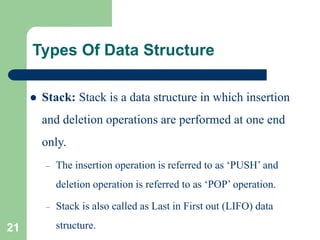
The document provides an overview of data structures and algorithms. It defines data structures as collections of data organized in a way that allows efficient access and modification. Algorithms are sets of instructions to solve problems or accomplish tasks. Common categories of algorithms include sort, search, delete, insert, and update. Data structures can be classified as primitive, linear, or non-linear. Linear structures include arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues while non-linear structures include trees and graphs. Common operations on data structures are searching, insertion, deletion, traversing, sorting, and merging.
















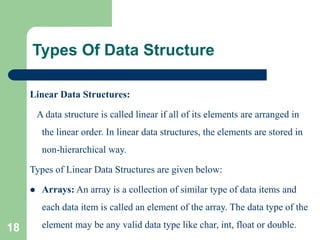
![Types Of Data Structure
The elements of array share the same variable name but each
one carries a different index number known as subscript. The
array can be one dimensional, two dimensional or
multidimensional.
The individual elements of the array age are:
age[0], age[1], age[2], age[3],......... age[98], age[99].
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch1-220312161656/85/Ch1-19-320.jpg)