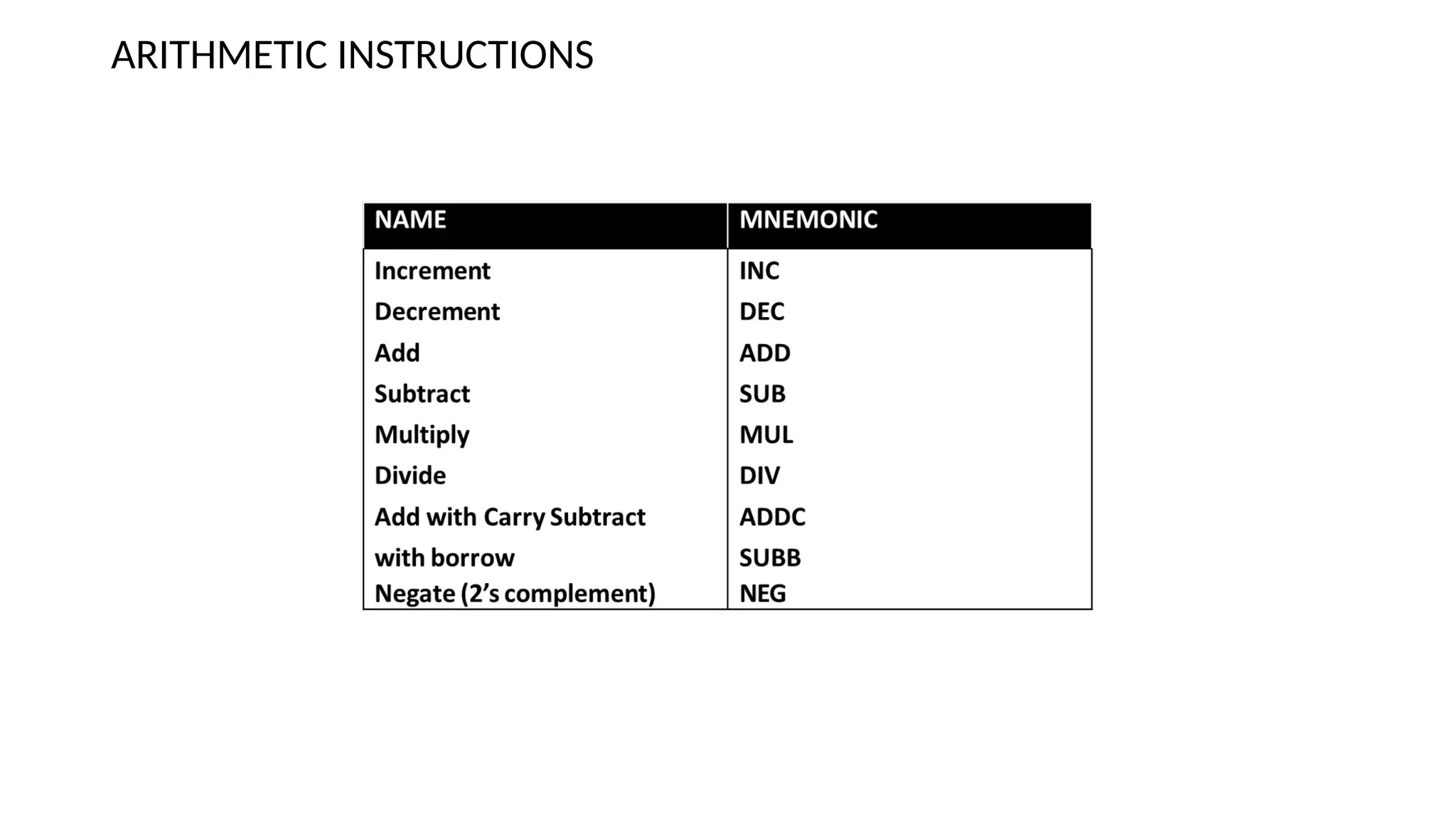
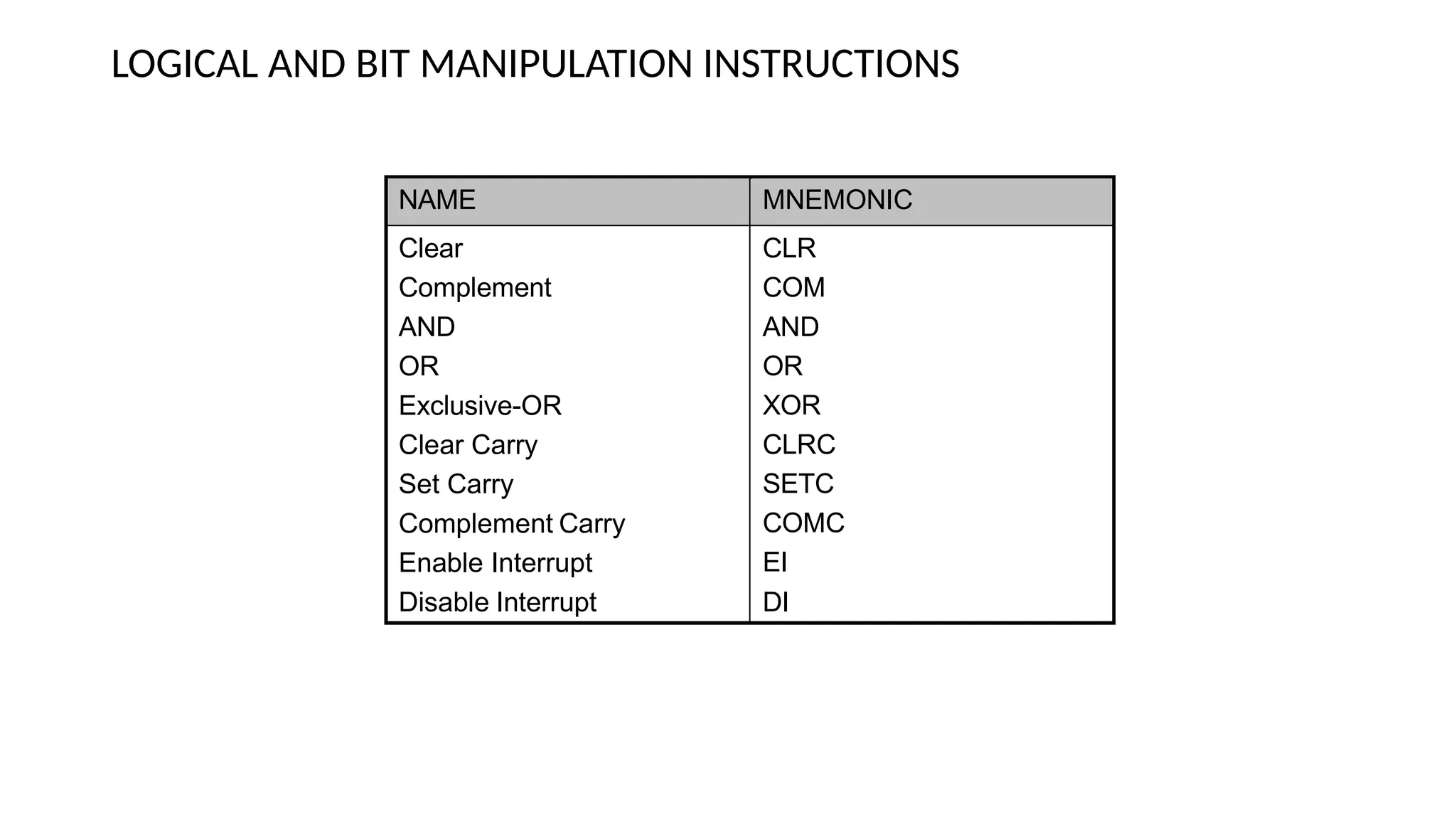
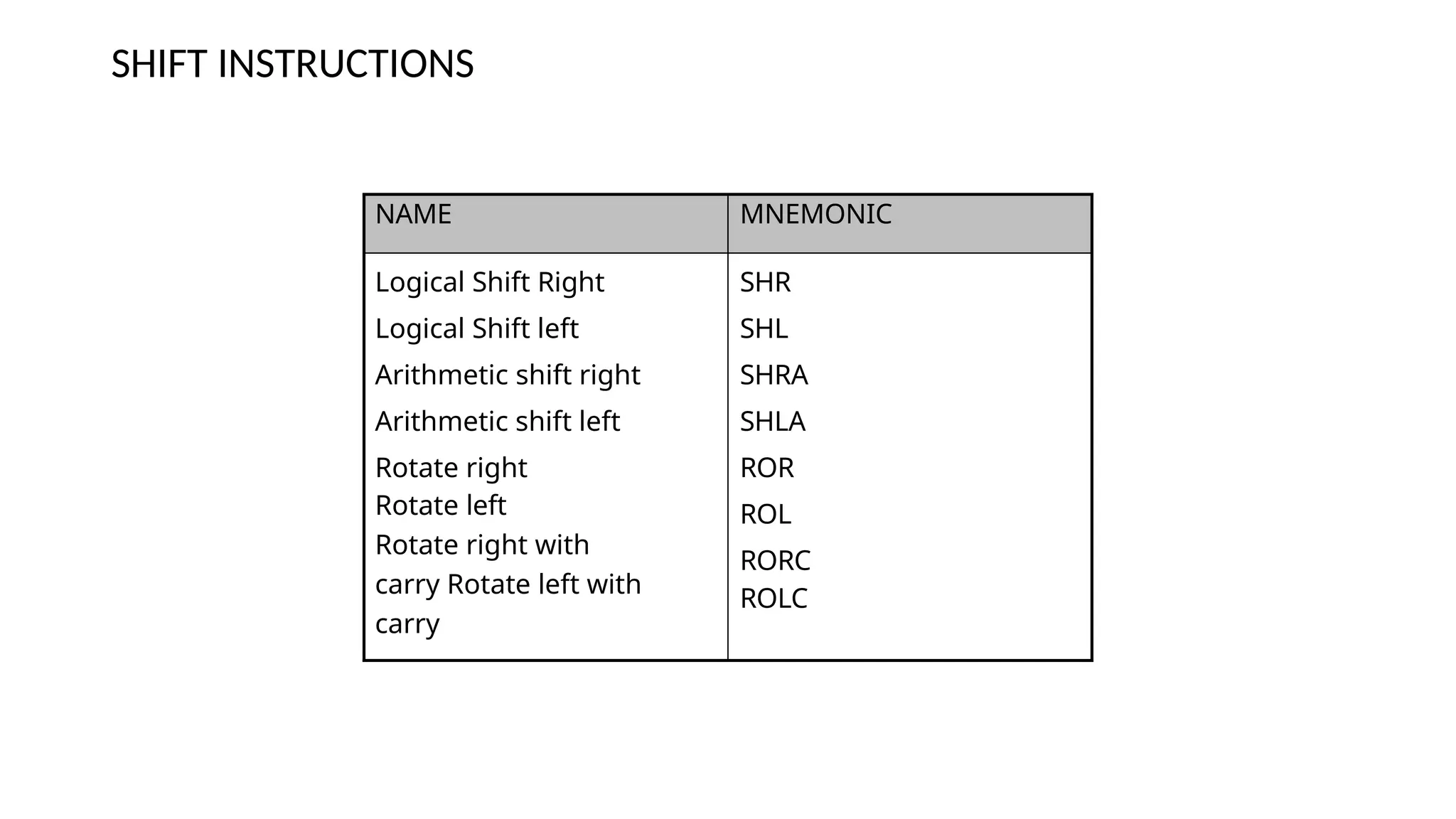
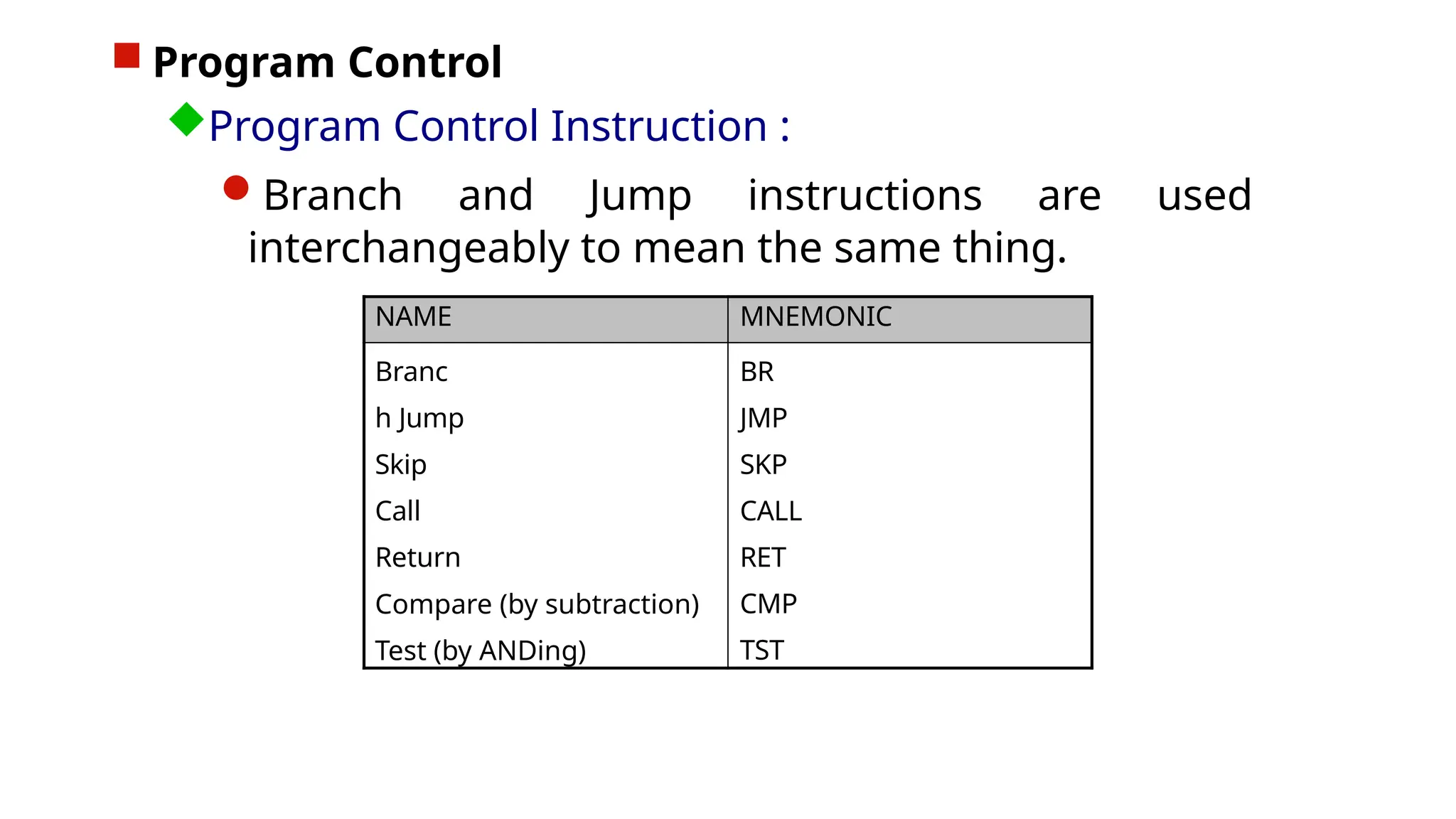
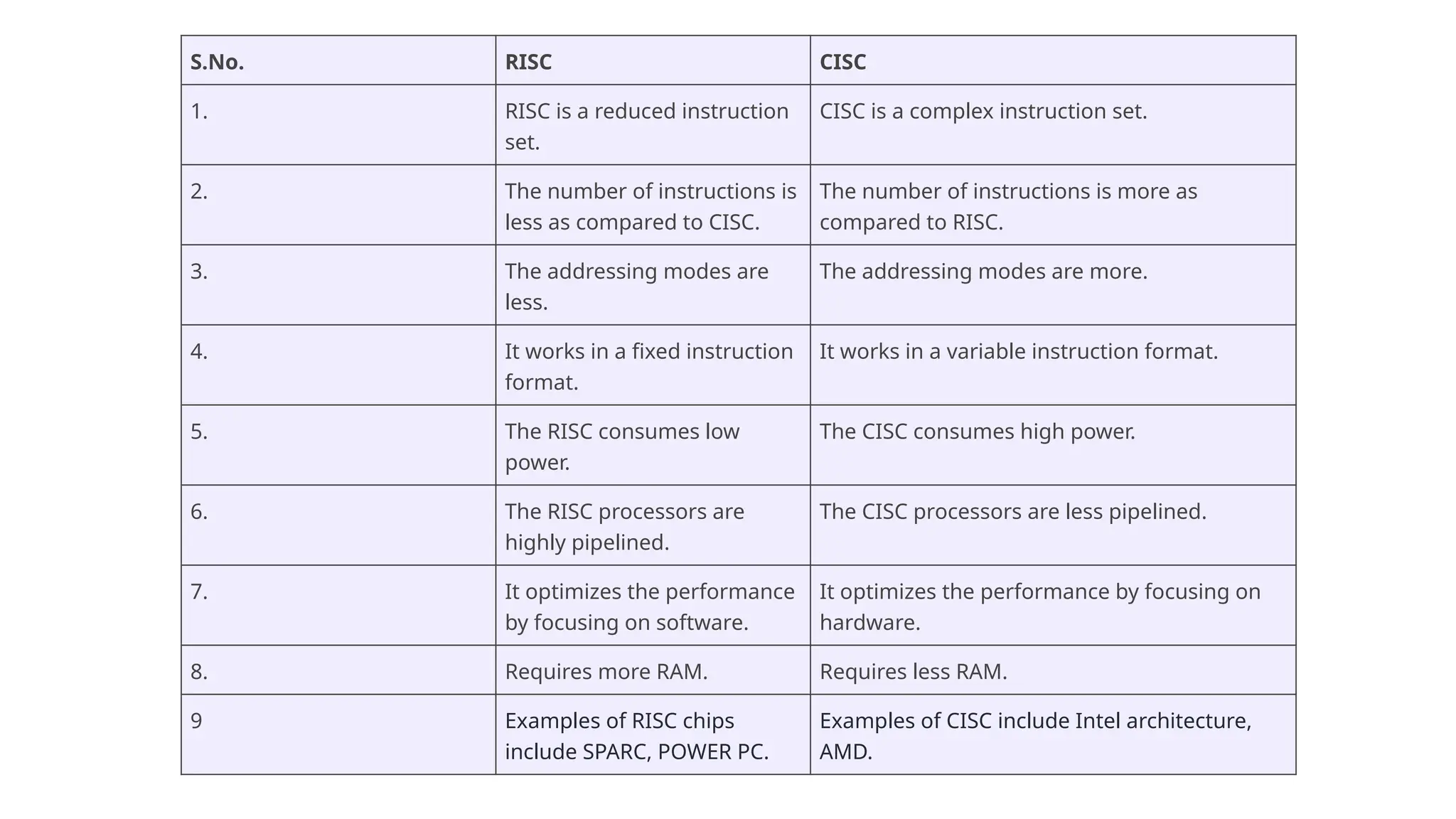
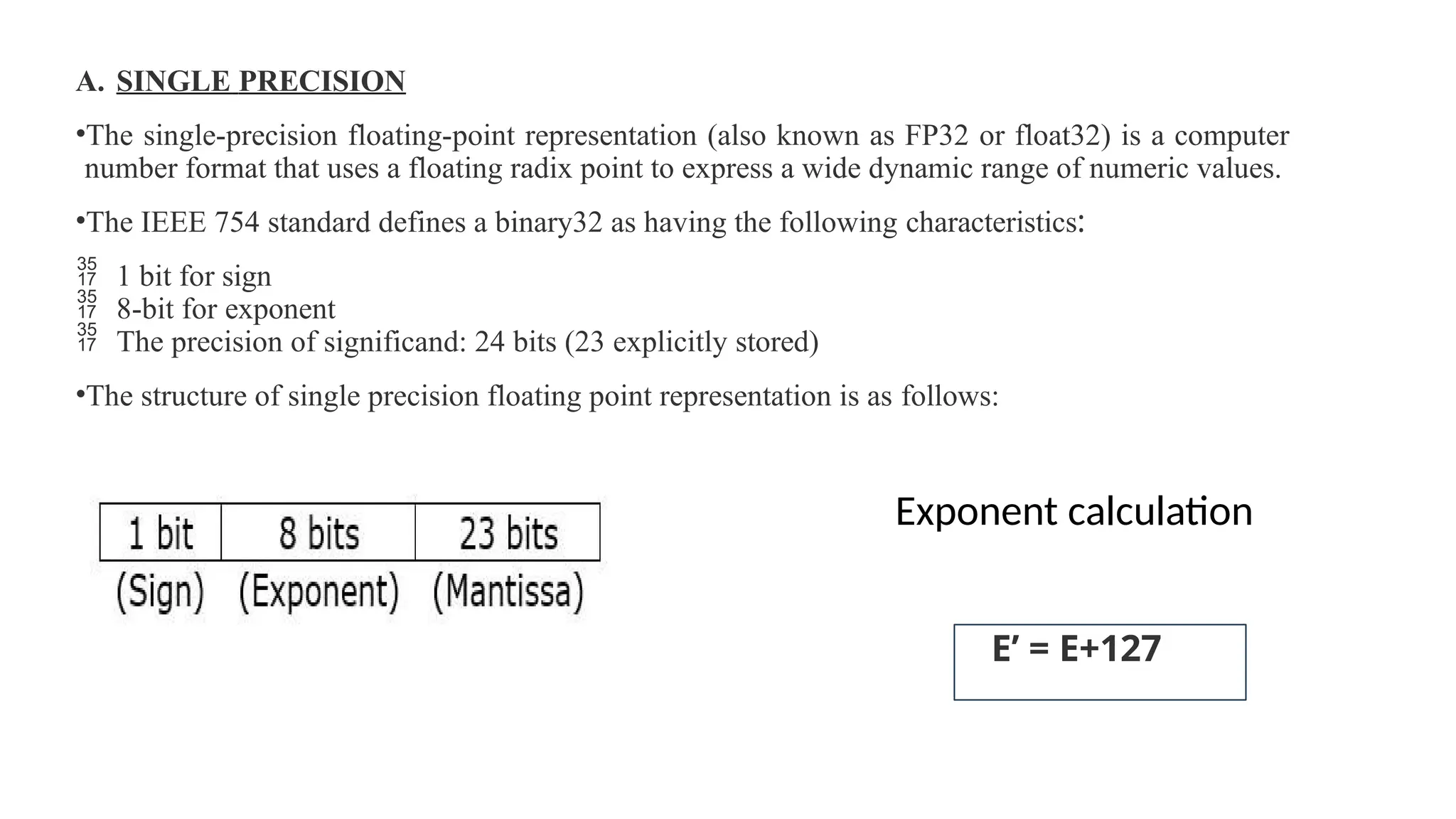
The document discusses computer instructions categorized into data transfer, data manipulation, and program control instructions, elaborating on their functions and examples. It also contrasts RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) and CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) architectures, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Furthermore, it covers IEEE standards for floating point representation, detailing single and double precision formats.



![MODE ASSEMBLY CONVENTION REGISTER TRANSFER
Direct Address LD ADR ACßM[ADR]
Indirect Address LD @ADR ACßM[M[ADR]]
Relative Address LD $ADR ACßM[PC+ADR]
Immediate Address LD #NBR ACßNBR
Index Address LD ADR(X) ACßM[ADR+XR]
Register LD R1 ACßR1
Register Indirect LD (R1) ACßM[R1]
Autoincrement LD (R1)+ ACßM[R1], R1ßR1+1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatransferanddatamanipulationfloatingpoint-241023154704-06a611f7/75/Data-transfer-and-data-manipulation-floating-point-pptx-5-2048.jpg)