The document explains one-hot encoding and label encoding as techniques for converting categorical features into numerical values for machine learning models. One-hot encoding allows models to utilize categorical data while improving performance but can lead to increased dimensionality, sparsity, and potential overfitting. It provides Python code examples to illustrate how to implement these encodings using the 'car_details.csv' dataset.


![Code
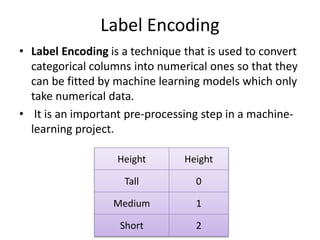
# Import label encoder
from sklearn import preprocessing
df = pd.read_csv('car_details.csv')
# label_encoder object knows
# how to understand word labels.
label_encoder = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
# Encode labels in column 'species'.
df['Manu']= label_encoder.fit_transform(df['Manufacturer'])
df['Manu'].unique()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment8-240720092250-7563aa20/85/Data-Preprocessing-One-Hot-Encoding-Method-4-320.jpg)


![Python code
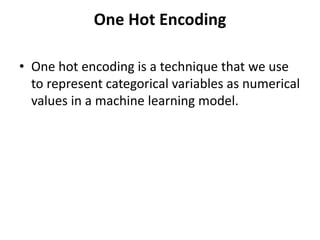
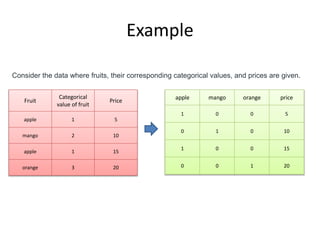
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
# Retrieving data
data = pd.read_csv('car_details.csv')
# Converting type of columns to category
data['Manu'] = data['Manufacturer'].astype('category')
data['Model'] = data['Model'].astype('category')
# Assigning numerical values and storing it in another columns
data['Manu_new'] = data['Manu'].cat.codes
data['Model_new'] = data['Model'].cat.codes
# Create an instance of One-hot-encoder
enc = OneHotEncoder()
# Passing encoded columns
enc_data = pd.DataFrame(enc.fit_transform(
data[['Manu_new', 'Model_new']]).toarray())
# Merge with main
#New_df = data.join(enc_data)
print(enc_data.head(30))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment8-240720092250-7563aa20/85/Data-Preprocessing-One-Hot-Encoding-Method-9-320.jpg)