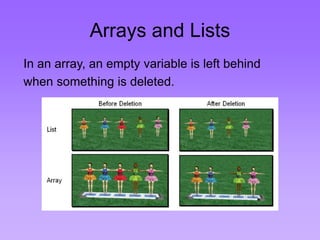
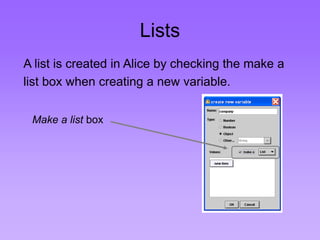
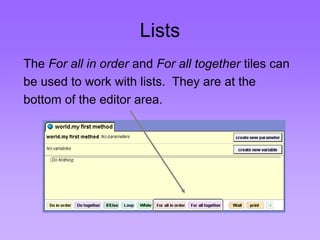
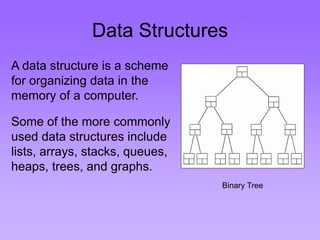
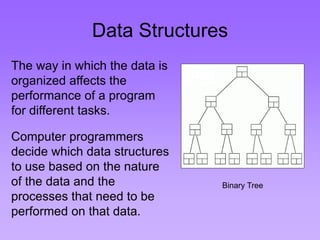
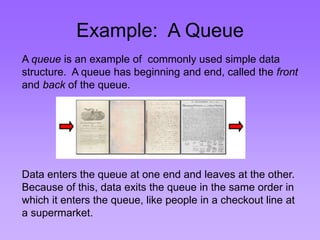
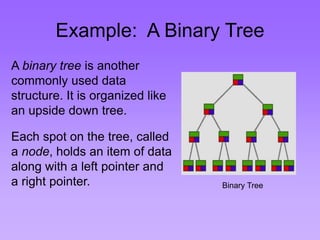
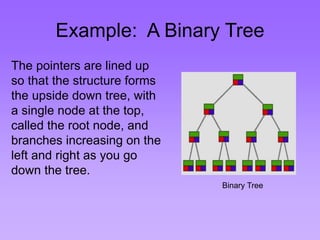
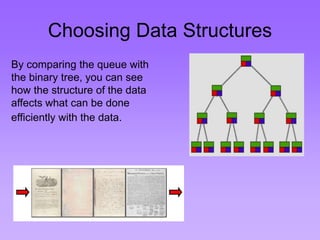
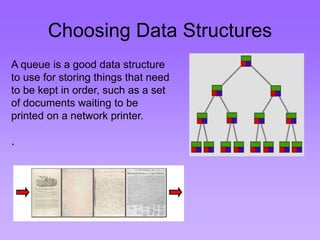
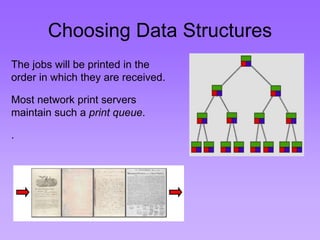
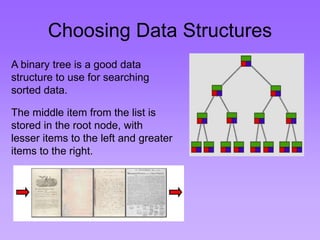
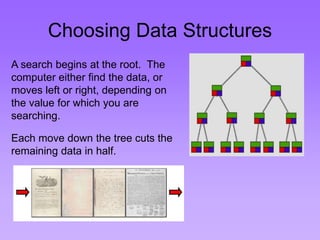
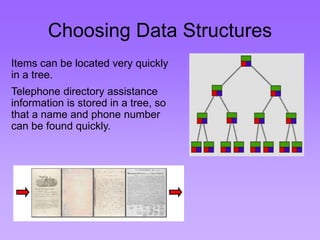
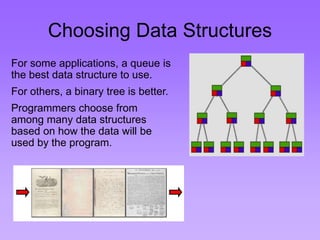
This document provides an introduction to common data structures including lists, arrays, stacks, queues, heaps, trees, and graphs. It explains that data structures organize data in memory and that the choice of data structure affects program performance for different tasks. The document then gives examples of queues and binary trees, explaining their structures and uses. It concludes that programmers choose appropriate data structures based on how the data will be used.


![Arrays
An array is an indexed set of variables, such as
dancer[1], dancer[2], dancer[3],… It is like a set of
boxes that hold things.
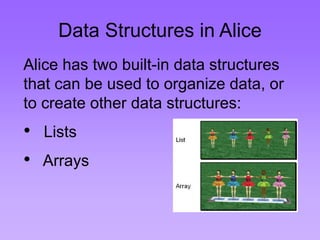
A list is a set of items.
An array is a set of
variables that each
store an item.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09c-datastructureslistsarrays-140902210900-phpapp01/85/data-structures-16-320.jpg)