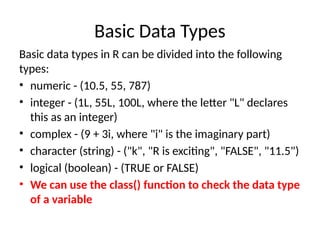
R is a widely-used open-source programming language for statistical computing and data visualization, supporting various techniques for data analysis and machine learning. It is available on multiple platforms and has extensive community support and libraries. The document provides guidance on installing R, creating variables, basic data types, mathematical and string functions.