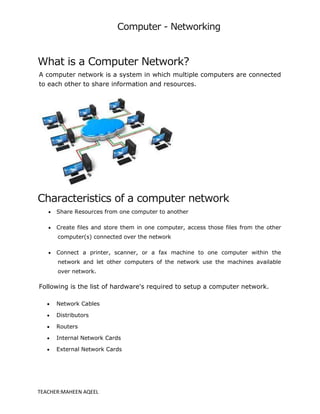
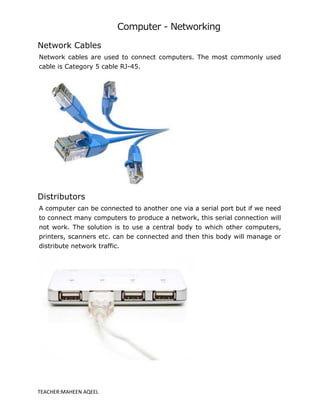
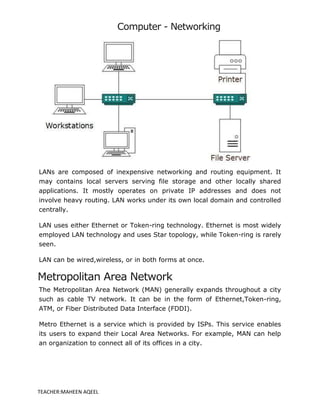
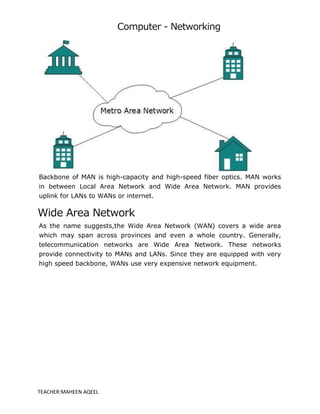
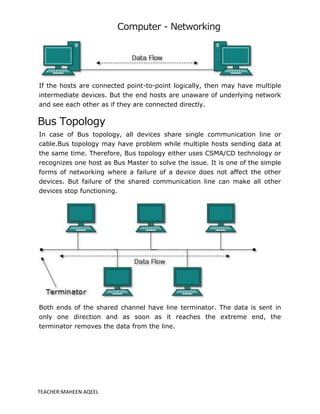
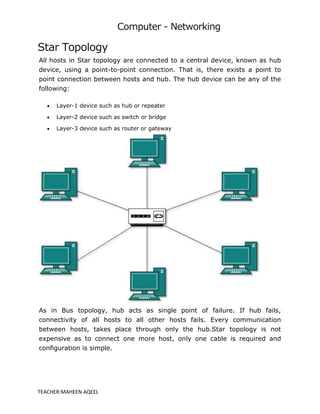
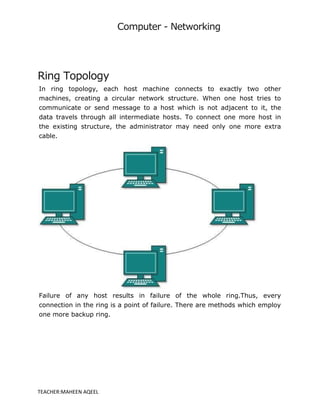
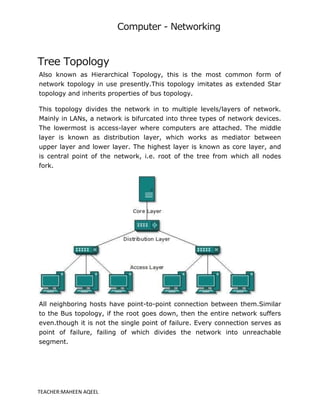
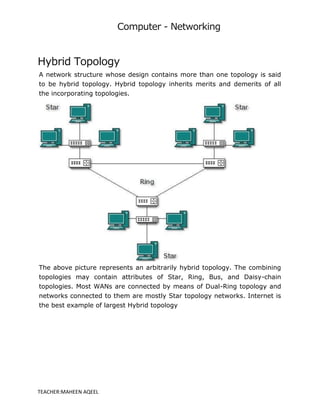
A computer network is a system that connects multiple computers to share resources and information, utilizing hardware such as network cables, routers, and network cards. Networks can be classified by geographical span (e.g., PAN, LAN, MAN, WAN), inter-connectivity, administration, and architecture, with topologies like star, bus, and ring defining their structure. The internet serves as the largest example of a network, while intranets are restricted to internal users within organizations.