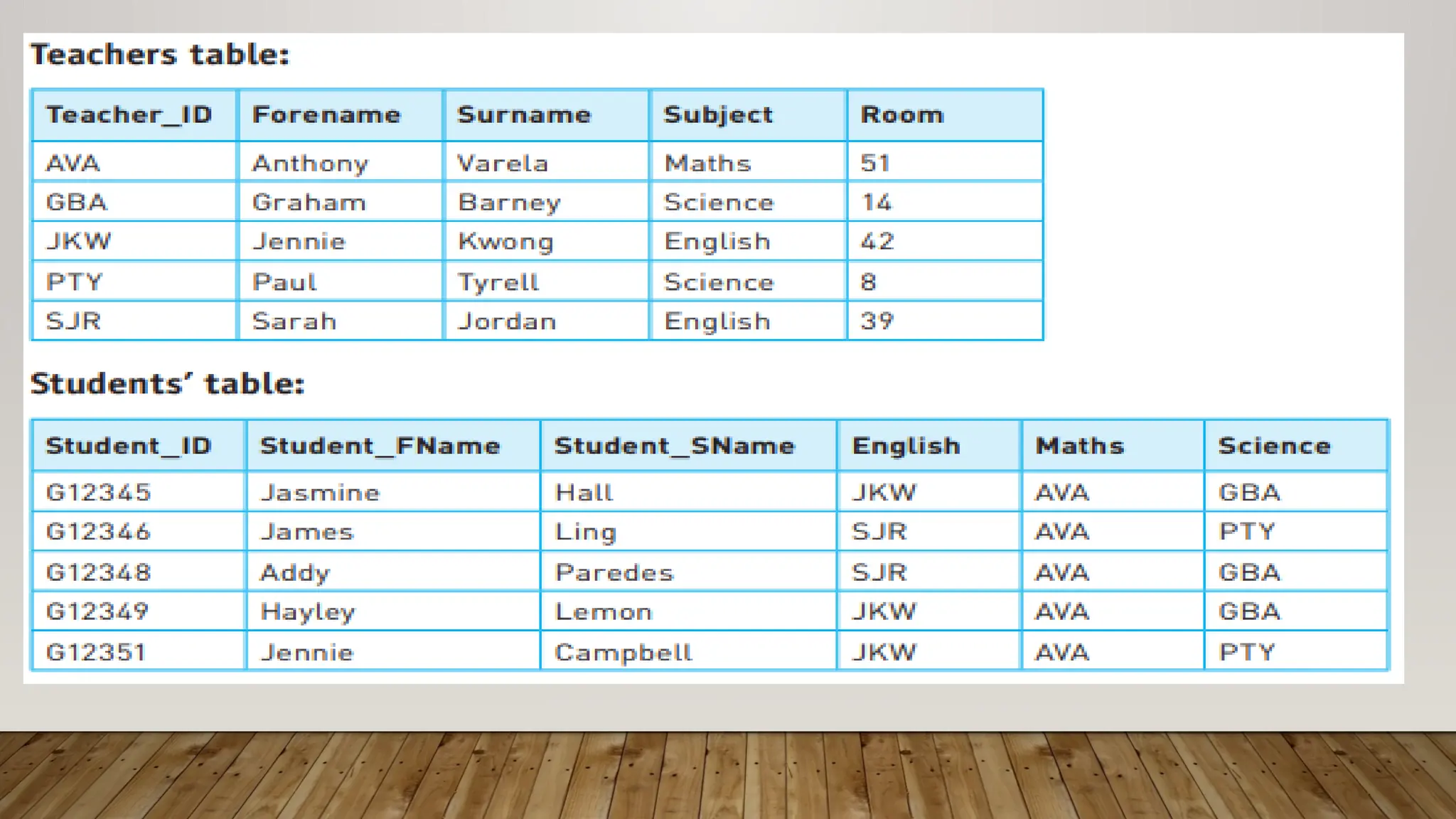
A database is an organized collection of data, managed by a database program that stores and retrieves data systematically. Data is organized into fields, records, and files, with types including flat-file and relational databases, the latter of which links multiple tables to optimize storage. Key fields such as primary and foreign keys ensure data integrity, while various data types support different kinds of information, including alphanumeric, numeric, and boolean data.