Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times



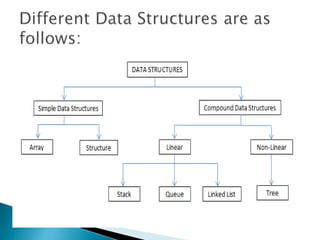
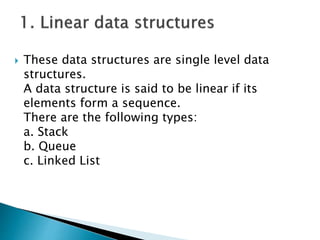

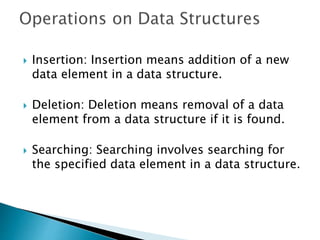
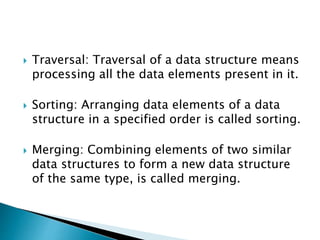


Data structures allow for the effective organization and processing of data as a single unit. They involve determining how to logically represent data, choosing a data structure type, and developing operations to apply to the data. Common simple data structures include arrays and structures, while more complex structures include stacks, queues, linked lists, and trees. Key operations on data structures are insertion, deletion, searching, traversal, sorting, and merging.











