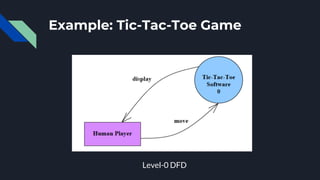
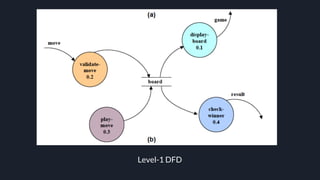
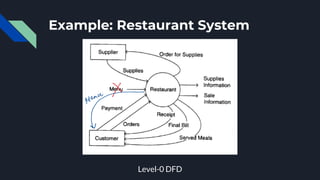
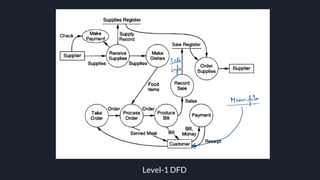
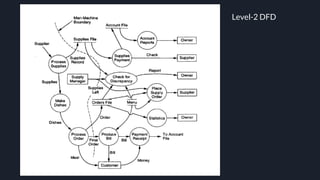
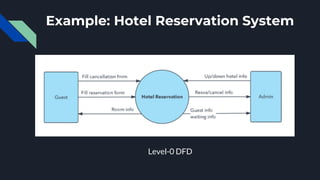
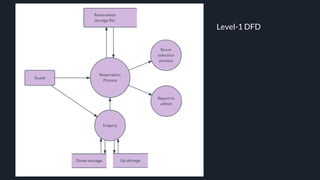
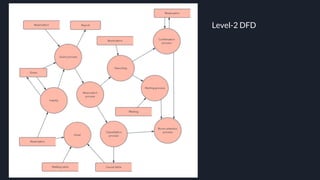
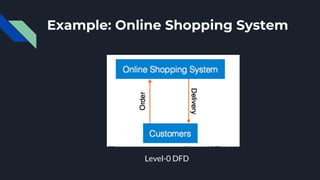
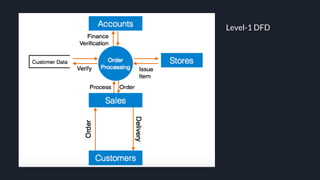
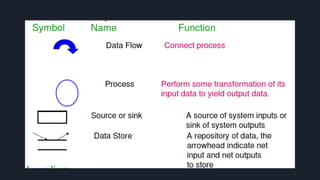
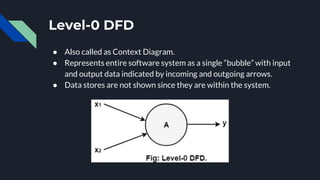
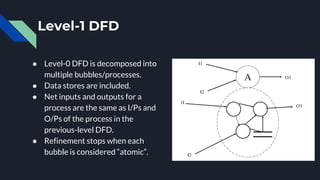
Data flow diagrams (DFDs) visually represent how data flows through a system, highlighting transformations from inputs to outputs without addressing control flow or procedural details. DFDs can be hierarchically organized into leveled sets, where each level provides increasing detail about data processing. A data dictionary accompanies DFDs, identifying data flows uniquely and defining their relationships.




![Data Dictionary
Ɣ In a DFD, data flows are identified by unique names. (All
components should be named uniquely)
Ɣ The data dictionary is a repository of various data flows defined
in a DFD.
Ɣ X = A+B : X consists of data elements A and B.
Ɣ X = A|B : X consists of either A or B.
Ɣ X = [A] : X consists of optional data element A.
Ɣ X = A*: X consists of one or more occurrences of A.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataflowdiagramspdf-241206122137-bbc77a76/85/DATA-FLOW-DIAGRAMS-pdf-for-college-student-pdf-8-320.jpg)