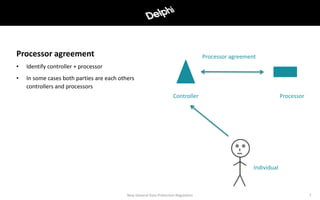
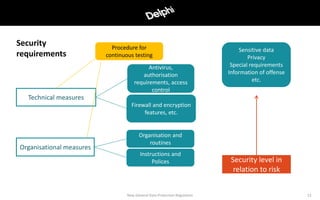
The document outlines the new EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) effective from May 25, 2018, which applies to all EU companies and public bodies and includes significant penalties for non-compliance. It details the responsibilities of data controllers and processors, the principles for lawful processing, and the necessary security measures to protect personal data. The document emphasizes the importance of compliance and the implementation of privacy by design in organizational practices.