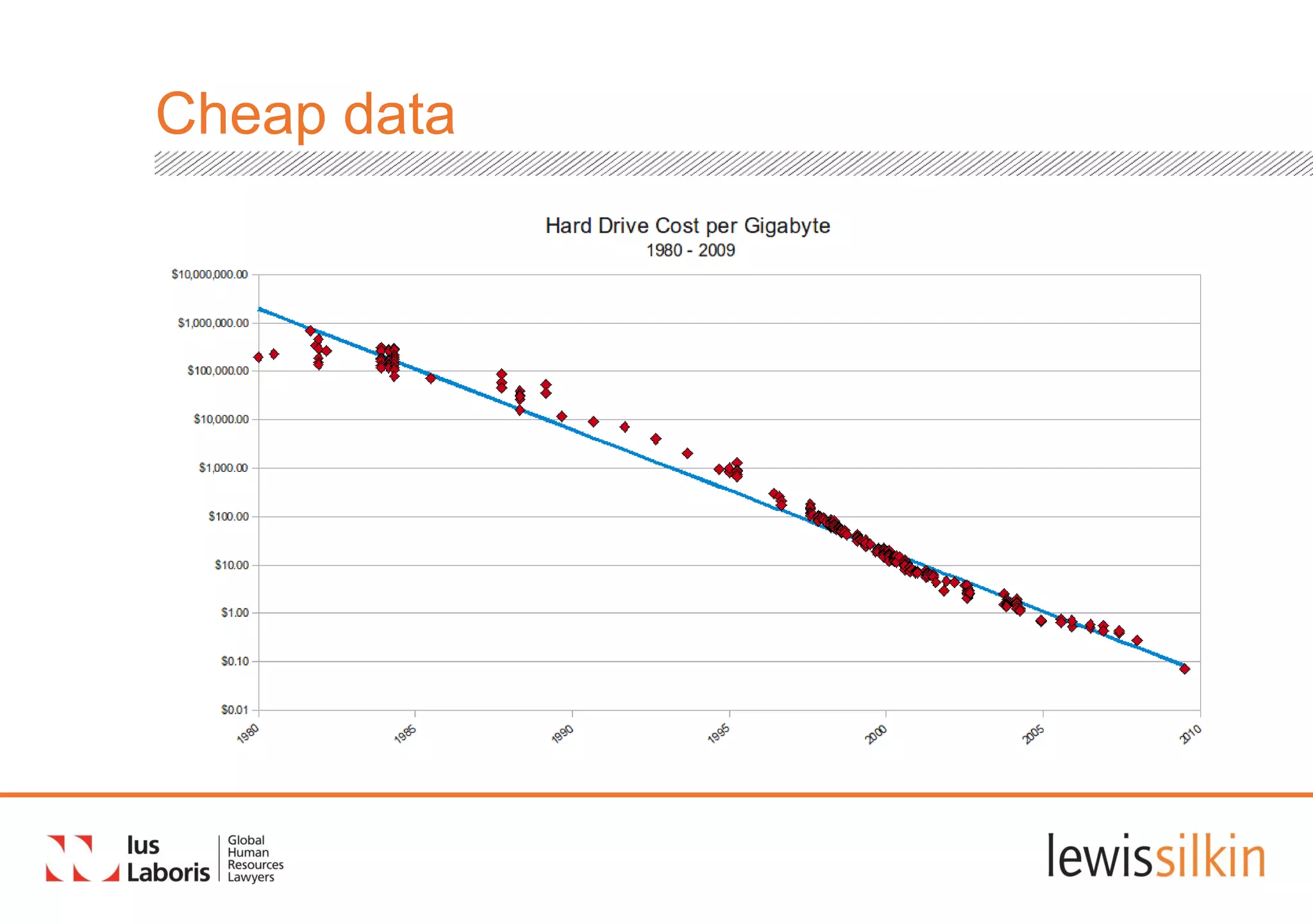
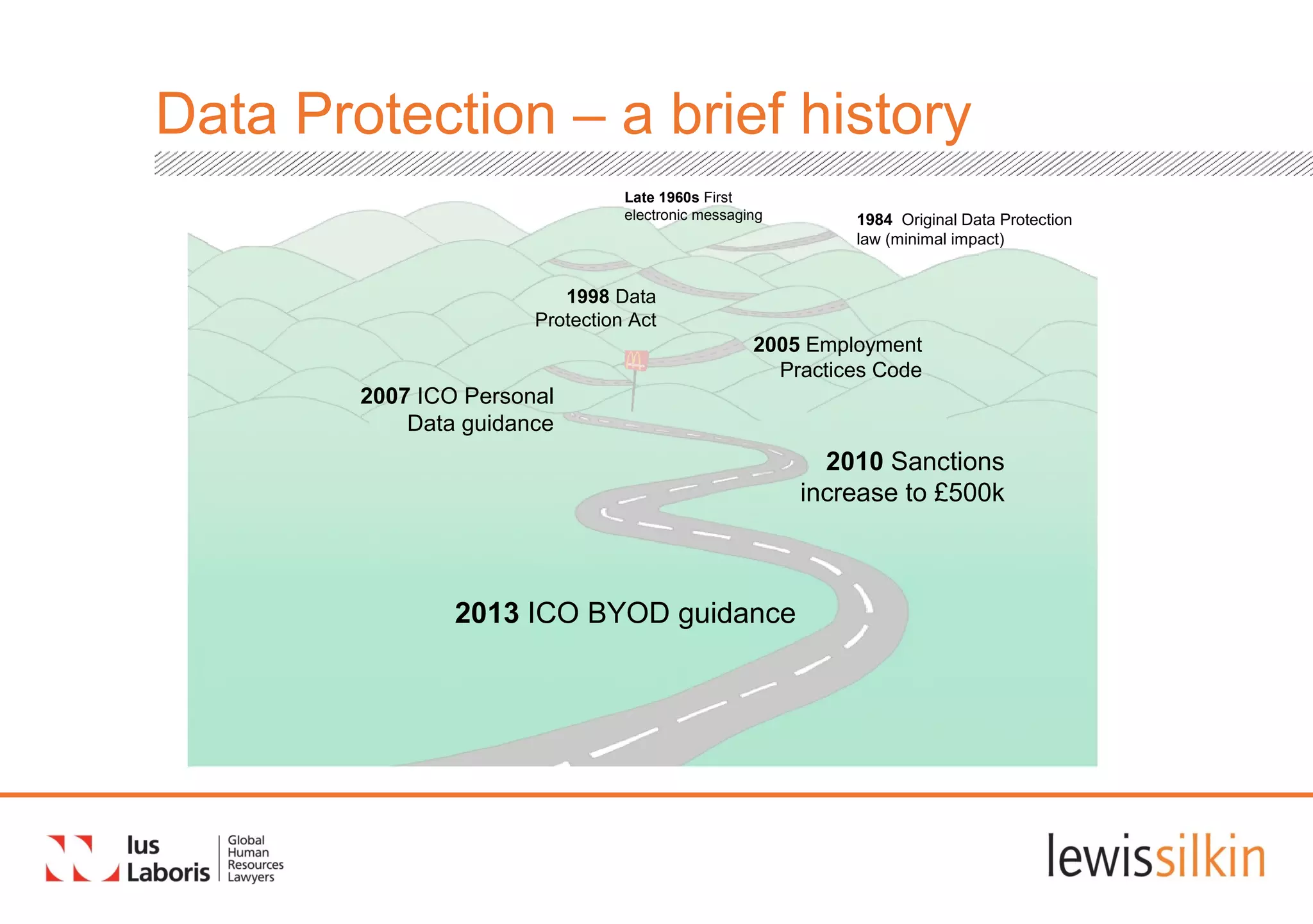
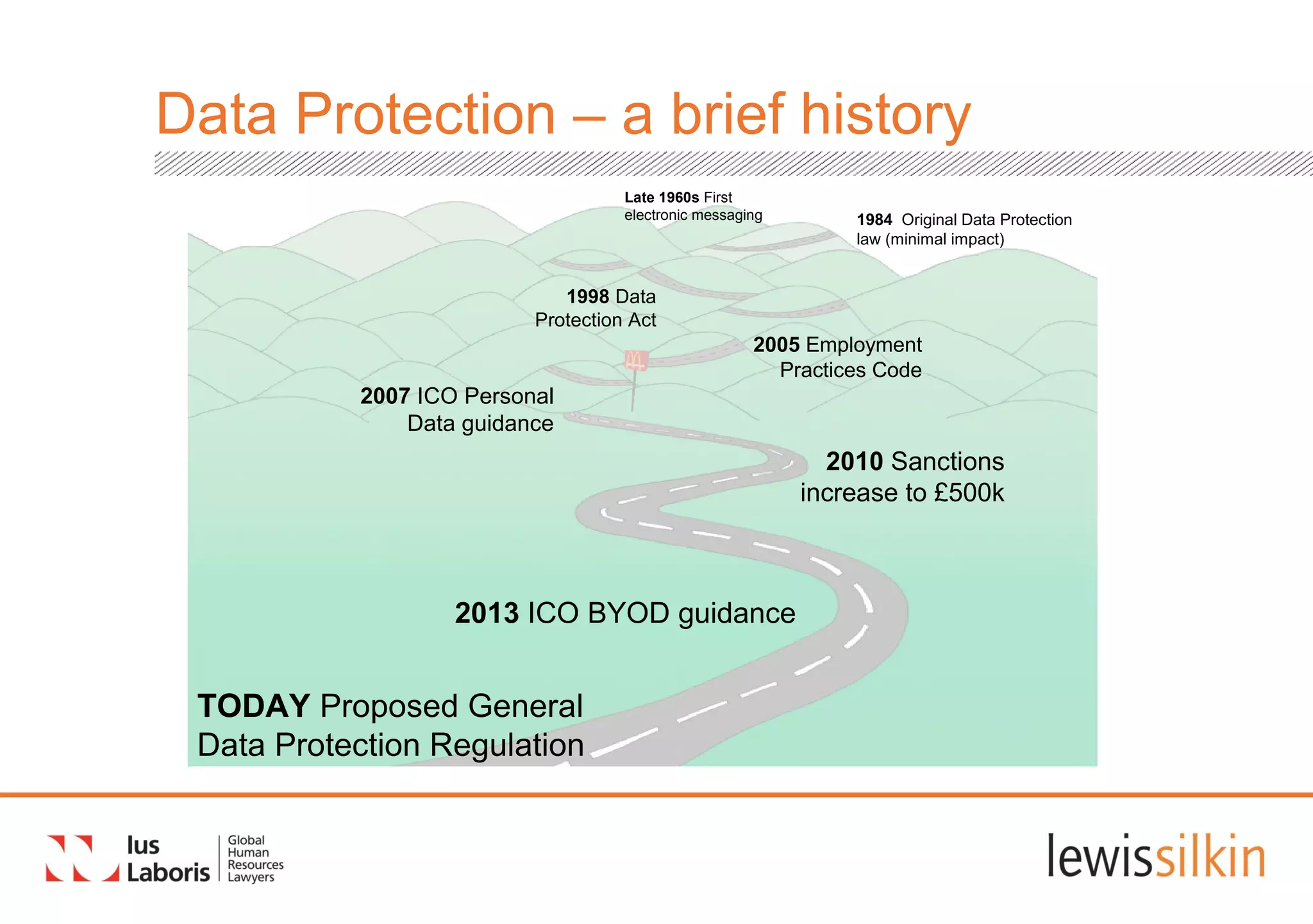
The document summarizes proposed changes to data protection regulations in the European Union. The key points are:
1) The proposed General Data Protection Regulation aims to standardize data protection laws across EU states through a single set of rules and increased individual rights and enforcement.
2) The regulation proposes stricter obligations for organizations around data documentation, security, privacy by design, and appointing data protection officers. It also strengthens individual rights like the "right to be forgotten."
3) Non-compliance could result in fines of up to 2% of global annual turnover. Organizations are advised to review their data processing and protection practices in preparation for the new regulations.