This document provides an overview of the merge sort algorithm, explaining its divide and conquer approach to sorting an array by recursively dividing it into two halves and then merging the sorted halves. It includes the steps of the algorithm and a code example in C++ that demonstrates the implementation of the merge and mergesort functions. The lecture is from the International Islamic University, Islamabad, and is presented by Engr. Rashid Farid Chishti.


![MergeSort(arr[], L, R)
If r > l
1. Find the middle point to divide the array into two
halves: middle M = L + (R-L)/2
2. Call mergeSort for 1st half: Call mergeSort(arr, L, M)
3. Call mergeSort for 2nd half: Call mergeSort(arr, M+1,R)
4. Merge the two halves sorted in step 2 and 3:
Call merge(arr, L, M, R)
Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ds20mergesort-240518111334-9a66af15/85/Data-Structures-and-Agorithm-DS-20-Merge-Sort-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
void merge(int a[], int low, int high, int mid) {
int i, j, k, c[50];
i = low; k = low; j= mid + 1;
while (i <= mid&& j <= high) {
// Comparesthe elements of two subarrays
// and merges then
if (a[i] <a[j]) {
c[k] =a[i]; k++; i++;
}
else {
c[k] =a[j]; k++; j++;
}
}
while (i <= mid) { // Copies the remaining
// elements of left array, if there is any
c[k] = a[i]; k++; i++;
}
5
Example 1: Merge Sort
1
while (j <= high) { //Copies the
// remaining elements of right array,
// if there is any
c[k] = a[j]; k++; j++;
}
for (i = low; i < k; i++) {
a[i] = c[i];
}
}
void mergesort (int a[],int low, int high)
{
int mid;
if (low < high) {
mid=(low+high)/2;
mergesort(a,low,mid);
mergesort(a,mid+1,high);
merge(a,low,high,mid);
}
}
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ds20mergesort-240518111334-9a66af15/85/Data-Structures-and-Agorithm-DS-20-Merge-Sort-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![int main() {
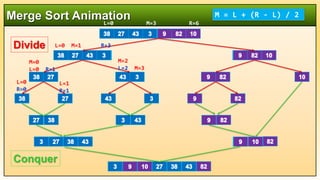
int i, arr[] = {38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10};
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout<<"before sorting : ";
for (i = 0 ; i < sz ; i++)
cout <<" "<<arr[i];
mergesort(arr,0, sz-1);
cout<<"nSorted array : ";
for (i=0; i<sz; i++)
cout <<" "<< arr[i];
cout << endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
6
Example 1: Merge Sort
3 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ds20mergesort-240518111334-9a66af15/85/Data-Structures-and-Agorithm-DS-20-Merge-Sort-pptx-6-320.jpg)