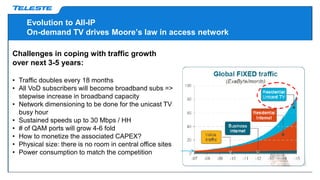
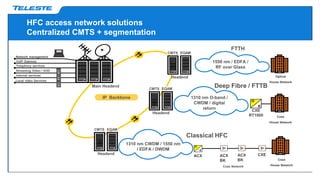
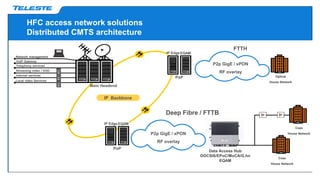
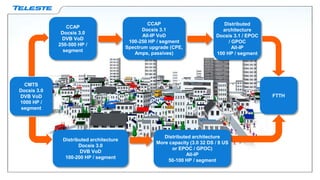
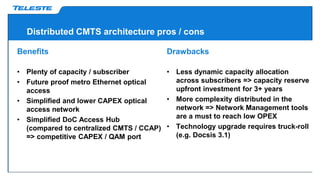
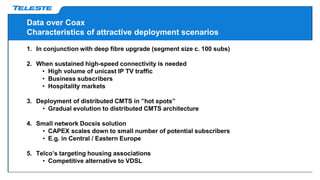
Data over coax is presented as the best last mile access technology before full fiber to the home (FttH). On-demand TV services are driving exponential growth in network traffic that will double every 18 months. Distributed cable modem termination system (CMTS) architectures using data over coax can provide high bandwidth to typical fiber to the last amplifier (FttLA) or fiber to the building (FttB) segment sizes of 100 subscribers in a future-proof way. Data over coax is a promising solution when sustained high speeds are needed, such as for IPTV traffic, businesses, or WiFi hotspots. Deploying distributed CMTS in network "hot spots" is seen as an attractive migration path