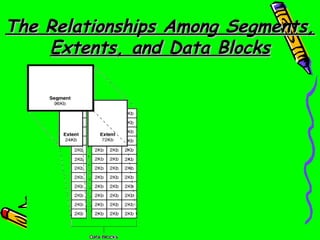
This presentation discusses database storage concepts in Oracle including blocks, extends, segments, and tablespaces. It defines each concept as follows:
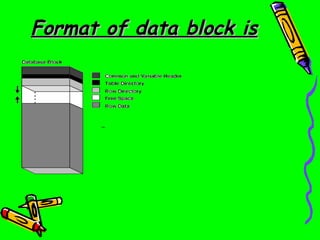
Blocks are the smallest logical unit of storage in Oracle and represent a specific number of bytes on disk. Extents are collections of contiguous data blocks that make up segments. Segments store specific data structures like tables or indexes and are made up of one or more extents. Tablespaces logically store segments and physically store data in associated datafiles.