The document explains data preprocessing, an essential step in preparing raw data for machine learning, which involves cleaning and formatting data for improved model accuracy. It details various preprocessing techniques, including importing datasets, handling missing values, encoding categorical data, and feature scaling, alongside introducing Python libraries like NumPy and Pandas. Additionally, it covers the creation and manipulation of NumPy arrays, including indexing, data types, reshaping, and basic operations such as joining, splitting, and sorting arrays.






![Import NumPy
• import numpy
• import numpy as np
import numpy
arr = numpy.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(arr)
import numpy as np
arr = numpy.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(arr)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-7-320.jpg)
![Create a NumPy ndarray Object
• The array object in NumPy is called ndarray.
• We can create a NumPy ndarray object by
using the array() function.
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(arr)
print(type(arr))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-8-320.jpg)
![Dimensions in Arrays
• 0-D Arrays
• 1-D Arrays
import numpy as np
arr = np.array(42)
print(arr)
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(arr)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-9-320.jpg)
![Array cont…
• 2-D Arrays
• 3-D arrays
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(arr)
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]])
print(arr)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-10-320.jpg)
![Check Number of Dimensions?
• NumPy Arrays provides the ndim attribute
that returns an integer that tells us how many
dimensions the array have.
import numpy as np
a = np.array(42)
b = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
c = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
d = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]]])
print(a.ndim)
print(b.ndim)
print(c.ndim)
print(d.ndim)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-11-320.jpg)
![NumPy Array Indexing
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(arr[0])
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(arr[2] + arr[3])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-12-320.jpg)
![Cont…
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9,10]])
print('2nd element on 1st row: ', arr[0, 1])
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9,10]])
print('5th element on 2nd row: ', arr[1, 4])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-13-320.jpg)
![Cont…
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]])
print(arr[0, 1, 2])
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9,10]])
print('Last element from 2nd dim: ', arr[1, -1])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-14-320.jpg)









![Slicing arrays
• taking elements from one given index to
another given index.
• [start:end]
• [start:end:step]
• If we don't pass start its considered 0
• If we don't pass end its considered length of
array in that dimension
• If we don't pass step its considered 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-24-320.jpg)
![import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[1:5])
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[4:])
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[:4])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-25-320.jpg)
![import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[-3:-1])
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[1:5:2])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-26-320.jpg)
![import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
print(arr[1, 1:4])
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
print(arr[0:2, 1:4])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-27-320.jpg)
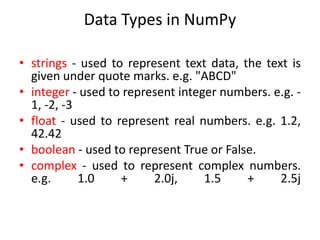
![Cont…
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4], dtype='i4')
print(arr)
print(arr.dtype)
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1.1, 2.1, 3.1])
newarr = arr.astype(int)
print(newarr)
print(newarr.dtype)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-29-320.jpg)
![NumPy Array Shape/Reshape
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]])
print(arr.shape)
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12])
newarr = arr.reshape(2, 3, 2)
print(newarr)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-30-320.jpg)
![NumPy Array Iterating
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
for x in arr:
print(x)
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]],
[[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]])
for x in arr:
for y in x:
for z in y:
print(z)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-31-320.jpg)
![Iterating Arrays Using nditer()
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])
for x in np.nditer(arr):
print(x)
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
for idx, x in np.ndenumerate(arr):
print(idx, x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-32-320.jpg)
![Joining NumPy Arrays
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2))
print(arr)
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2), axis=1)
print(arr)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-33-320.jpg)
![Joining Arrays Using Stack Functions
• Stacking Along Rows
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
arr = np.stack((arr1, arr2), axis=1)
print(arr)
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
arr = np.hstack((arr1, arr2))
print(arr)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-34-320.jpg)
![Stacking Along Columns
• Stacking Along Height (depth)
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
arr = np.vstack((arr1, arr2))
print(arr)
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
arr = np.dstack((arr1, arr2))
print(arr)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-35-320.jpg)
![Splitting NumPy Arrays
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
newarr = np.array_split(arr, 3)
print(newarr)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-36-320.jpg)
![NumPy Searching Arrays
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 4])
x = np.where(arr == 4)
print(x)
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
x = np.where(arr%2 == 0)
print(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-37-320.jpg)
![Sorting Arrays
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([3, 2, 0, 1])
print(np.sort(arr))
import numpy as np
arr = np.array(['banana', 'cherry', 'apple'])
print(np.sort(arr))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-38-320.jpg)

![Generate Random Float
• Generate Random Array
– x = random.randint(100, size=(3, 5))
– x = random.rand(3, 5)
– x = random.choice([3, 5, 7, 9])
from numpy import random
x = random.rand()
print(x)
from numpy import random
x=random.randint(100, size=(5))
print(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessingass1-240718102448-0d554cdd/85/Data-Preprocessing-Introduction-for-Machine-Learning-40-320.jpg)