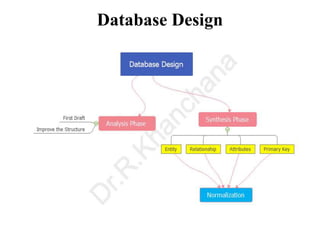
This document discusses database design and data modeling concepts. It covers:
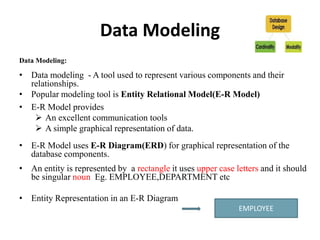
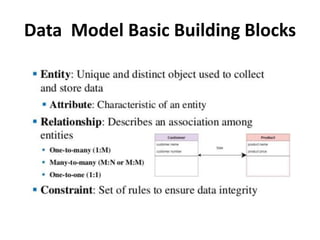
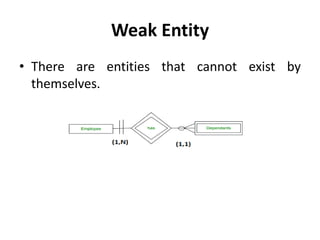
- Data modeling using entity-relationship diagrams to graphically represent database components like entities and relationships.
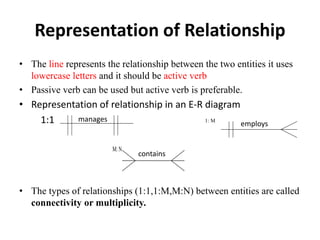
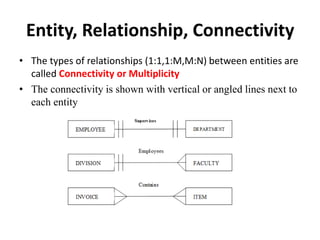
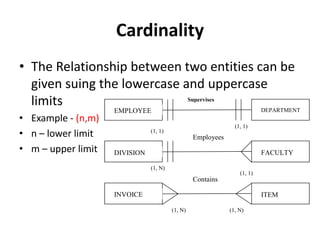
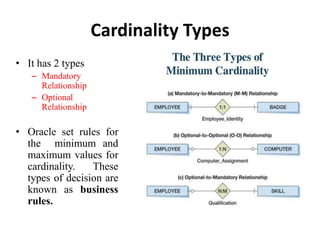
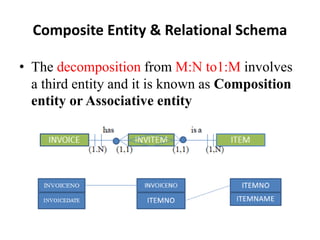
- Relationship types (1:1, 1:M, M:N), connectivity, cardinality, and other ERD elements.
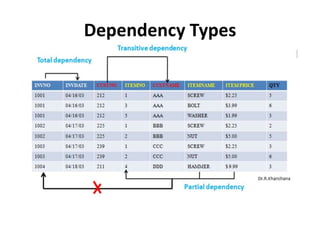
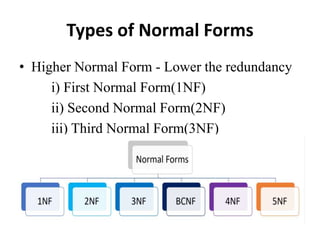
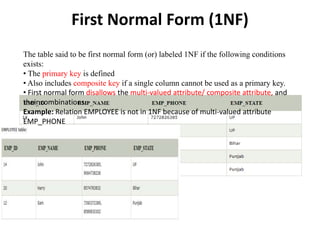
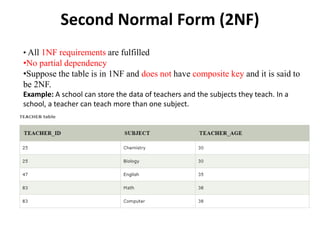
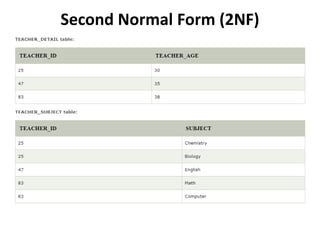
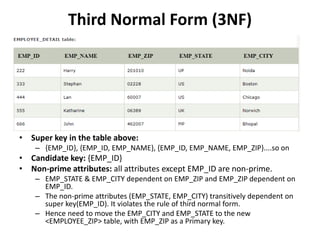
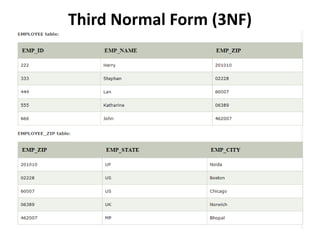
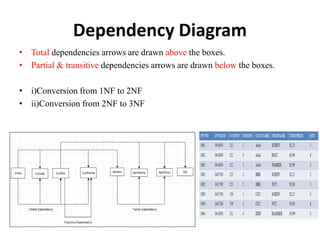
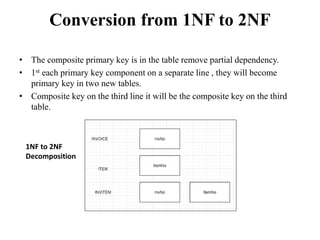
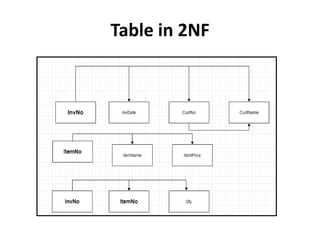
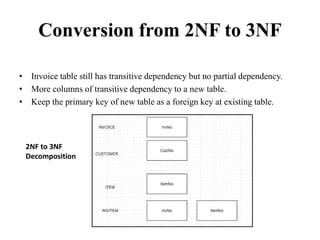
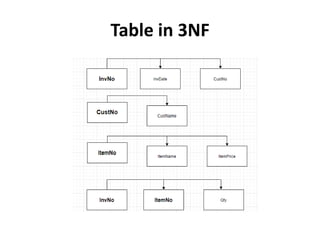
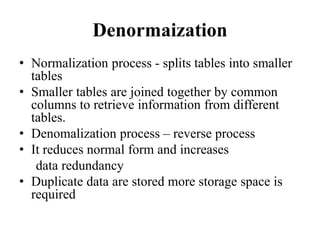
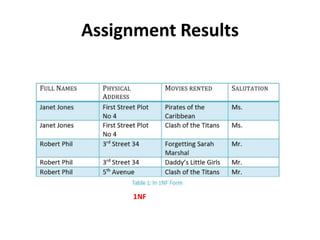
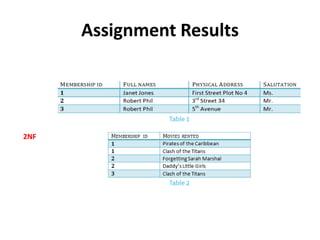
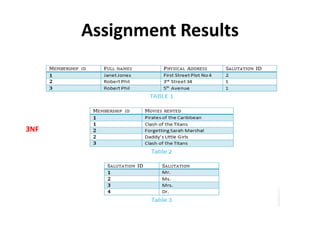
- Database normalization forms (1NF, 2NF, 3NF) and how they reduce data anomalies by eliminating entity redundancies and dependencies.
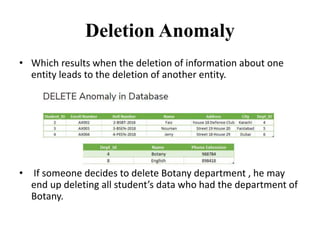
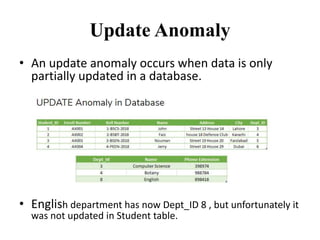
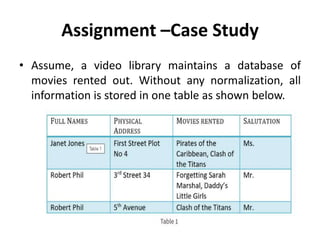
- The three common types of data anomalies - insertion, deletion, and update anomalies - and how normalization addresses them.
- An overview of other normalization forms like BCNF, 4NF, 5NF and dependency diagrams for tracking dependencies across tables.