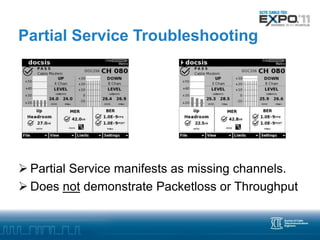
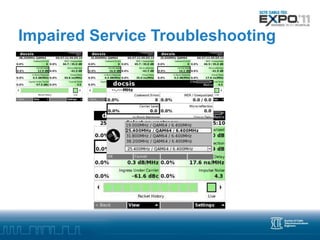
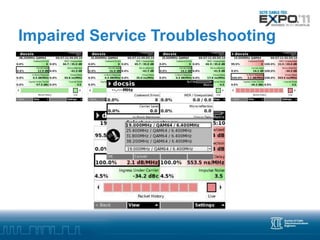
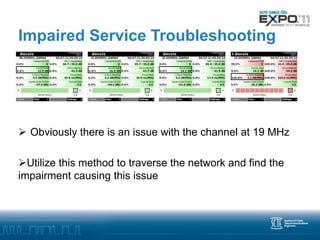
Advanced troubleshooting is needed for DOCSIS 3.0 networks using bonded channels. Partial service, where one channel is down, may not impact users but is hard to detect. Impaired service, where a channel has errors, can impact users through packet loss and reduced throughput. Troubleshooting impaired channels requires tools that test each upstream channel individually to locate any physical layer issues causing errors. Monitoring codeword errors and individual channel statistics is key to locating problems in a bonded DOCSIS 3.0 plant.