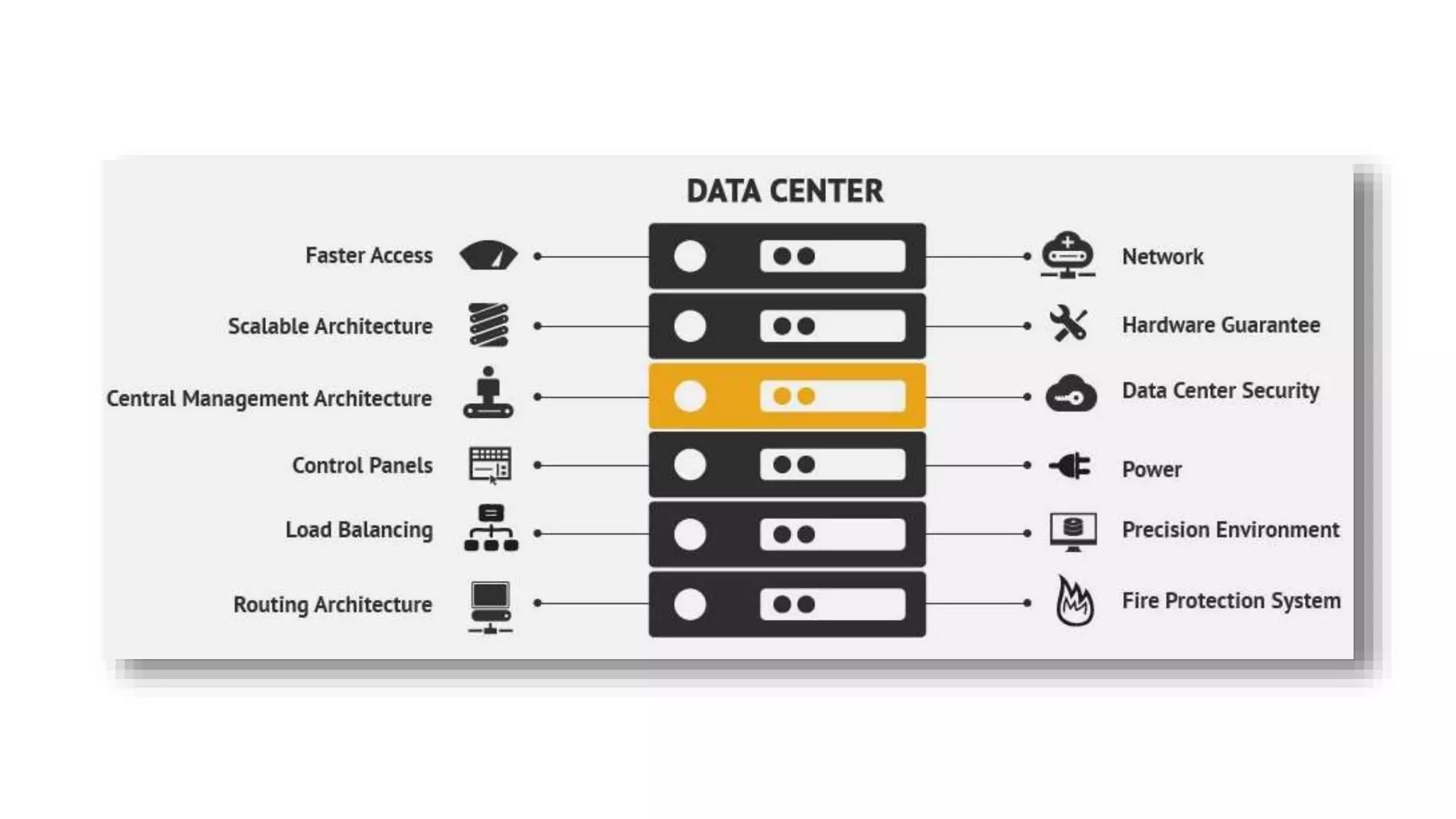
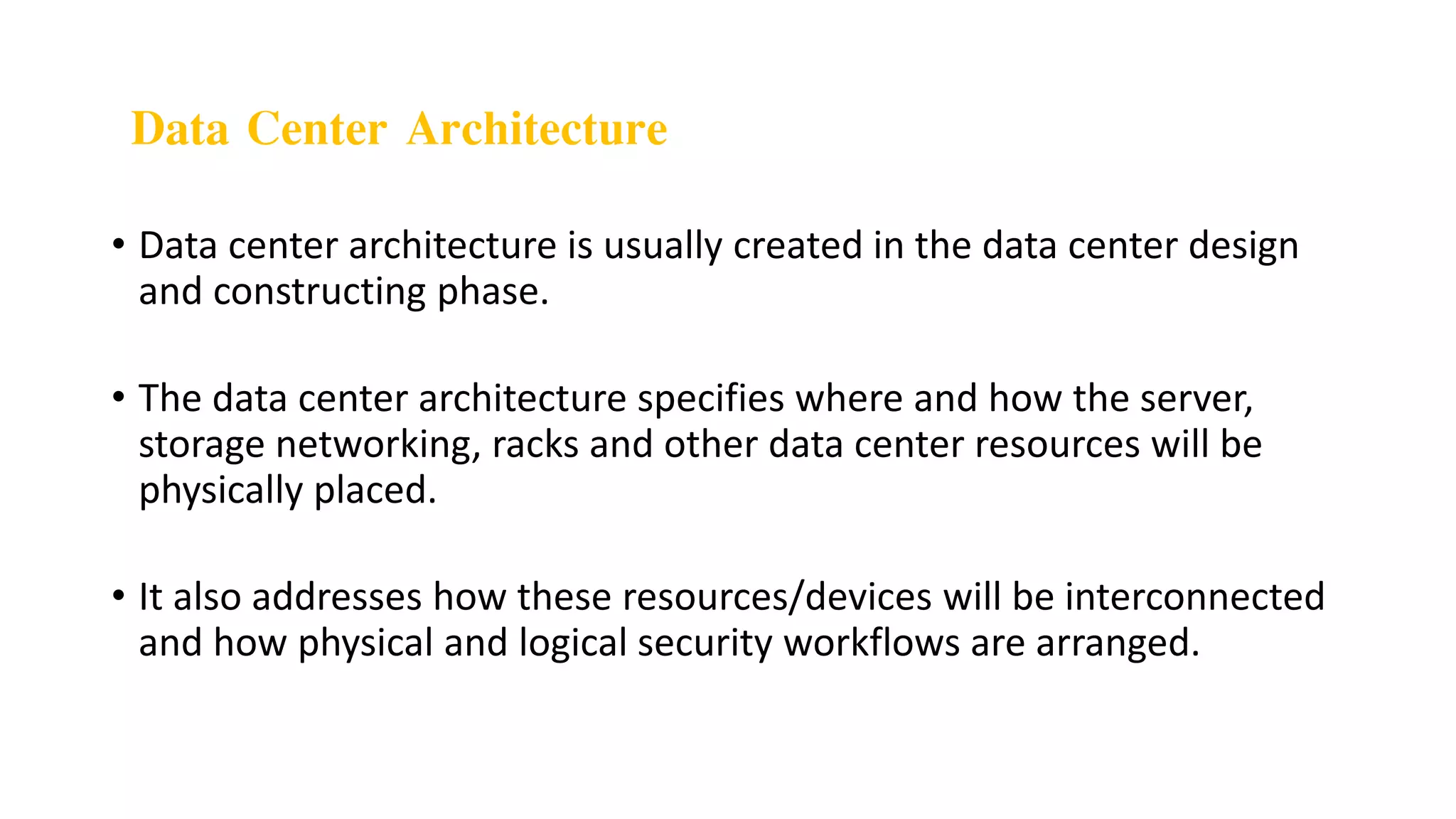
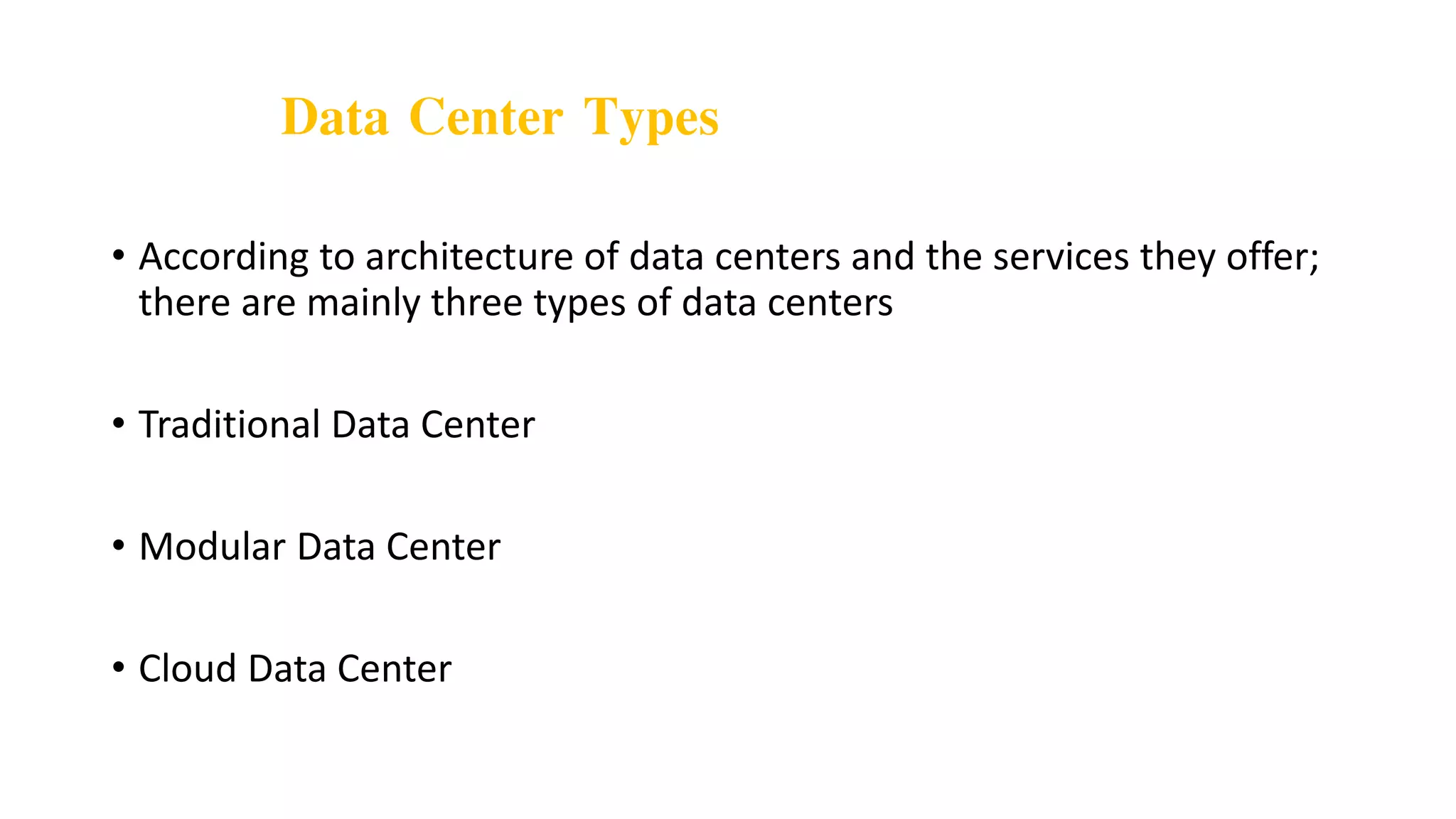
Data centers are facilities that house large amounts of computing equipment and data for collecting, storing, processing, and accessing data. Data center architecture involves planning how servers, storage, networking equipment, and other resources will be physically arranged and interconnected. There are three main types of data centers - traditional, modular, and cloud - depending on their architecture and services. Data centers support important business applications and activities like email, CRM, analytics, and collaboration. Their core components include networking, storage, and computing resources.