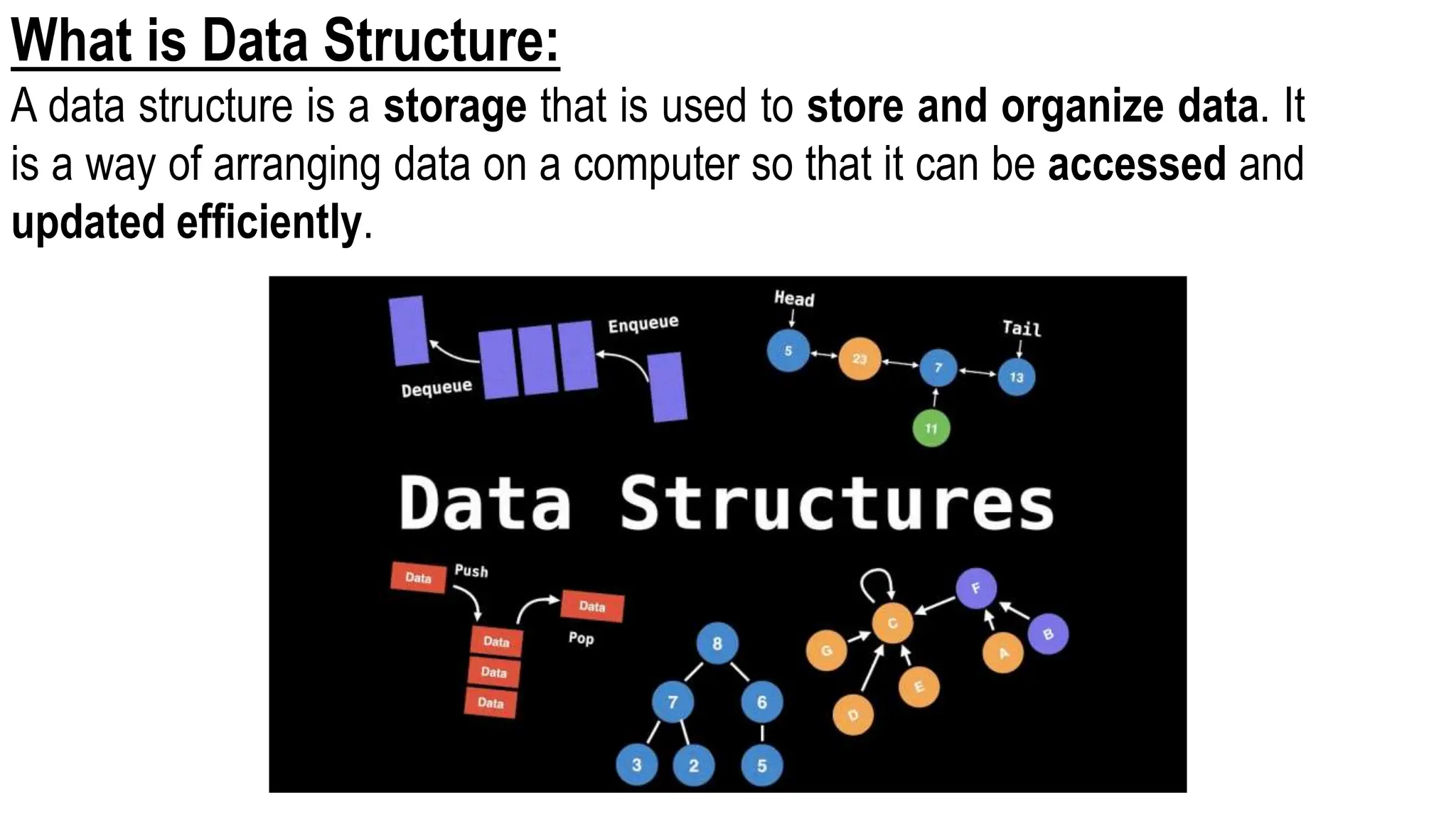
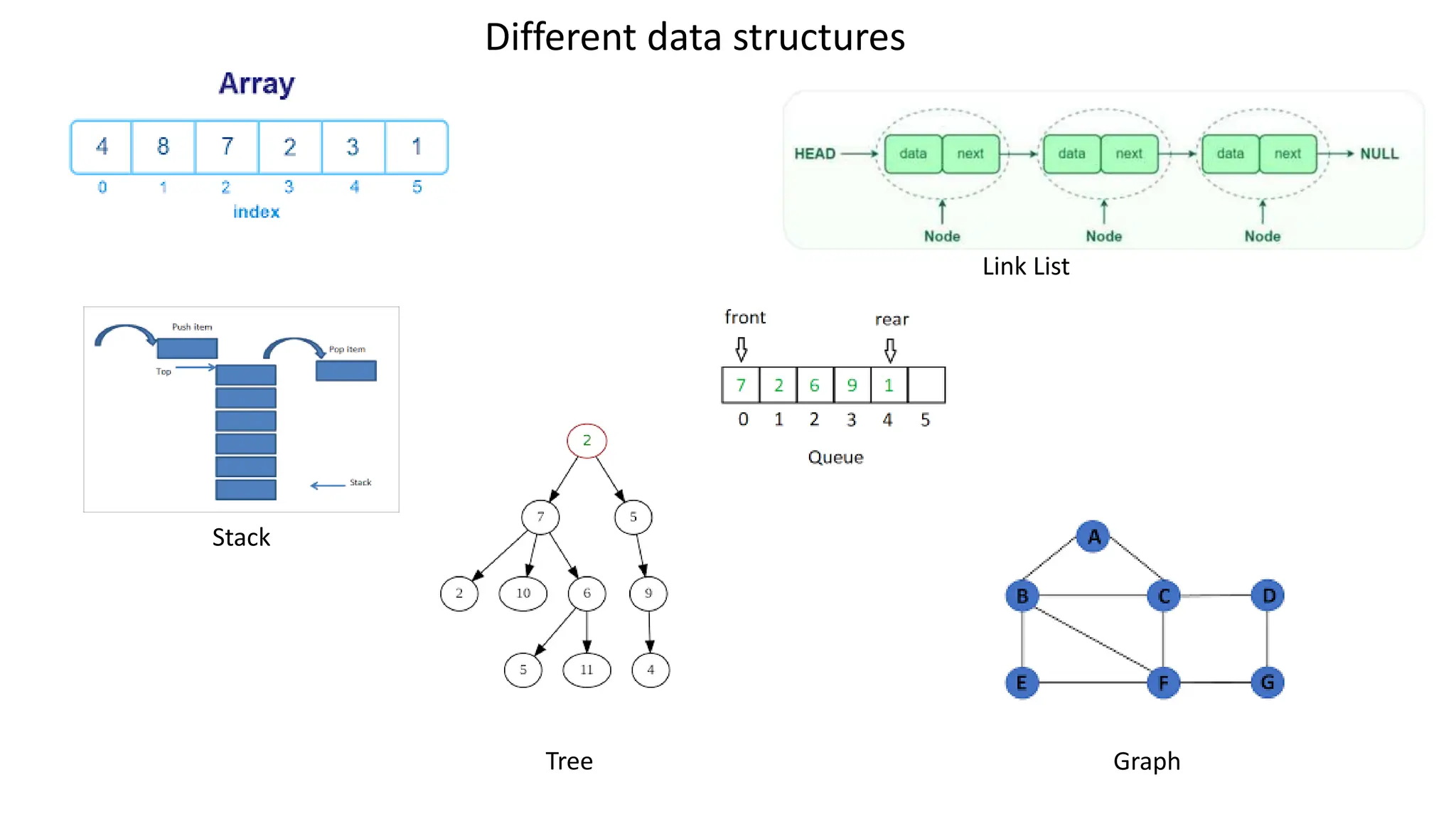
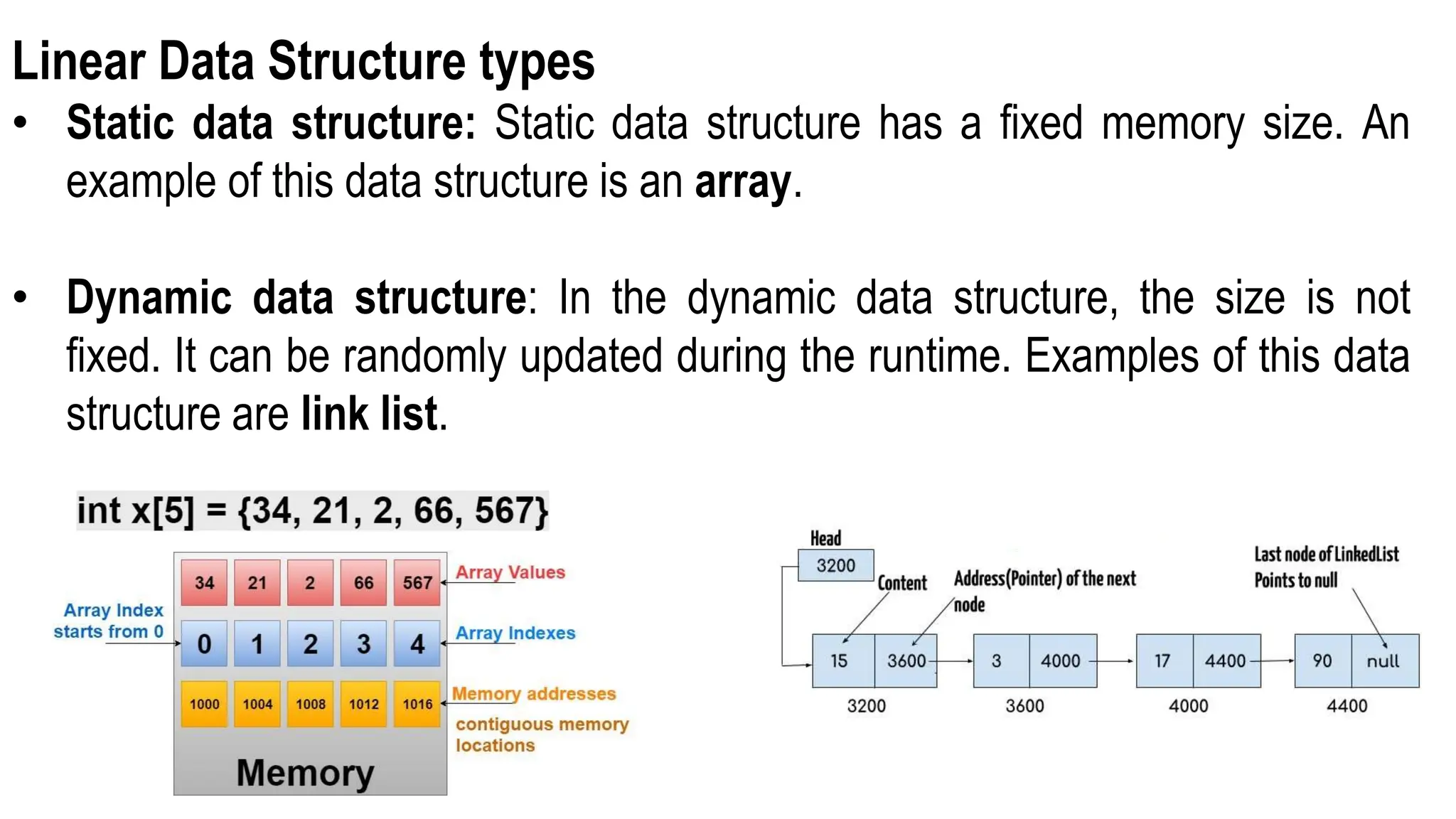
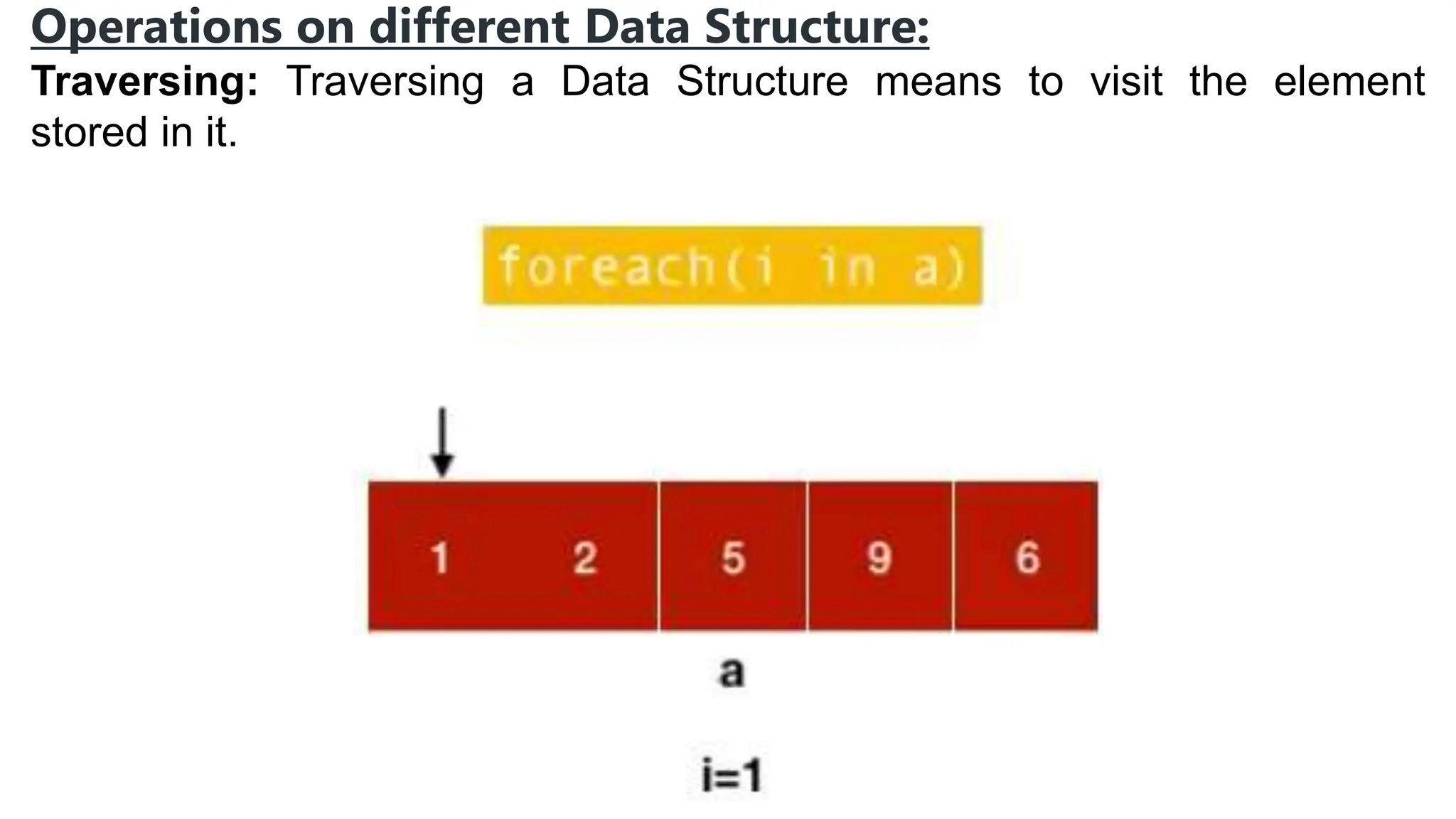
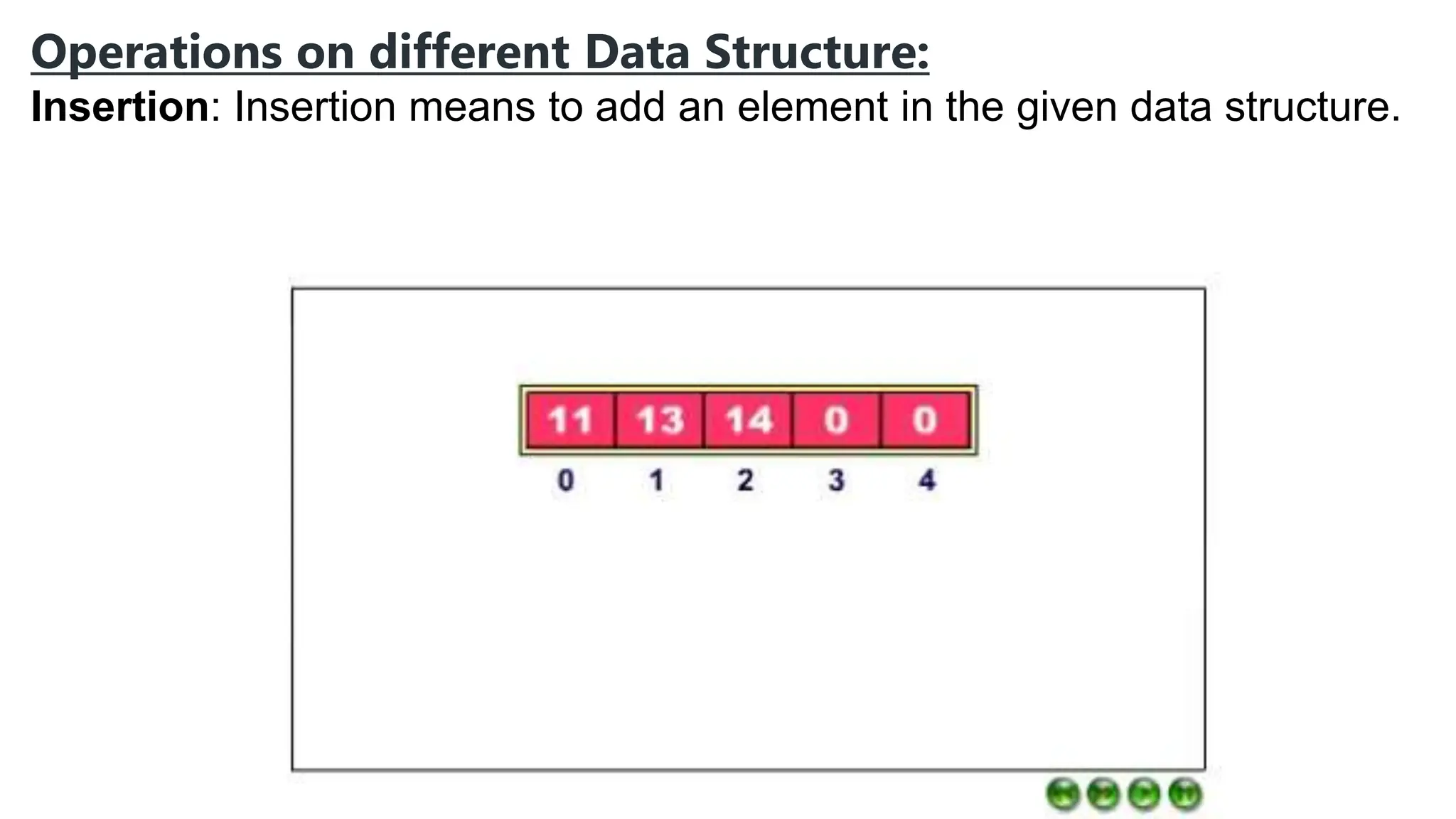
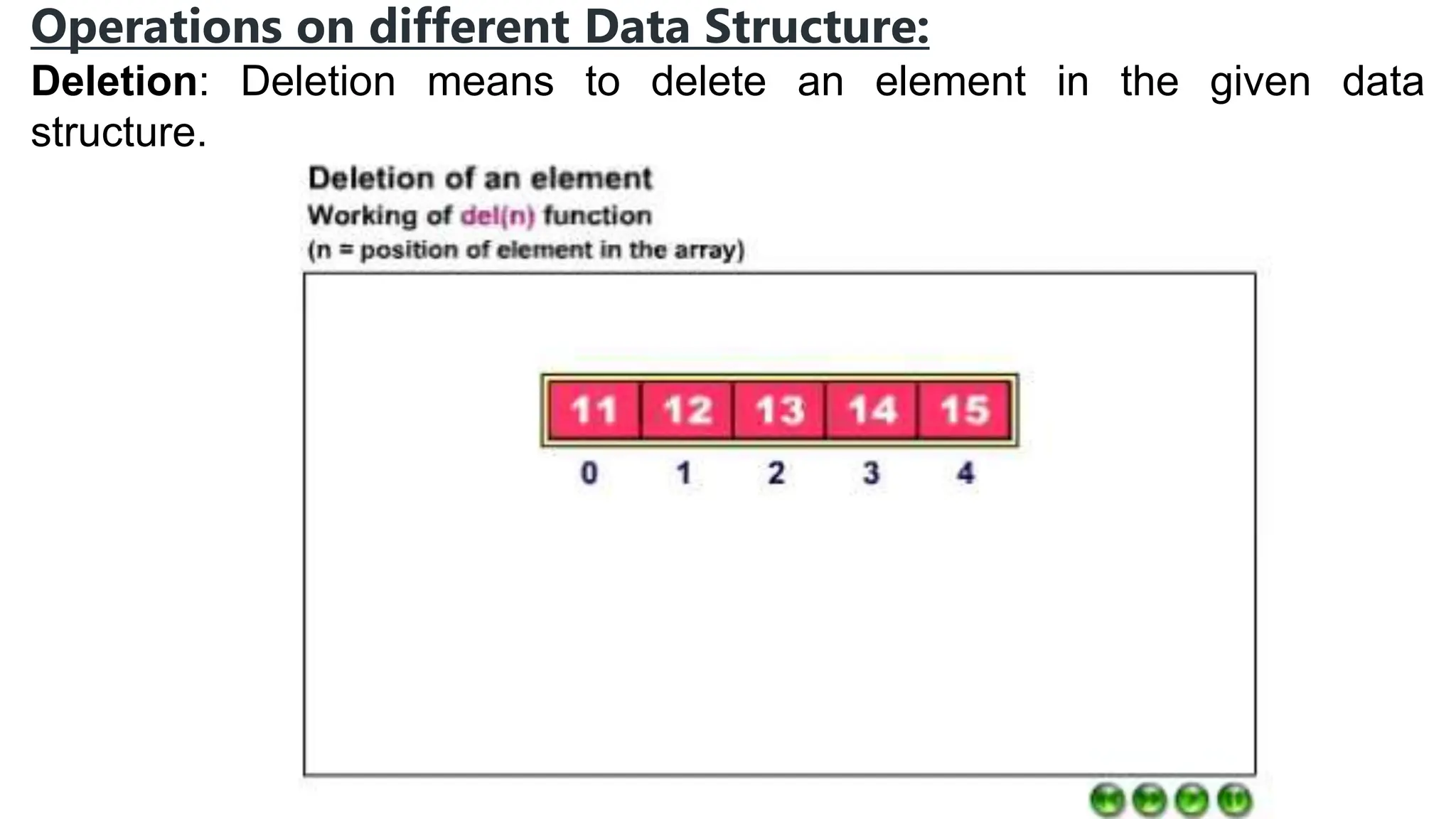
Computer science focuses on problem-solving through algorithms that can be transformed into efficient programs, reliant on knowledge of data structures and algorithms. Data structures are methods for storing and organizing data, classified into linear and non-linear types, each with specific characteristics and operations like traversing, insertion, deletion, updating, searching, and sorting. Understanding data structures enhances coding efficiency in terms of time, space, and resource management.