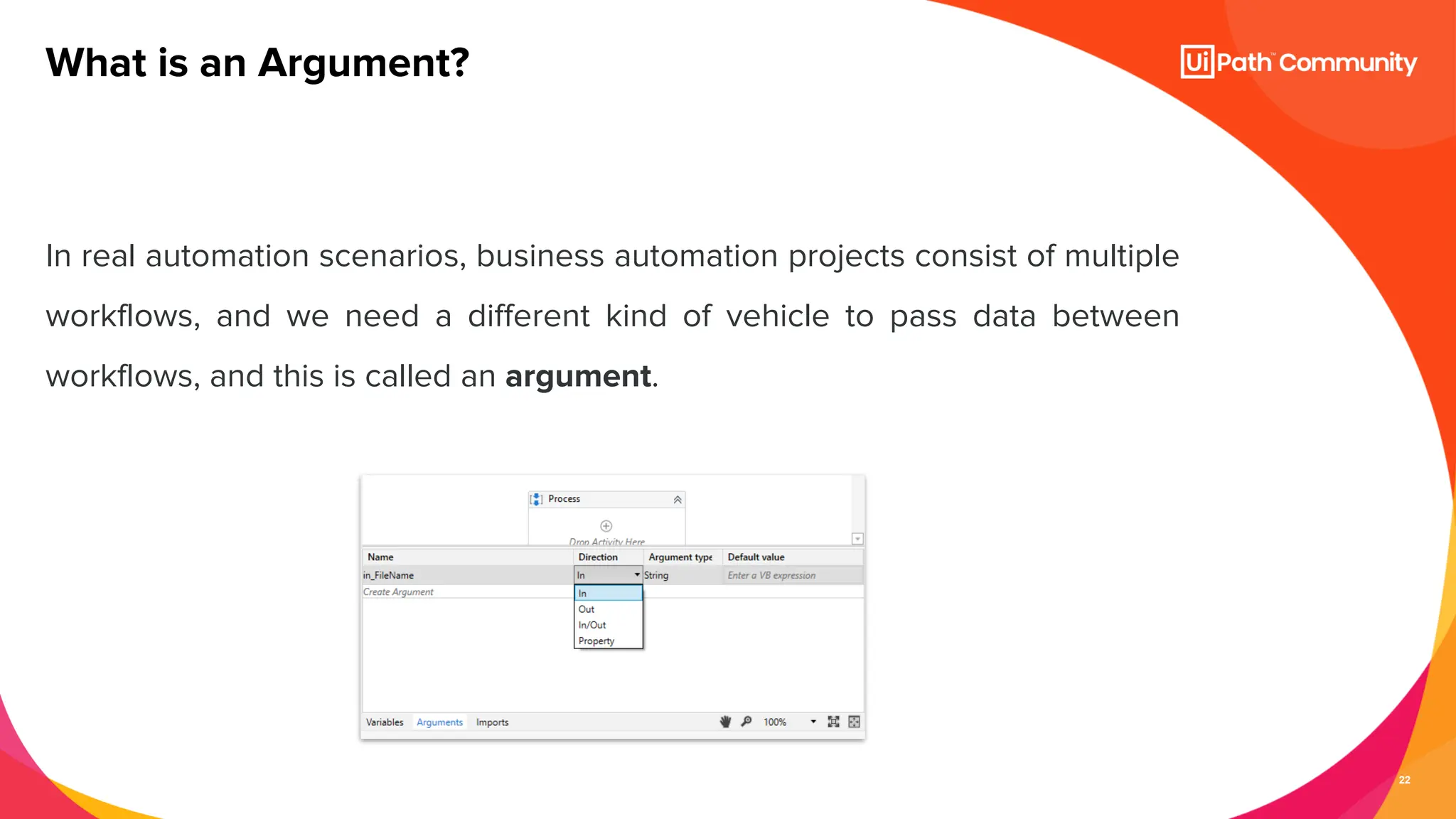
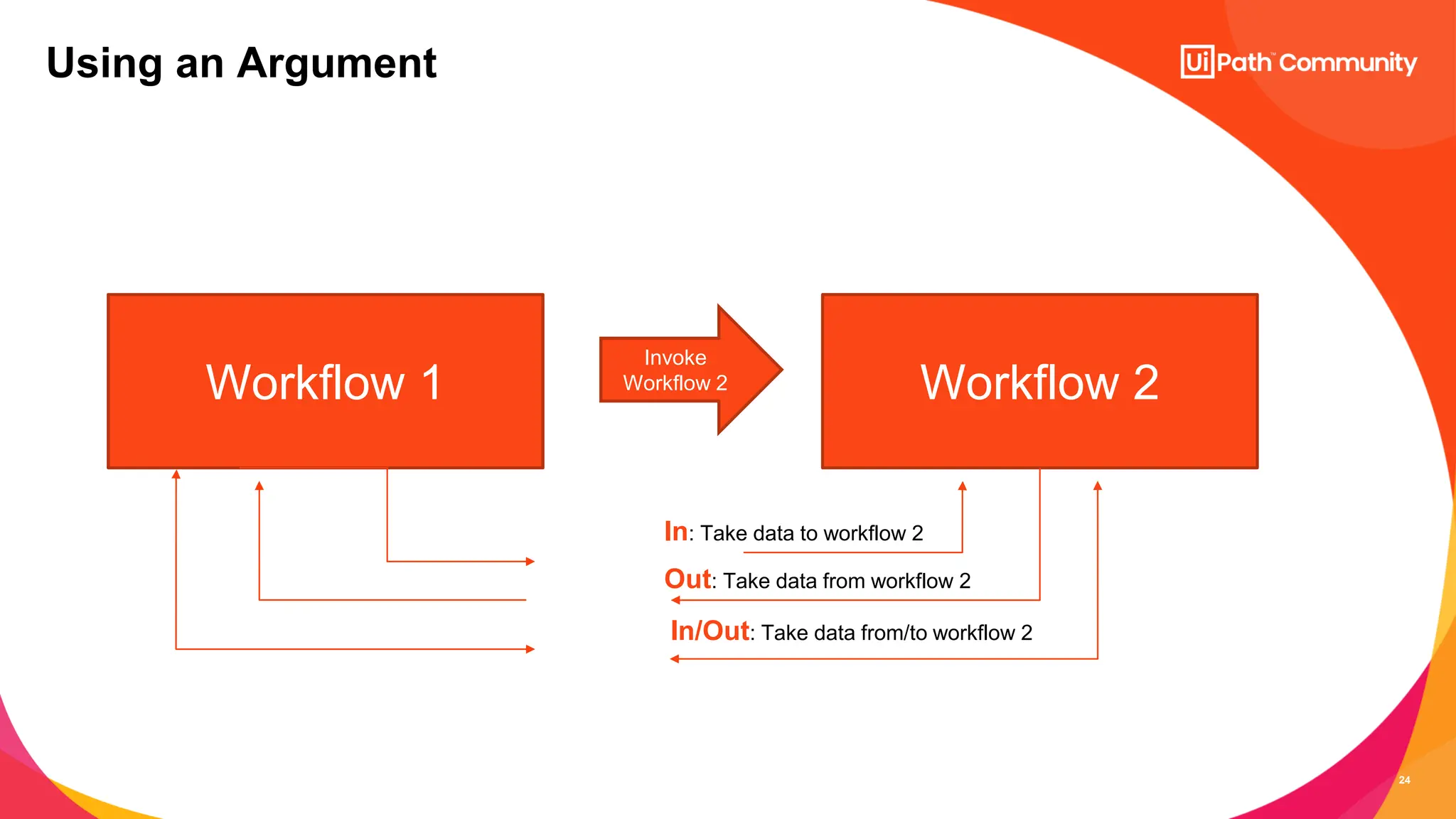
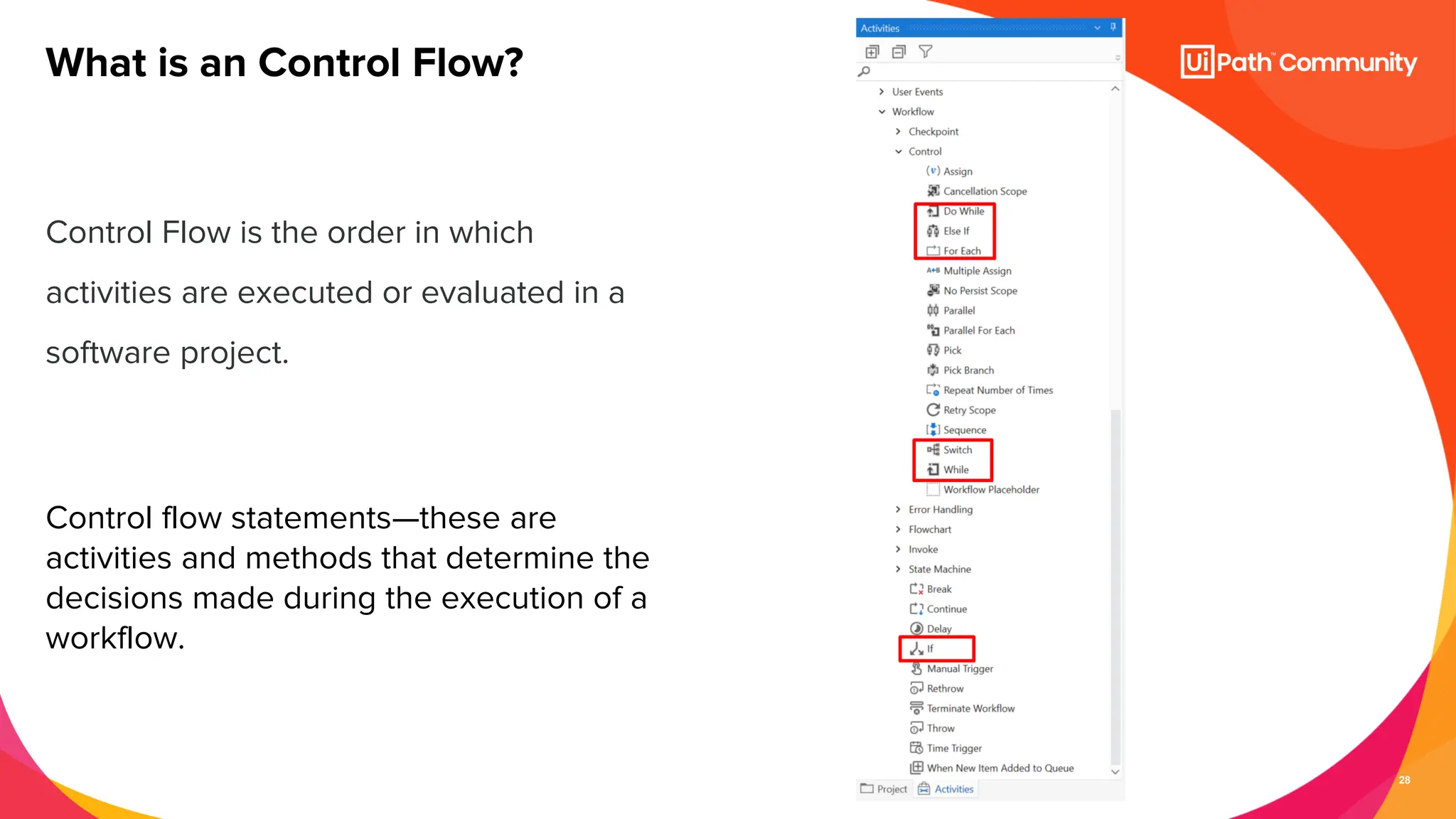
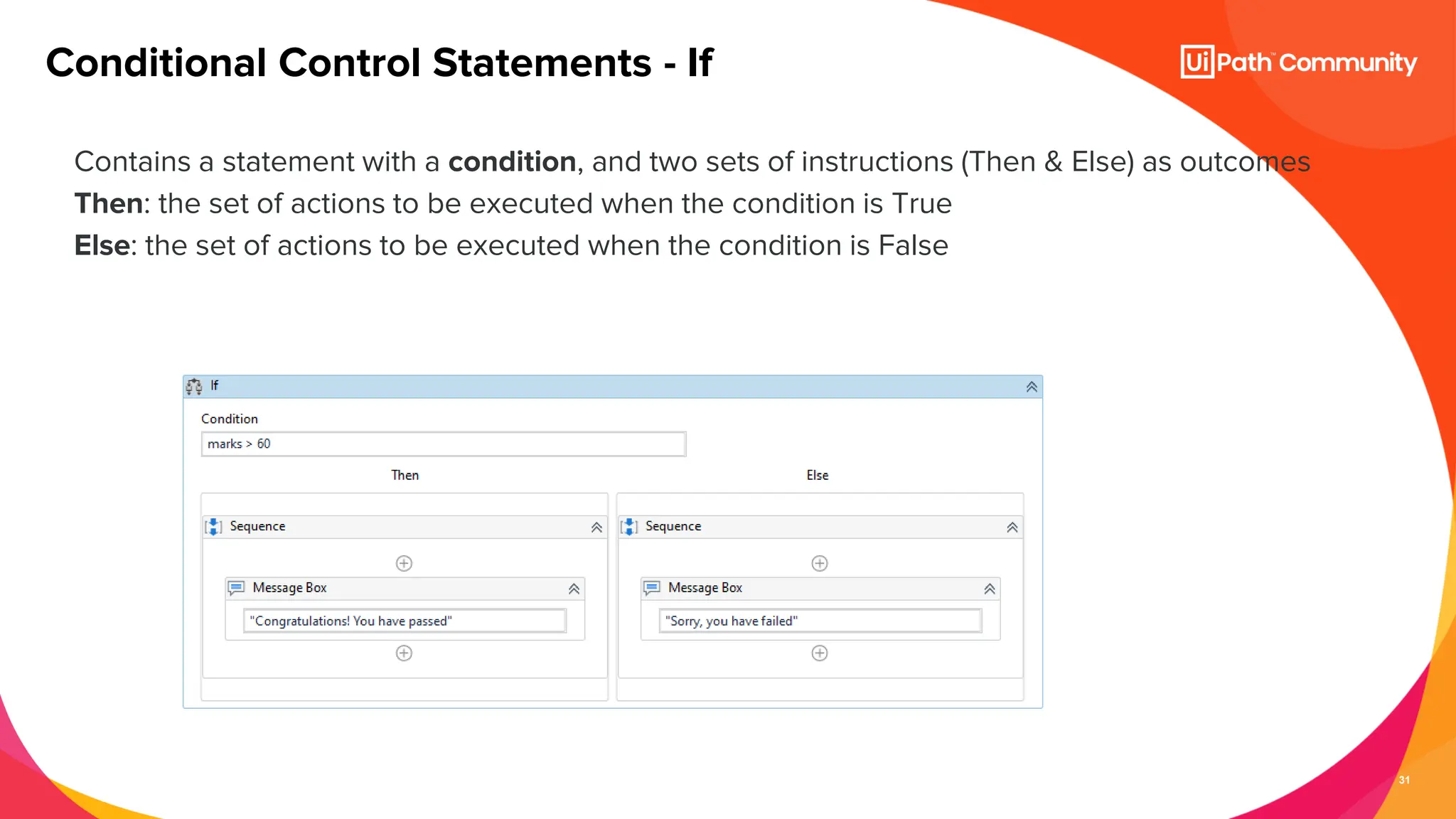
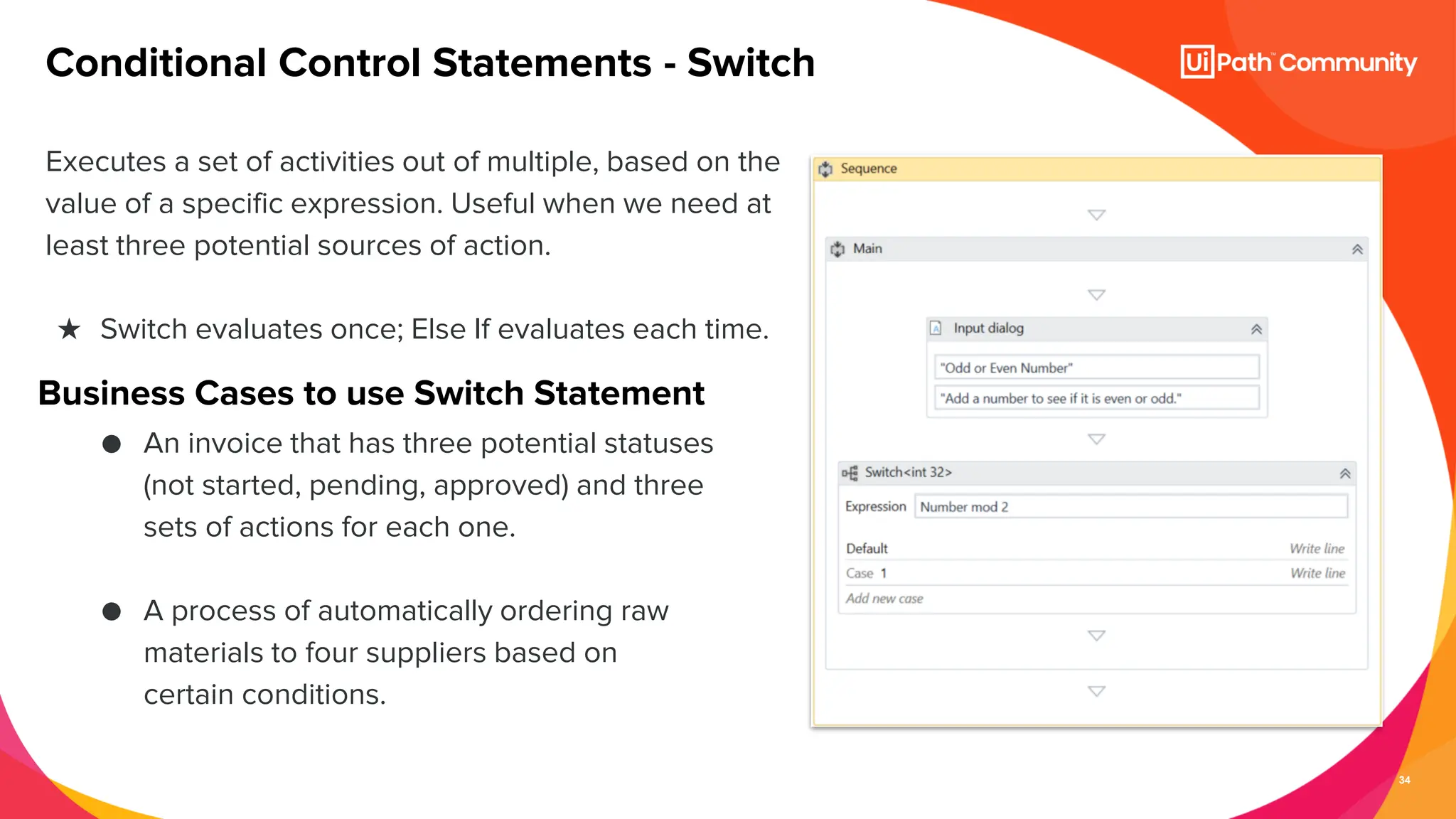
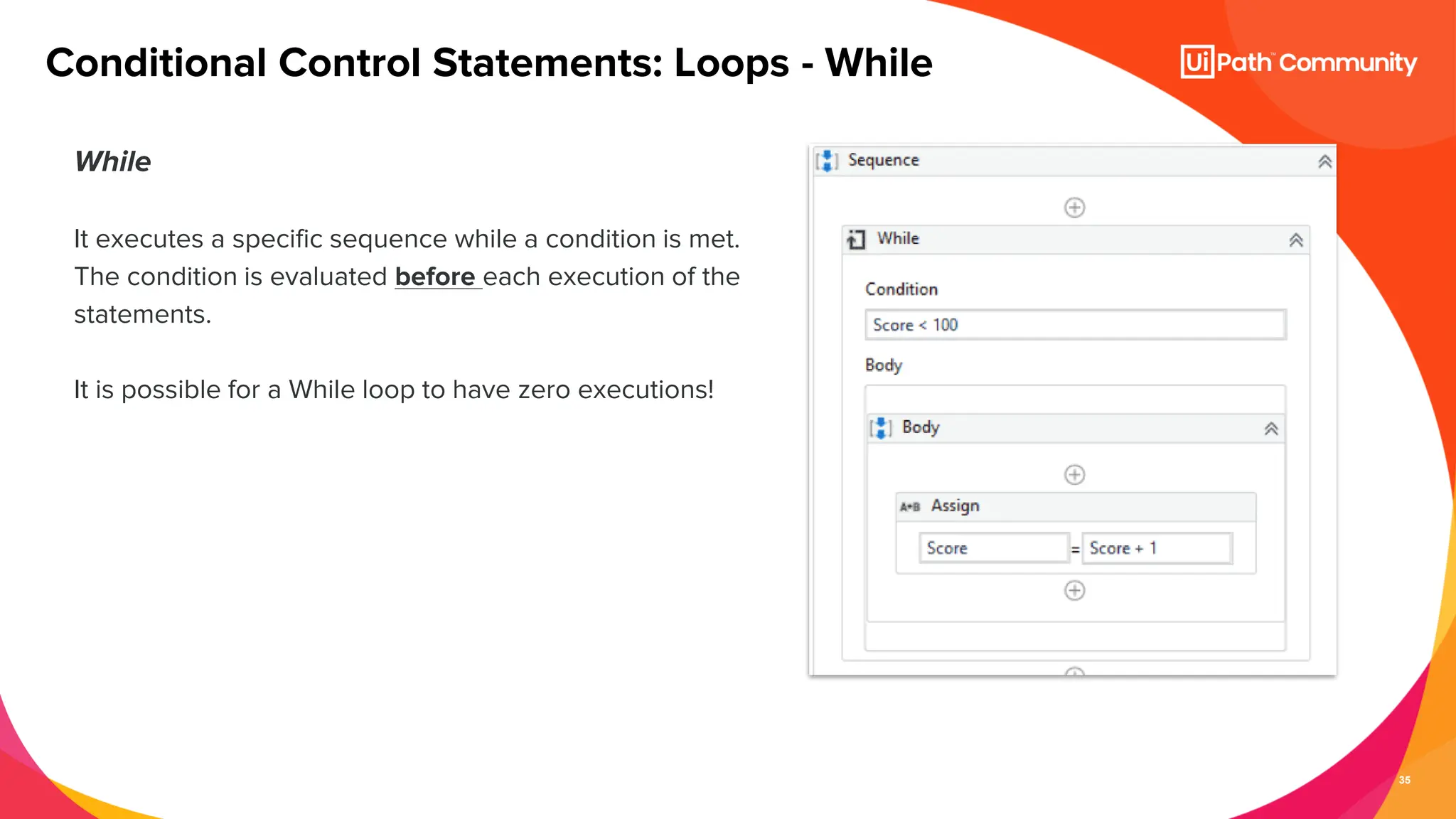
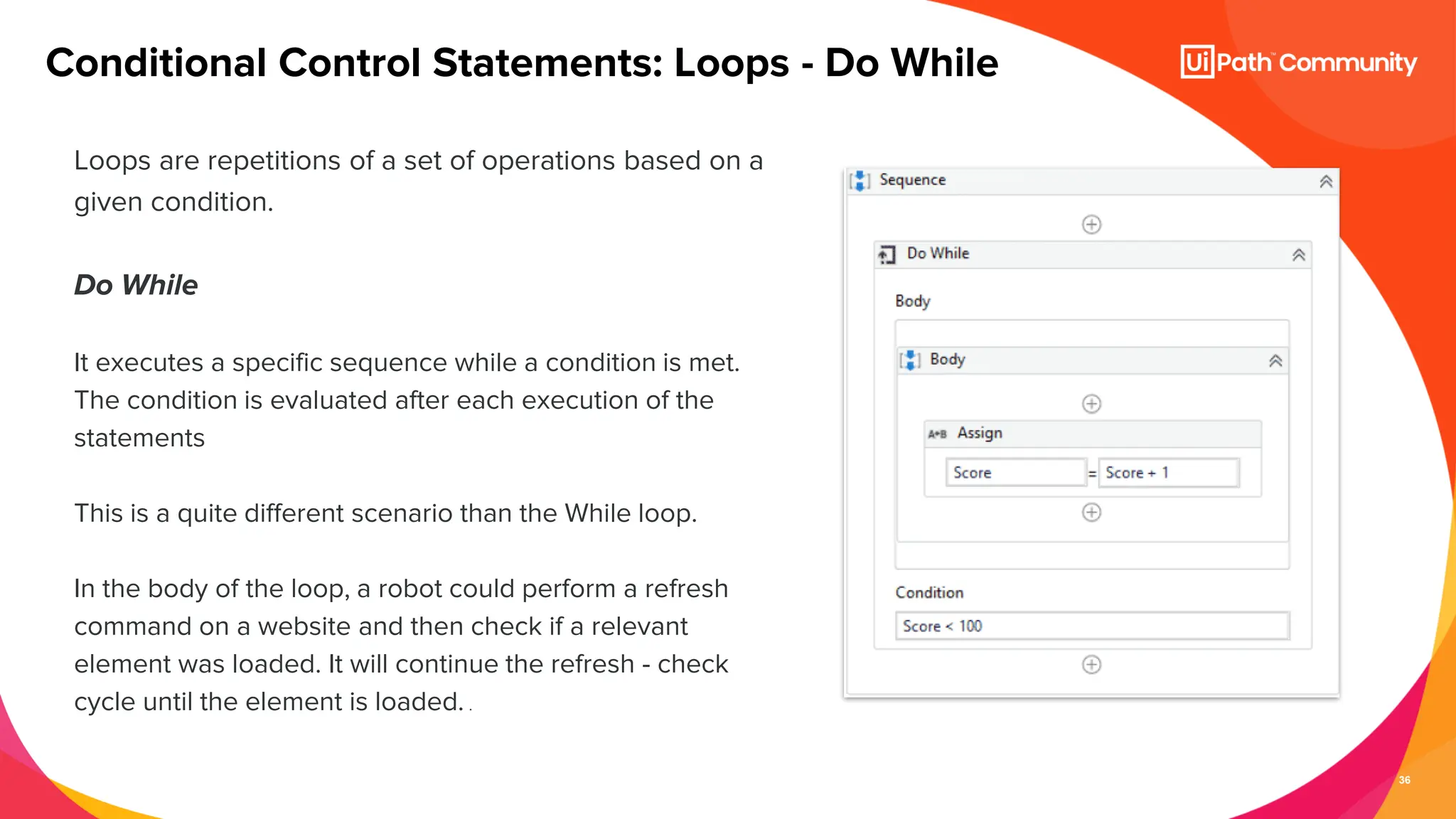
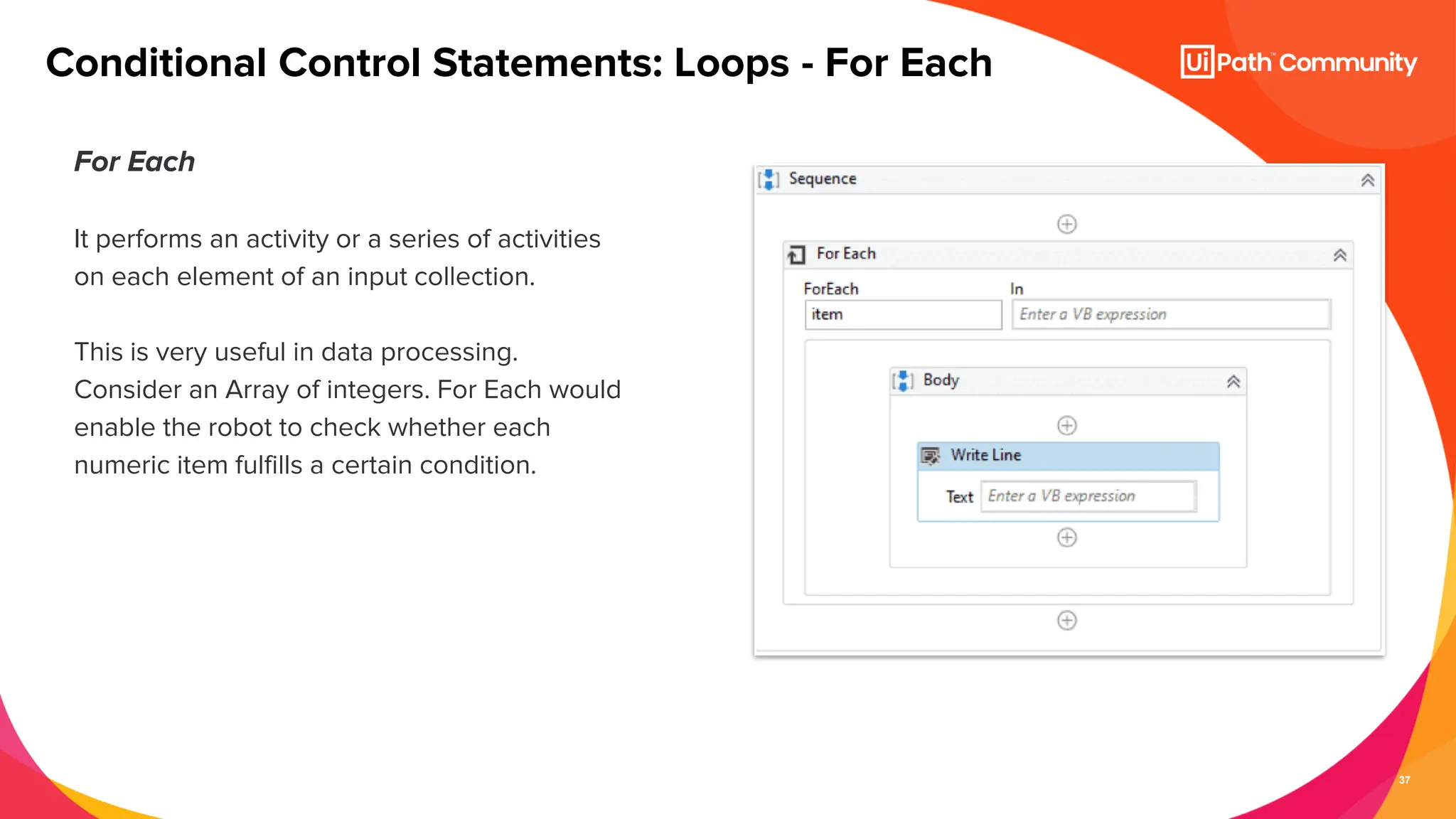
The document details a session on UiPath Studio fundamentals aimed at student developers, covering key concepts such as variables, data types, workflow layouts, arguments, and control flows essential for automation. It emphasizes the importance of variables in data processing and the various ways they can be created and configured, along with the role of workflows in structuring automation projects. The session also introduces control flow mechanisms, explaining conditional statements and loops used to direct the order of operations within workflows.